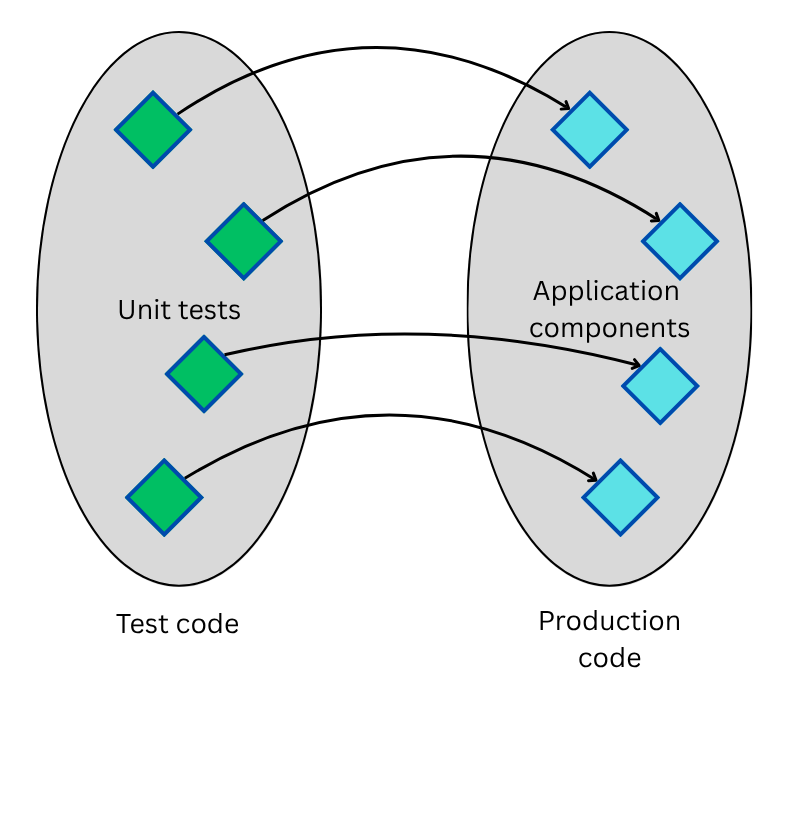
Unit testing with JUnit
Introduction to Testing in Java

Maria Milusheva
Senior Software Engineer
Unit testing - definition
Two key concepts:
Unit - the smallest testable part of an application, such as a method
Unit testing - A test that focuses on verifying the correctness of a single "unit" of code in isolation from other parts of the application
Unit testing is about details
Notes:
Unit testing is about small pieces of logic, not the big picture
Other types of testing focus on the big picture (e.g. integration)
JUnit gets its name because its primary use case is unit testing
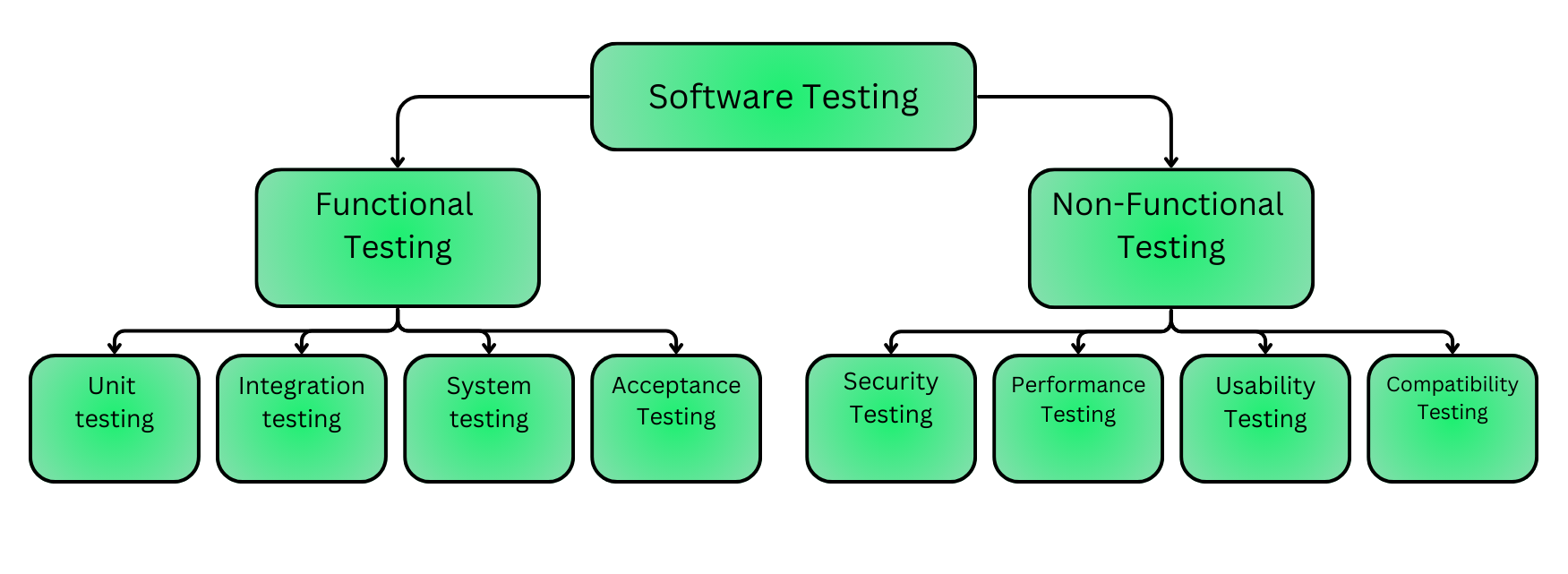
Types of testing - brief overview
- In this course we will discuss mostly unit and integration tests
- But there are many types of testing!
