Integration testing
Introduction to Testing in Java

Maria Milusheva
Senior Software Engineer
Defining integration testing
- Integration - the process of combining individual software components or subsystems into a unified system that functions cohesively.
- Integration test - a test that verifies the interaction between multiple components or modules of an application to ensure they work together correctly. It often involves testing with external dependencies.

Dependencies
- Software dependency - a relationship between software components where one component relies on the other to work properly
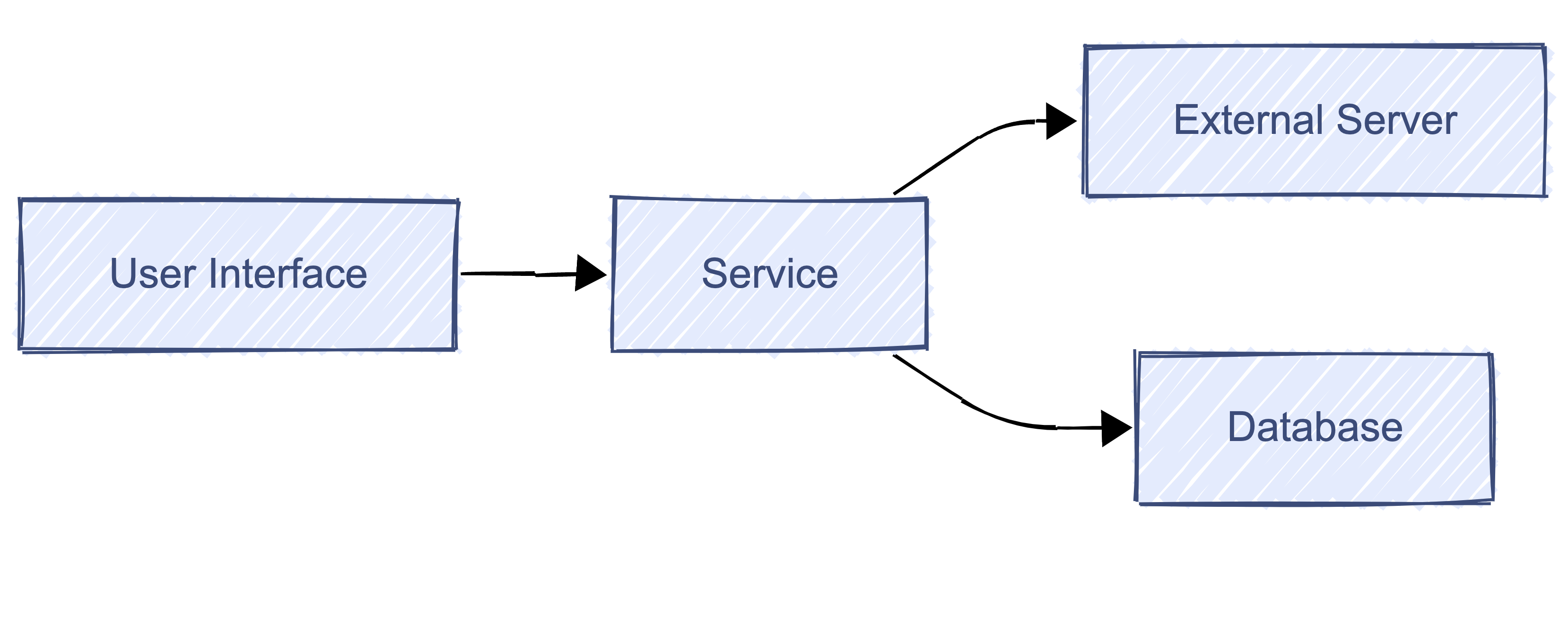
1 Chart made using Mermaid: https://mermaid.live
Integration testing vs. unit testing
Unit tests:
- Test individual components in isolation
- Failures pinpoint issues with a specific part of the code
- Faster to write and run
- Use various tools to avoid testing dependencies
- Assert on exact results and outcomes
Integration tests:
- Test multiple components and their interactions
- Failures require deeper analysis to trace
- Can be heavy and take longer to set up and run
- Tests real interactions with real dependencies
- May assert on general behaviors instead of exact results
Example: Foreign exchange
Suppose we are building a currency exchange app:
public class ExchangeApp { private EuropeanCentralBankServer bank; // Enables ExchangeApp to use the bank server public ExchangeApp(EuropeanCentralBankServer bank) { this.bank = bank; // Save the object passed through the constructor }public double convertEuroTo(String currency, double amount) { double rate = this.bank.getRateEuroTo(currency); return amount * rate; // Use the return values of the bank method in calculations } }
Integration testing foreign exchange
Integration testing verifies both the convertEuroTo method and EuropeanCentralBankServer:
@Test void convert_convertsWithoutError() { EuropeanCentralBankServer bank = new EuropeanCentralBankServer(); ExchangeApp exchangeApp = new ExchangeApp(bank); // Pass bank object to constructordouble amount = 1000.0; String currency = "USD"; // convertEuroTo calls getRateEuroTo from the bank object double result = exchangeApp.convertEuroTo(currency, amount); assertTrue(result > 0); // Can't predict exact value, can only sanity test }
Let's practice!
Introduction to Testing in Java

