Introduction to testing
Introduction to Testing in Java

Maria Milusheva
Senior Software Engineer
What is testing?
Software Testing:
- Process of evaluating software to determine whether it meets specified requirements
Testing can be:
- Manual - necessary but limited and less reliable
- Automated - powerful way to execute hundreds of tests and checks in seconds
We'll use JUnit 5 for automated testing

Edge cases
"If it's not tested, it's broken."$^1$
Edge case - input or condition that is at the extreme or boundary of what is considered typical or expected
Examples: variables at maximum capacity, null or empty variables, negative values

1 Quote originally by Bruce Eckel
Example of unexpected behavior at an edge case
Consider the following code:
public int addTwoNumbers(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
⚠ Consider inputs 2147483647 (integer max value) and 1
➡ The output is -2147483648 (integer min value)
Recall: Variable sizes - primitives have limited size
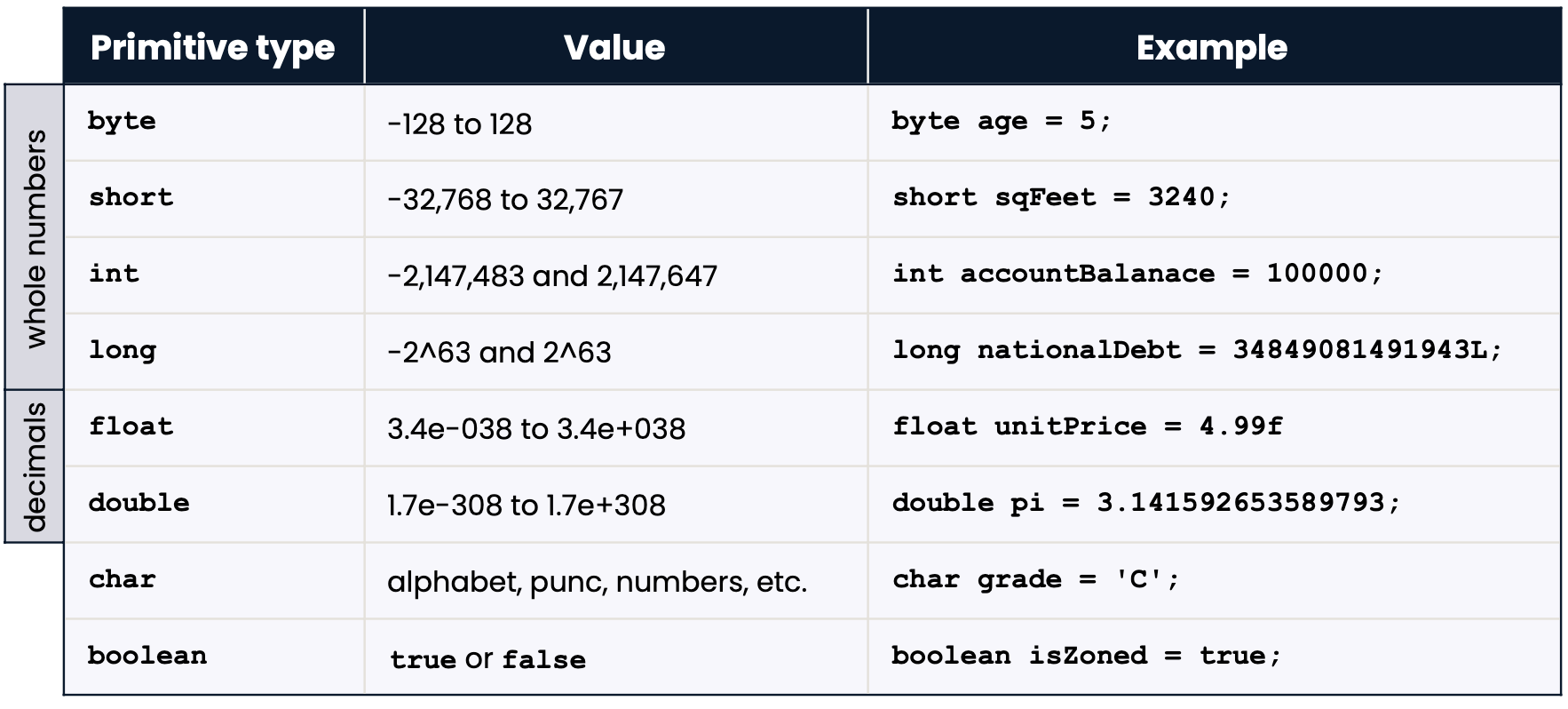
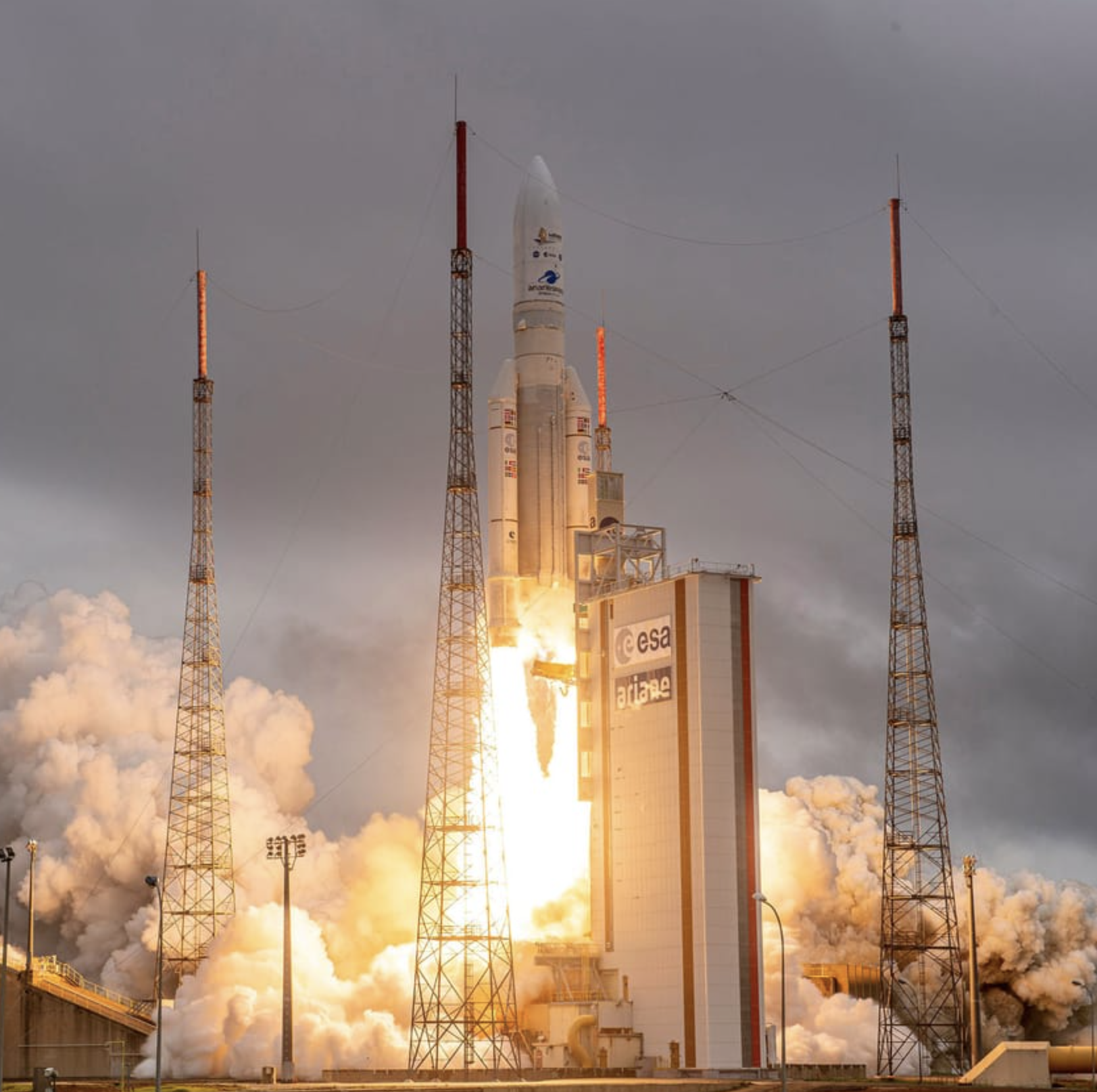
Example: Ariane 5 launch
First flight of the Ariane 5 rocket in 1996:
- Spent over 8 years in development
- Cost over $370 million
- Exploded 37 seconds after launch
- Explosion was caused by software error: short overflow

Benefits of testing
- Guards against edge case bugs
- Leads to better understanding of the project and its requirements
- Speeds up development in the long run
- Automates enforcing requirements
- Guards against human error

1 https://books.google.com/books/about/Clean_Architecture.html?id=8ngAkAEACAAJ
Let's practice!
Introduction to Testing in Java

