Wrapper classes
Data Types and Exceptions in Java

Jim White
Java Developer
Java 8 primitives
Wrapper classes
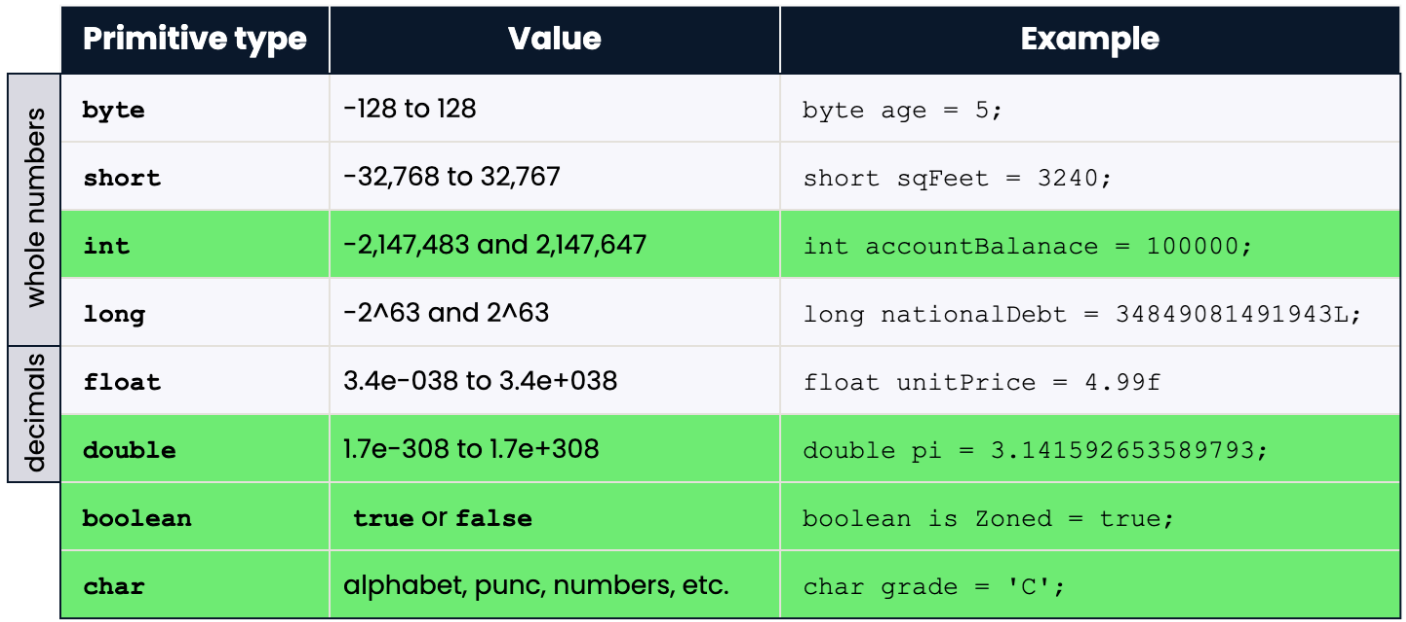
- Each primitive type has an equivalent wrapper class
| primitive | Wrapper Class |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
| char | Character |
Wrapping primitives
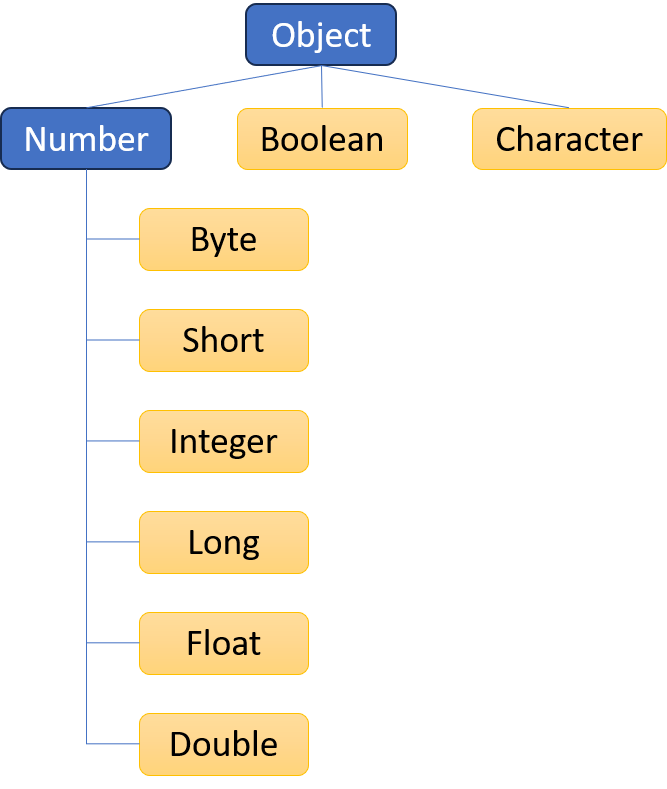
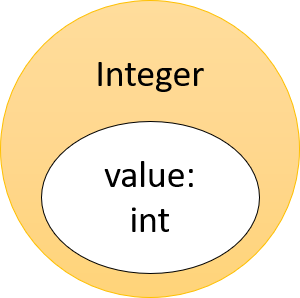
- Instances of a wrapper class hold a single primitive
- Example:
Integerholds a singleintprimitive value
- Example:
Wrapper details
- Wrapper classes have additional fields and methods
- Fields (like max value) about the type
- Methods to work with the wrapped primitive type
- Wrapper classes are in base language
- Use them without
import(more on imports later)
- Use them without
Creating wrapper objects
- Assign a primitive to a variable of the wrapper type
- Syntax:
Wrapper-typevariable=primitive-value;
- Syntax:
Integer age = 12;
Double cost = 150250.55;
Float interest = 5.5f;
Character grade = 'A';
Boolean isActive = true;
- Wrapper objects can also have no value (
null)
Integer age = null;
Using wrapper objects
Integer age = 12;
- Print them
System.out.println(age); // Displays 12 - Get their primitive value
int x = age.intValue(); // x is assigned 12 - Perform other operations on them
double z = age.doubleValue(); //z is 12.0 String y = age.toString(); // y is assigned "12" Integer teenAge = 16; int smaller = age.compareTo(teenAge); // smaller is -1 since 12 < 16
Wrapper Static Methods
- Wrapper classes come with static methods
- Used to perform operations on the associated primitives
int x = Integer.sum(8,12); // x is 20 int y = Integer.remainderUnsigned(102, 10); // y is 2 - Used to convert between String and primitive
int z = Integer.parseInt("123"); // z is 123; boolean ans = Boolean.parseBoolean("false"); // ans is false
1 See https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Integer.html for more on the Integer wrapper
