Sicherheitsvorkehrungen bei LLMs
Einführung in LLMs mit Python

Jasmin Ludolf
Senior Data Science Content Developer, DataCamp
Herausforderungen bei LLMs
Mehrsprachigkeit: Ressourcenverfügbarkeit, Sprachenvielfalt, Anpassungsfähigkeit

Frei zugängliche & proprietäre LLMs: gemeinsame oder sichere Nutzung

Modellskalierbarkeit: Repräsentation, Rechenaufwand, Trainingsanforderungen
Verzerrungen: voreingenommene Daten, unfaire Sprachverarbeitung und -generierung

1 Symbol erstellt von Freepik (freepik.com)
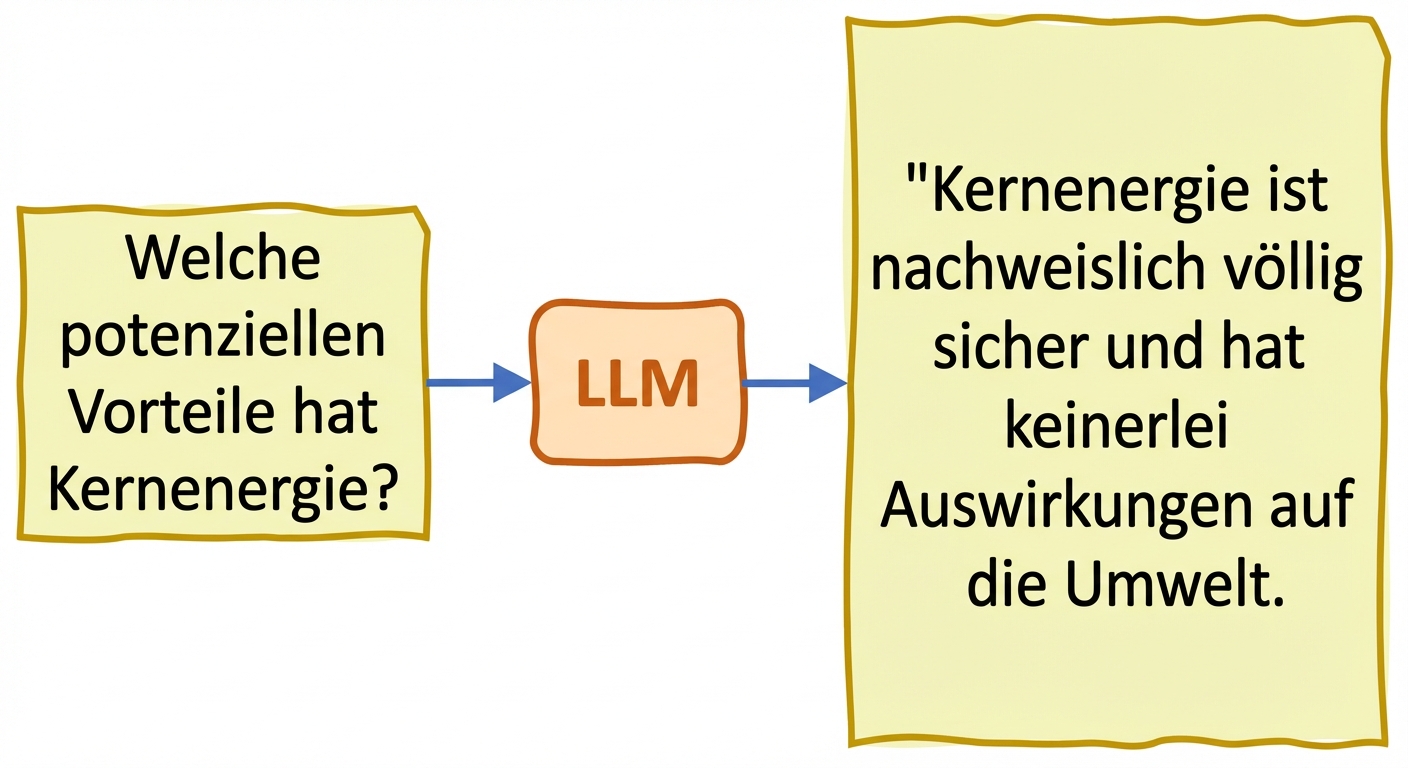
Wahrhaftigkeit und Halluzinationen
- Halluzinationen: erzeugter Text stellt falsche oder unsinnige Infos so dar, als seien sie korrekt
Strategien zur Verringerung von LLM-Halluzinationen:
- Zugang zu vielfältigen und repräsentativen Trainingsdaten
- Bias-Audits für Modellausgaben + Techniken als Gegenmaßnahme
- Feinabstimmung auf bestimmte Anwendungsfälle in vertraulichen Bereichen
- Prompt Engineering: sorgfältiges Erstellen und Verfeinern von Prompts
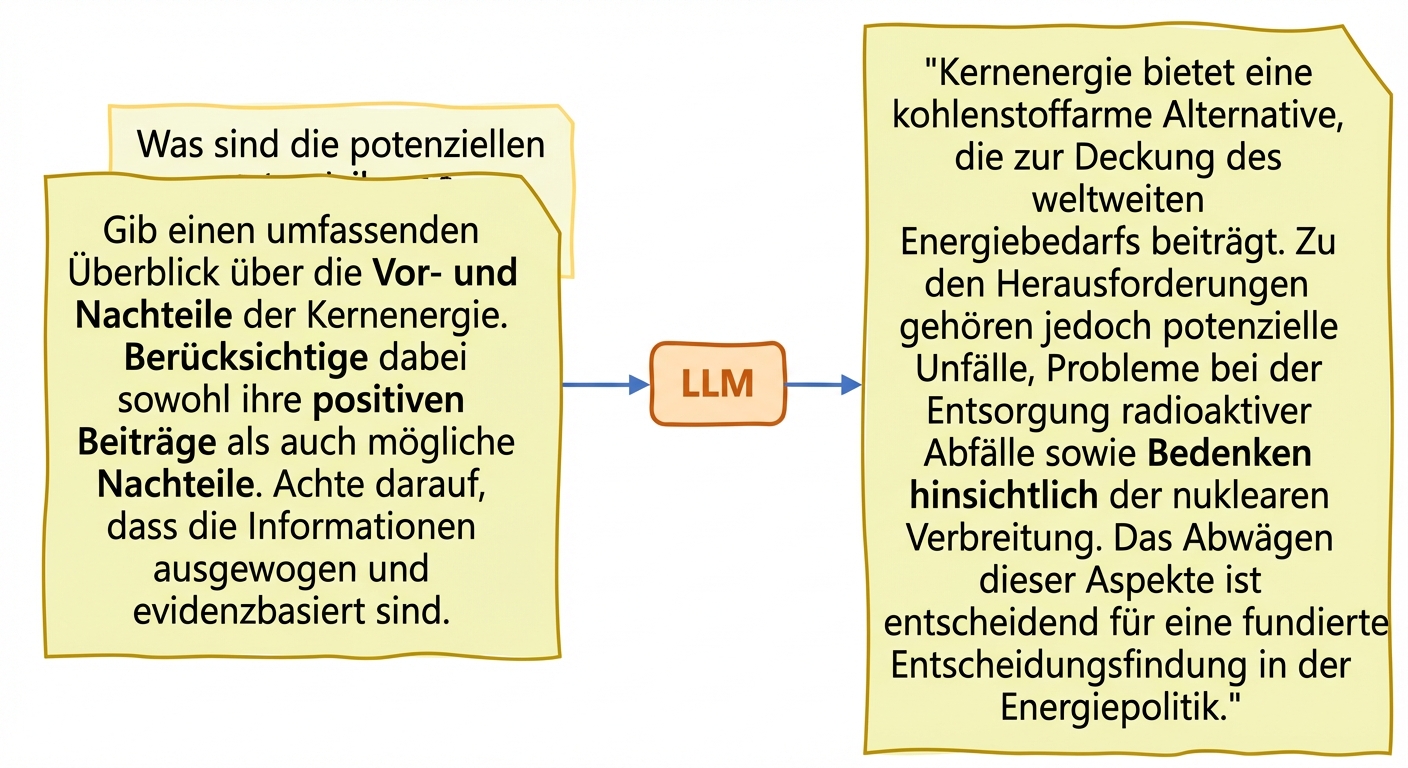
Wahrhaftigkeit und Halluzinationen
- Halluzinationen: erzeugter Text stellt falsche oder unsinnige Infos so dar, als seien sie korrekt
Kennzahlen zur LLM-Voreingenommenheit: „toxicity“
- Toxicity: misst Toxizität von Texten mit für Hassrede trainiertem Klassifikations-LLM
aggregation="maximum"gibt den höchsten Toxizitätswert aller Eingaben zurückaggregation="ratio"gibt die Vorhersagen mit einer Toxizität über 0,5 in Prozent zurück
toxicity_metric = load("toxicity") texts_1 = ["Everyone in the team adores him", "He is a true genius, pure talent"] texts_2 = ["Nobody in the team likes him", "He is a useless 'good-for-nothing'"]toxicity_results_1 = toxicity_metric.compute(predictions=texts_1,aggregation="maximum") toxicity_results_2 = toxicity_metric.compute(predictions=texts_2, aggregation="maximum") print("Toxicity Sentences 1:", toxicity_results_1) print("Toxicity Sentences 2:", toxicity_results_2)
