Risikoklassifizierung
Grundlagen des KI-Gesetzes der Europäischen Union

Dan Nechita
Lead Technical Negotiator, EU AI Act
Anbieter oder Betreiber?
- Anbieter entwickeln KI, Betreiber nutzen KI
- Anbieter haben die meisten Sicherheitspflichten
- Auch Betreiber haben bestimmte Pflichten
- Beispiel: Microsoft (Anbieter), Versicherungsgesellschaft (Betreiber)

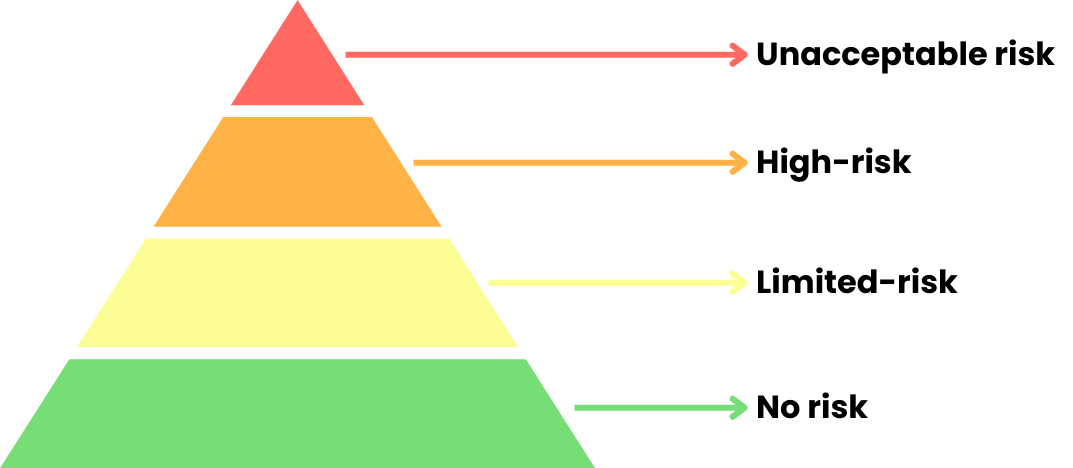
Die Risikopyramide
Die Pflichten hängen von der Zweckbestimmung sowie von der Risikostufe ab: unannehmbares Risiko, hohes Risiko, begrenztes Risiko und kein Risiko.
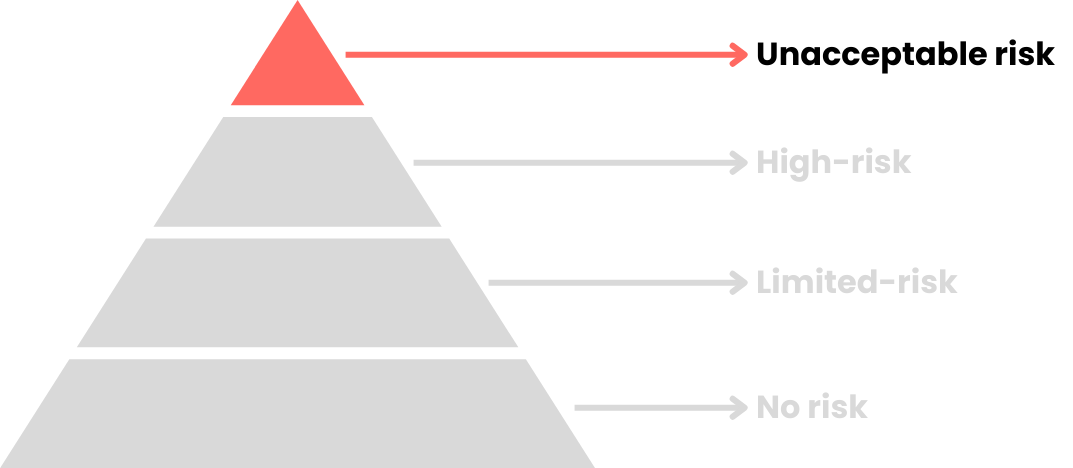
Unannehmbares Risiko
Die Pflichten hängen von der Zweckbestimmung sowie von der Risikostufe ab: unannehmbares Risiko, hohes Risiko, begrenztes Risiko und kein Risiko.
