Maps
Data Types and Exceptions in Java

Jim White
Java Developer
Maps are lookup tables
- Maps serve as lookup table data structures
- Store a "value" at a specific "key"
- Use the "key" to retrieve the stored "value"
- Example: calling a doctor
- They lookup a health record (the value object) given a name/birth date (the key)

Map interface
Mapinterface defines operations on the key and value pairs- How to store or "put" a value into the store at a specific key
- How to "remove" the value at the key from the
Map - How to retrieve the value given a key
- Several implementations of
Mapthat are similar in behavior- A popular implementations of
MapisHashMap
- A popular implementations of
1 See https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/21/docs/api/java.base/java/util/Map.html for details
HashMap keys and values
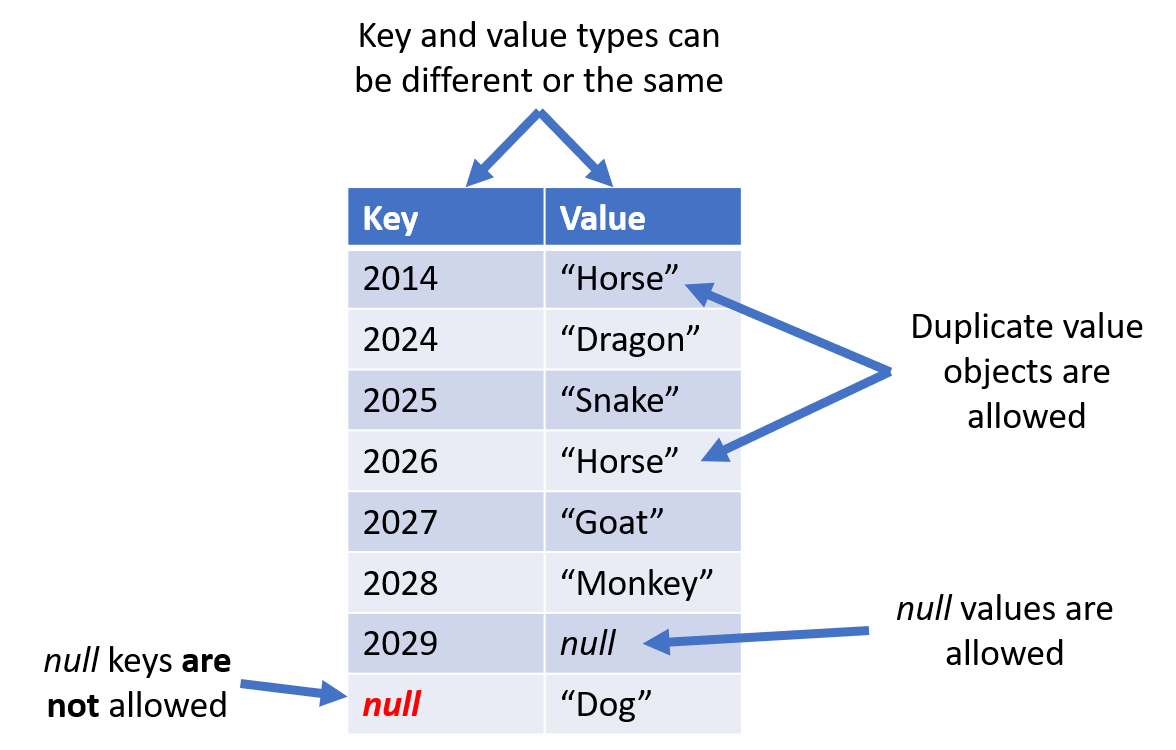
HashMap construction
HashMap<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
The parameterized/ generic constructor for a
HashMaprequires two typesThe first type = the key type

The second type = the value type


- Requires import of
java.util.HashMap
HashMap methods
- Use
.put(key,value)to add a key/value pairs to the table - Use
.remove(key)to remove the key/value pair specified at the key - Use
.get(key)to retrieve the value from the table at the key
import java.util.HashMap
...
HashMap<Integer, String> map
= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(0, "Jim");
map.put(1, "James");
map.put(3, null);
map.put(4, "James");
map.remove(0);
System.out.println(map);
{1=James, 3=null, 4=James}
String nickname = map.get(1);
System.out.println(nickname);
James
Collections
java.util.Collectionsis a supporting class- Used to aid in sorting, filling, copying, searching, and more
- Only has
staticmethods
- Only has
1 See https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase//21/docs/api/java.base/java/util/Collections.html
Collection methods
- Add many objects to a
ListaddAll(List list, Object a, b, ...)
- Return a count of an object in a collection
frequency(Collection c, Object o)
- Reorder the objects in a
Listreverse(List list)
- Sort the objects in a
Listsort(List list)
- Replace all the objects in a
Listwith another objectfill(List a, Object o)
ArrayList<String> x = new ArrayList<String>(); Collections.addAll(x, "milk", "bread", "eggs", "milk"); System.out.println(x);int cnt = Collections.frequency(x, "milk"); System.out.println(cnt);Collections.reverse(x); System.out.println(x);Collections.sort(x); System.out.println(x);Collections.fill(x, "sugar"); System.out.println(x);
[milk, bread, eggs, milk]2[milk, eggs, bread, milk][bread, eggs, milk, milk][sugar, sugar, sugar, sugar]
Arrays
- Sometimes need to convert an array (e.g.,
int[]) to aList- Java arrays are not resizable and we may need to grow/shrink the elements
Listhas greater capability (searching, sorting, etc.)
java.util.Arraysis another supporting class- Allows converting a Java array to a
List
- Allows converting a Java array to a
Arrays example
String[] arrayCountries = {"France", "Japan", "Brazil", "Egypt", "China"};
List<String> countries = Arrays.asList(arrayCountries);
System.out.println(countries);
[France, Japan, Brazil, Egypt, China]
Let's practice!
Data Types and Exceptions in Java