Wrapper Static Fields
Example static fields on wrapper classes
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); // Maximum value an int can have
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); // Minimum value an int can have
2147483647
-2147483648
System.out.println(Boolean.TRUE); // Corresponding to the primitive value of true
System.out.println(Boolean.FALSE); // Corresponding to the primitive value of false
true
false
Wrapper Static Fields
Example static fields on wrapper classes
System.out.println(Character.SPACE_SEPARATOR); // Unicode for the regular space like ' '
System.out.println(Character.LINE_SEPARATOR); // Unicode for line return like '\n'
12
13
Interesting Wrapper Methods
| Wrapper Method | Returns |
|---|---|
| Boolean.logicalAnd(boolean a, boolean b) | boolean |
| Boolean.logicalOr(boolean a, boolean b) | boolean |
| Boolean.parseBoolean(String s) | boolean |
| Character.getNumericValue(char ch) | Unicode int value of the char |
| Character.isDigit(char ch) | boolean |
| Character.isLowerCase(char ch) | boolean |
| Character.isWhitespace(char ch) | boolean |
| Double.parseDouble(String s) | double |
| Double.longValue() | the Double value, rounded down, as a Long |
Why Wrappers?
- Primitives have no methods (only operations)
- Wrapper classes come with useful methods
int score = Integer.parseInt("8");
- Wrapper classes come with useful methods
- Wrappers allow primitives to be used as objects; like putting them in a collection
- Learn about collections in the Chapter 2.
Wrappers can be null
- Wrappers allow instance or static variables of the type to be
null- Primitive instance or static variables have a default value when not initialized
int herAge; // age is 0 by default
Integer hisAge = null;
if (hisAge != null) {
// do something when hisAge is not set
}
Let's practice!
Data Types and Exceptions in Java