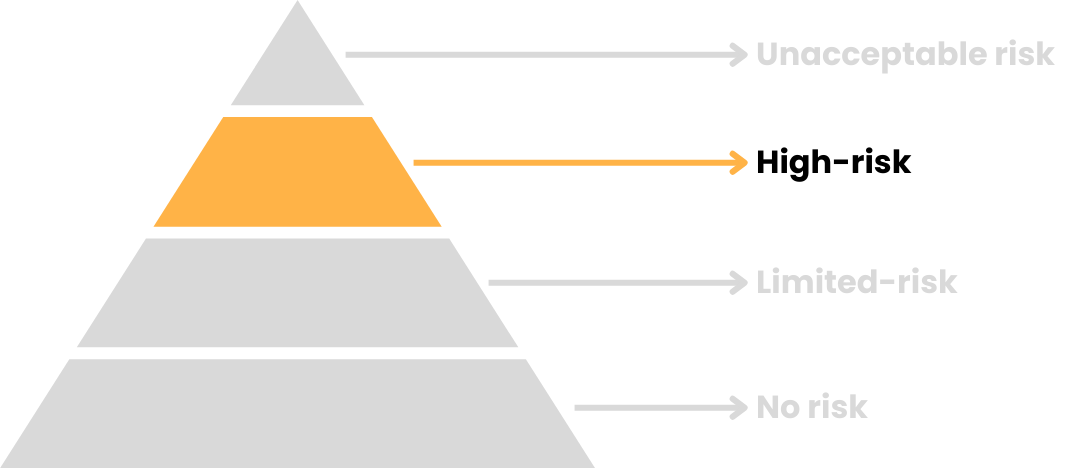
Hohes Risiko
Die Pflichten hängen von der Zweckbestimmung sowie von der Risikostufe ab: unannehmbares Risiko, hohes Risiko, begrenztes Risiko und kein Risiko.
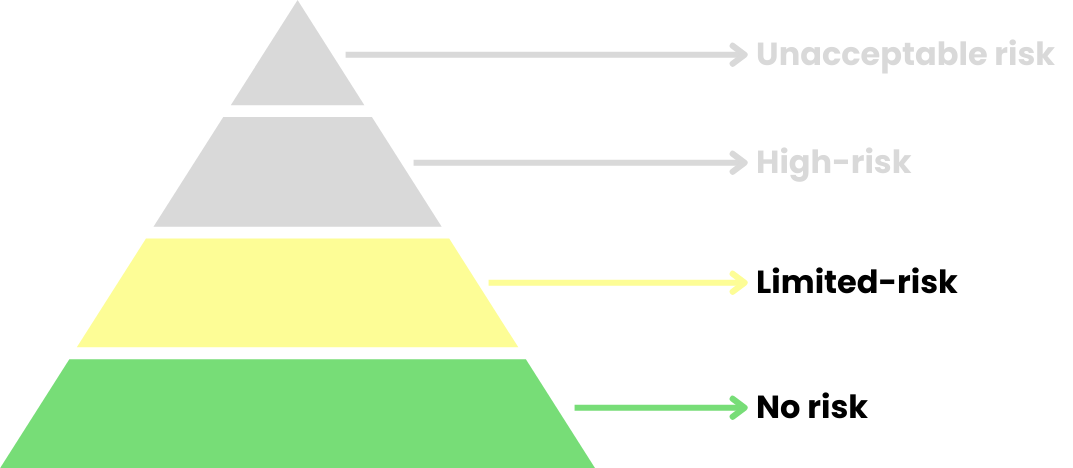
Begrenztes Risiko und kein Risiko
Chatbots, Deep Fakes und KI-generierte Inhalte sind die besten Beispiele dafür.
GPAI
- Anbieter von KI-Modellen mit allgemeinem Verwendungszweck (GPAI) haben risikobasierte Pflichten
- Grundlegende Transparenzpflichten sowie Pflichten zur Minderung systemischer Risiken
Lass uns üben!
Grundlagen des KI-Gesetzes der Europäischen Union

