Tracer des séries temporelles avec différentes variables
Introduction à la visualisation de données avec Matplotlib

Ariel Rokem
Data Scientist
Tracer deux séries temporelles ensemble
import pandas as pd
climate_change = pd.read_csv('climate_change.csv',
parse_dates=["date"],
index_col="date")
climate_change
co2 relative_temp
date
1958-03-06 315.71 0.10
1958-04-06 317.45 0.01
1958-07-06 315.86 0.06
... ... ...
2016-11-06 403.55 0.93
2016-12-06 404.45 0.81
[706 rows x 2 columns]
Tracer deux séries temporelles ensemble
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["co2"])ax.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["relative_temp"])ax.set_xlabel('Time') ax.set_ylabel('CO2 (ppm) / Relative temperature') plt.show()
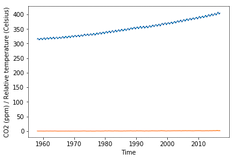
Utilisation de deux axes
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["co2"]) ax.set_xlabel('Time') ax.set_ylabel('CO2 (ppm)')ax2 = ax.twinx()ax2.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["relative_temp"]) ax2.set_ylabel('Relative temperature (Celsius)') plt.show()
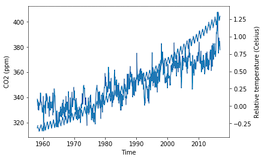
Séparation des variables par couleur
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["co2"], color='blue') ax.set_xlabel('Time') ax.set_ylabel('CO2 (ppm)', color='blue')ax2 = ax.twinx() ax2.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["relative_temp"], color='red') ax2.set_ylabel('Relative temperature (Celsius)', color='red') plt.show()
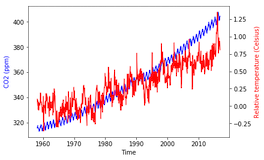
Colorisation des graduations
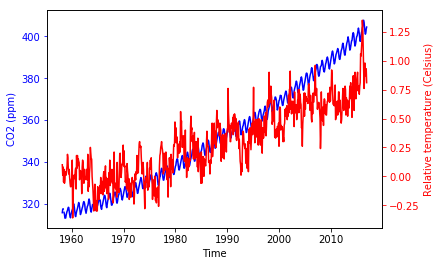
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["co2"], color='blue') ax.set_xlabel('Time') ax.set_ylabel('CO2 (ppm)', color='blue')ax.tick_params('y', colors='blue')ax2 = ax.twinx() ax2.plot(climate_change.index, climate_change["relative_temp"], color='red') ax2.set_ylabel('Relative temperature (Celsius)', color='red')ax2.tick_params('y', colors='red')plt.show()
Colorisation des graduations
Une fonction qui affiche un graphique des séries temporelles
def plot_timeseries(axes, x, y, color, xlabel, ylabel):
axes.plot(x, y, color=color)
axes.set_xlabel(xlabel)
axes.set_ylabel(ylabel, color=color)
axes.tick_params('y', colors=color)
Utilisation de notre fonction
fig, ax = plt.subplots() plot_timeseries(ax, climate_change.index, climate_change['co2'], 'blue', 'Time', 'CO2 (ppm)')ax2 = ax.twinx() plot_timeseries(ax2, climate_change.index, climate_change['relative_temp'], 'red', 'Time', 'Relative temperature (Celsius)')plt.show()
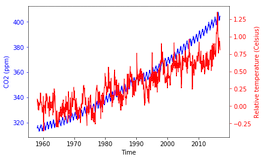
Créez votre propre fonction !
Introduction à la visualisation de données avec Matplotlib

