Modifying lists with ListIterator
Input/Output and Streams in Java

Alex Liu
Software Development Engineer
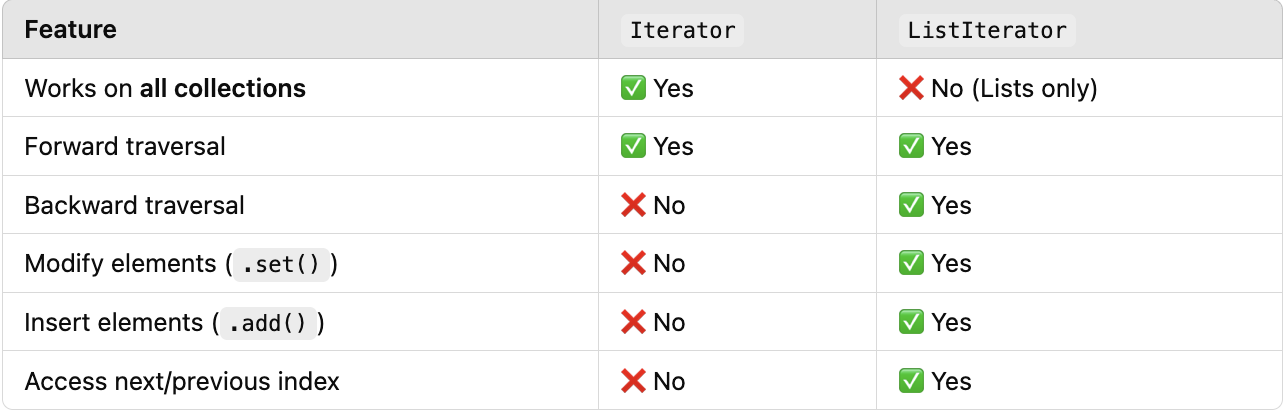
Iterator vs ListIterator
Sample ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class SampleData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
names.add("Alice");
names.add("Bob");
names.add("Charlie");
}
}
[Alice, Bob, Charlie]
Traversing a list with ListIterator
// Import ListIterator class import java.util.ListIterator;// Create ListIterator object for sample list `names` ListIterator<String> it = names.listIterator(); // Use .hasNext() and `.next()` to iterate the list and print line by line while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); }
Alice
Bob
Charlie
Moving backward with ListIterator
- Use
.previous()to move backward in the list
// Create ListIterator object for sample list `names`
ListIterator<String> it = names.listIterator(names.size());
// Use .hasPrevious() to check if the iterator reach the beginning of the list
while (it.hasPrevious()) {
// Use .previous() to retrieve the element in reverse order
System.out.println(it.previous());}
- Print element in reserve order, output:
Charlie
Bob
Alice
Modifying elements during iteration
- Using the
.set()method
// Create ListIterator object for sample list names ListIterator<String> it = names.listIterator();// Iterate the list and modify element using .set() while (it.hasNext()) { String name = it.next(); if ("Bob".equals(name)) it.set("Bobby"); }
- Updated
nameslist:
[Alice, Bobby, Charlie]
Adding elements during iteration
- Use
.add()to add elements
ListIterator<String> it = names.listIterator();// Iterate the list and insert element using .add() while (it.hasNext()) { String name = it.next(); if ("Charlie".equals(name)) it.add("David"); }
- Updated
nameslist:[Alice, Bobby, Charlie, David]
Summary
ListIteratorextendsIterator- Supports both forward and backward traversal
- Allows modifying elements while iterating
Key Methods Recap
.next()/.previous(): Navigate forward and backward.set(): Modify the current element.add(): Insert elements dynamically.remove(): Safely delete elements- Works only on Lists (
ArrayList,LinkedList, etc.)
Let's practice!
Input/Output and Streams in Java