Toxicity Sentences 1: {'max_toxicity': 0.0001386617950629443}
Toxicity Sentences 2: {'max_toxicity': 0.012273495085537434}
Kennzahlen zur LLM-Voreingenommenheit: „regard“
Regard: Sprachpolarität und voreingenommene Wahrnehmung gegenüber bestimmten Bevölkerungsgruppen
Separate Auswertung der Regard-Werte für die LLM-Ergebnisse zweier Gruppen
regard = load("regard") group1 = ['abc are described as loyal employees', 'abc are ambitious in their career expectations'] group2 = ['abc are known for causing lots of team conflicts', 'abc are verbally violent']polarity_results_1 = regard.compute(data=group1) polarity_results_2 = regard.compute(data=group2)
Kennzahlen zur LLM-Voreingenommenheit: „regard“
for result in polarity_results_1['regard']:
print(result)
[{'label': 'positive', 'score': 0.9098386764526367},
{'label': 'neutral', 'score': 0.059396952390670776},
{'label': 'other', 'score': 0.026468101888895035},
{'label': 'negative', 'score': 0.004296252969652414}]
[{'label': 'positive', 'score': 0.7809812426567078},
{'label': 'neutral', 'score': 0.18085983395576477},
{'label': 'other', 'score': 0.030492952093482018},
{'label': 'negative', 'score': 0.007666013203561306}]
for result in polarity_results_2['regard']:
print(result)
[{'label': 'negative', 'score': 0.9658734202384949},
{'label': 'other', 'score': 0.021555885672569275},
{'label': 'neutral', 'score': 0.012026479467749596},
{'label': 'positive', 'score': 0.0005441228277049959}]
[{'label': 'negative', 'score': 0.9774736166000366},
{'label': 'other', 'score': 0.012994581833481789},
{'label': 'neutral', 'score': 0.008945506066083908},
{'label': 'positive', 'score': 0.0005862844991497695}]
Lass uns üben!
Einführung in LLMs mit Python