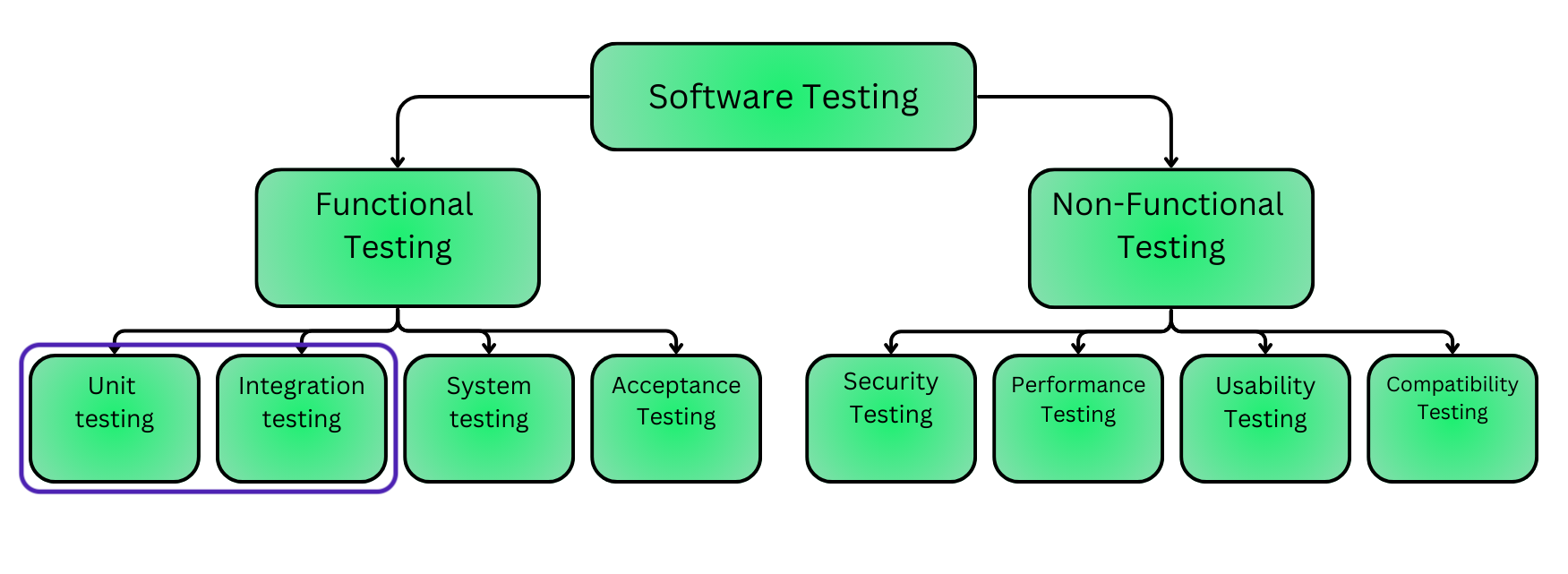
Types of testing - brief overview
- In this course we will discuss mostly unit and integration tests
- But there are many types of testing!
JUnit syntax: assertTrue() and assertFalse()
assertTrue()checks that a statement is true:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
assertTrue(list.isEmpty()); // No error
assertFalse()checks the opposite:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("A");
assertFalse(list.isEmpty()); // No error
assertNull() and assertNotNull()
null variables can lead to NullPointerException!
Assertions that check a variable is or isn't
null-assertNull()andassertNotNull()Common use case: checking a value retrieved from somewhere is not null
Map<String, Integer> catalogue = new HashMap<>();
catalogue.put("item1", 10);
// No errors
assertNotNull(catalogue.get("item1"));
assertNull(catalogue.get("item2"));
Asserting exceptions
Suppose we want to verify an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException is thrown:
public String getIndex(String[] array, int index) {
return array[index];
}
JUnit provides multiple ways to do this!
assertInstanceOf()
JUnit provides
assertThrows(), but it uses advanced Java syntax (lambda expressions)Can use
assertInstanceOf()like this:
try {
getIndex(new String[]{}, 4);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Pass the expected class of the exception and the exception itself
assertInstanceOf(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.class, e);
}
Naming unit tests
A typical project contains hundreds of unit tests
They should be lightweight and simple to understand
They should have informative names so that we can see at first glance what went wrong if one of them fails
For example: methodUnderTest_expectedBehavior_conditions()
Let's practice!
Introduction to Testing in Java

