Collections Framework Data Structures
Data Types and Exceptions in Java

Jim White
Java Instructor
What's a framework
- A framework is a set of reusable types providing generic functionality
- Example of types: classes and interfaces
- Enhances application's quality
- Avoid having to create everything from scratch
- Frameworks are delivered in a package or packages in Java
- Frameworks come with guidelines and rules for use

1 Photo by Ashkan Forouzani on Unsplash
Java Types
Two categories of types in Java:
- Primitive types
- byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, boolean
- Reference types
- Classes
- Interface
- Enums
- Arrays
- ...
The Collections Framework
- Collections Framework: Java's built-in set of generic data structure types
- A package of types to store and manipulate a group of objects
- Defined in the
java.utilpackage- We must use import to use the framework types
What about arrays?
- Java arrays can hold a group of objects or primitives
- Collections Framework offers an alternative set of data structures
- Both have pluses and minus
| Arrays | Collections |
|---|---|
| Not resizable | Dynamically sized (grow and shrink) |
| Stores primitives or objects | Stores only objects |
| Homogeneous - elements must be the same | heterogeneous - objects can be different |
Special notation to access [] elements |
Uses methods to access objects |
Special syntax for initialization {} |
Use new (no special initialization syntax) |
Collections Framework Types
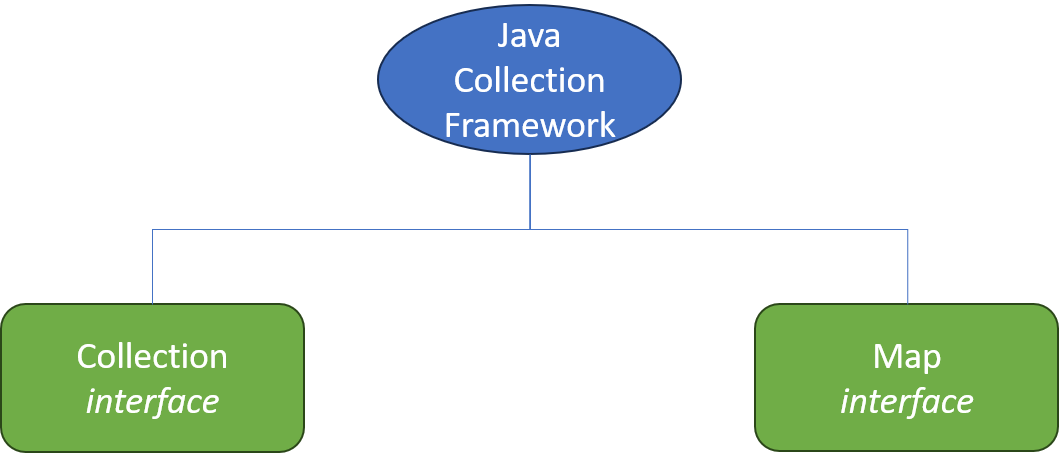
- Collections Framework are divided into two basic types:
CollectionandMap- Represented by two interfaces:
java.util.Collection&java.util.Map - Both have several implementing classes
- Represented by two interfaces:
import java.util.*;to use any of the Collections Framework types
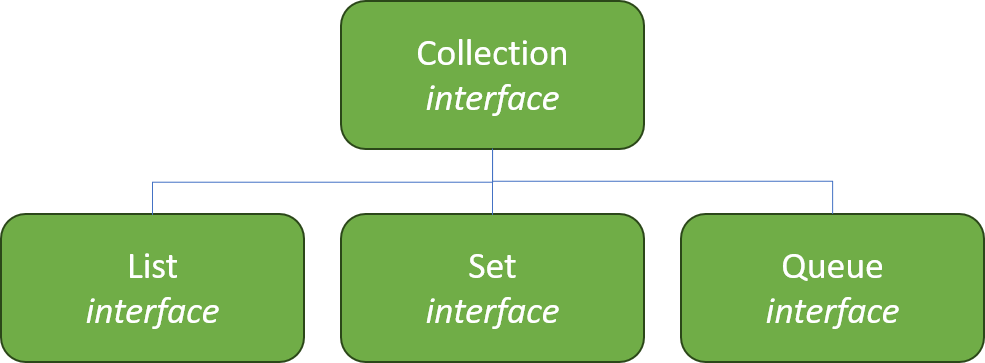
Collection
Collectiondefines many kinds of groupings of objects- These are defined by additional interfaces
- Ordered group of objects:
List - Unordered group of objects:
Set - First-in-first-out group of objects:
Queue- Operates like a line at a bank or ticket booth
.add(Object)and.remove(Object)methods to modify any Collection
Map
- Map data structures behave like a phone book or dictionary
- "key" objects -> to "value" objects
- In phone book, a name -> phone number
- In dictionary, a word -> word's definition
- Use the key object to modify a Map
.put(Object key, Object value)to add to a Map.remove(Object key)to remove from a Map
- Many types of Map - like
HashMap

Generics
- Collections and Maps are "parameterized"
- Java generics are used to specify the objects in a
CollectionorMap - Generic syntax:
<Class>with a parameterized type.< >called the diamond operator
- Java generics are used to specify the objects in a
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); // Construct with generics
Generics and type safety
- Generics allows for better type safety
- Restricts objects allowed in the contents of
CollectionandMap
- Restricts objects allowed in the contents of
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("hello"); // Adding a String is ok
list.add(new Integer(5)); // Trying to add an Integrer causes compiler error
Not using generics
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList(); // Legal but non-specific
list2.add("hello"); // Now any type of object can be added
list2.add(new Integer(5));
Variable declaration and assignment
- Variable declaration and assignment can be done separately
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); //Single line declaration and assignment
ArrayList<String> list2; // Variable declaration...
list2 = new ArrayList<String>(); //... and assignement can be 2 statements
Let's practice!
Data Types and Exceptions in Java

