Bag-of-Words representation
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Python

Fouad Trad
Machine Learning Engineer
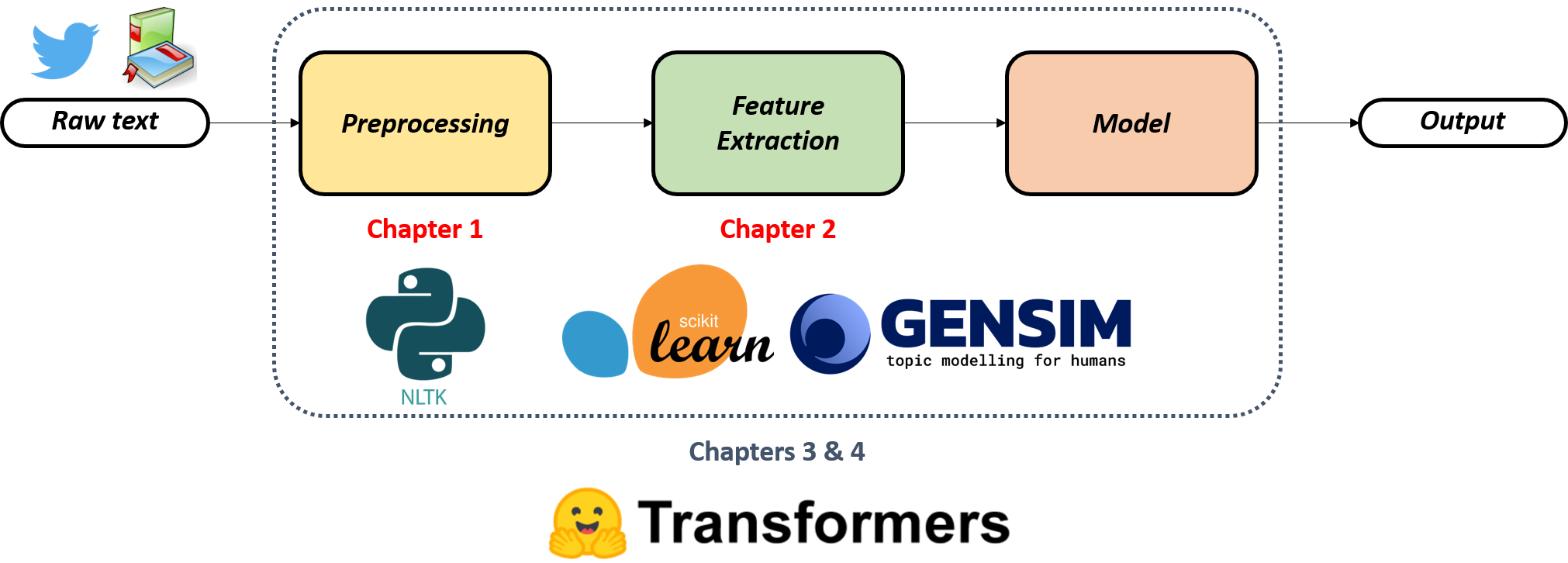
NLP workflow recap
Bag-of-Words (BoW)
- Foundational technique to represent text as numbers
- Represent text by counting how often each word appears
- Throws words in a bag and counts them
- Ignores grammar and order

BoW example

BoW example
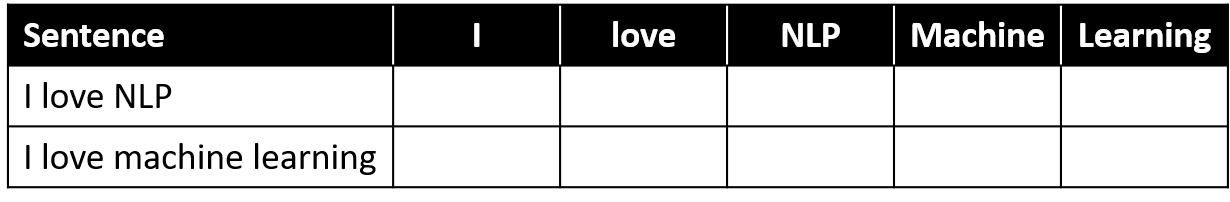
- Build a vocabulary of all unique words
BoW example

- Build a vocabulary of all unique words
- Count how many times each word from the vocabulary appears
BoW with code
reviews = ["I loved the movie. It was amazing!", "The movie was okay.", "I hated the movie. It was boring."]def preprocess(text):text = text.lower()tokens = word_tokenize(text)tokens = [word for word in tokens if word not in string.punctuation]return " ".join(tokens)cleaned_reviews = [preprocess(review) for review in reviews]print(cleaned_reviews)
['i loved the movie it was amazing',
'the movie was okay',
'i hated the movie it was boring']
BoW with code
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizervectorizer = CountVectorizer()vectorizer.fit(cleaned_reviews)print(vectorizer.get_feature_names_out())
['amazing' 'boring' 'hated' 'it' 'loved' 'movie' 'okay' 'the' 'was']
BoW output
X = vectorizer.transform(cleaned_reviews)# OR X = vectorizer.fit_transform(cleaned_reviews)print(X)
<Compressed Sparse Row sparse matrix of dtype 'int64'
with 16 stored elements and shape (3, 9)>
Sparse matrix: table mostly filled with zeros
BoW output
print(X.toarray())
[[1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1]
[0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1]
[0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1]]
print(vectorizer.get_feature_names_out())
['amazing' 'boring' 'hated' 'it' 'loved' 'movie' 'okay' 'the' 'was']
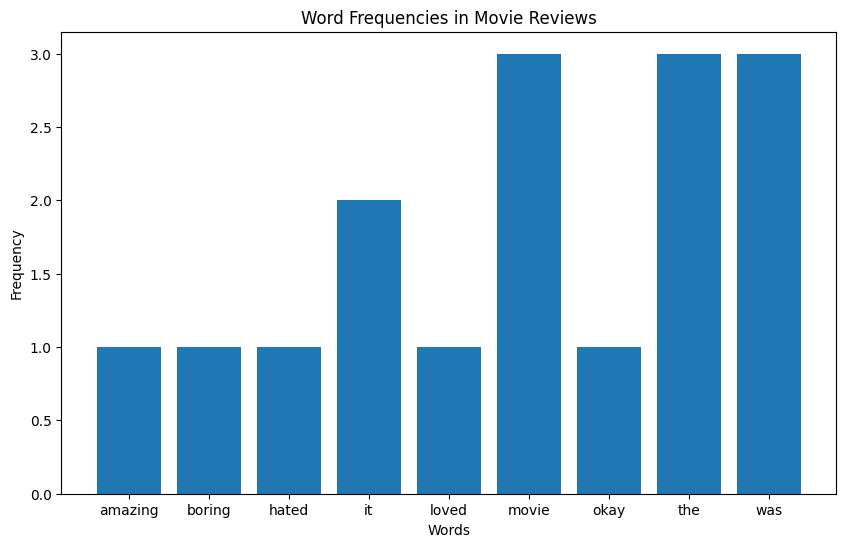
Word frequencies
import numpy as npword_counts = np.sum(X.toarray(), axis=0)words = vectorizer.get_feature_names_out()
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.bar(words, word_counts)plt.title("Word Frequencies in Movie Reviews")plt.xlabel("Words") plt.ylabel("Frequency") plt.show()
Let's practice!
Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Python

