Chat roles and system messages
Working with DeepSeek in Python

James Chapman
Curriculum Manager, DataCamp
Chat models
Single-turn tasks
- Text generation
- Text transformation
- Classification

Chat models
Single-turn tasks
- Text generation
- Text transformation
- Classification
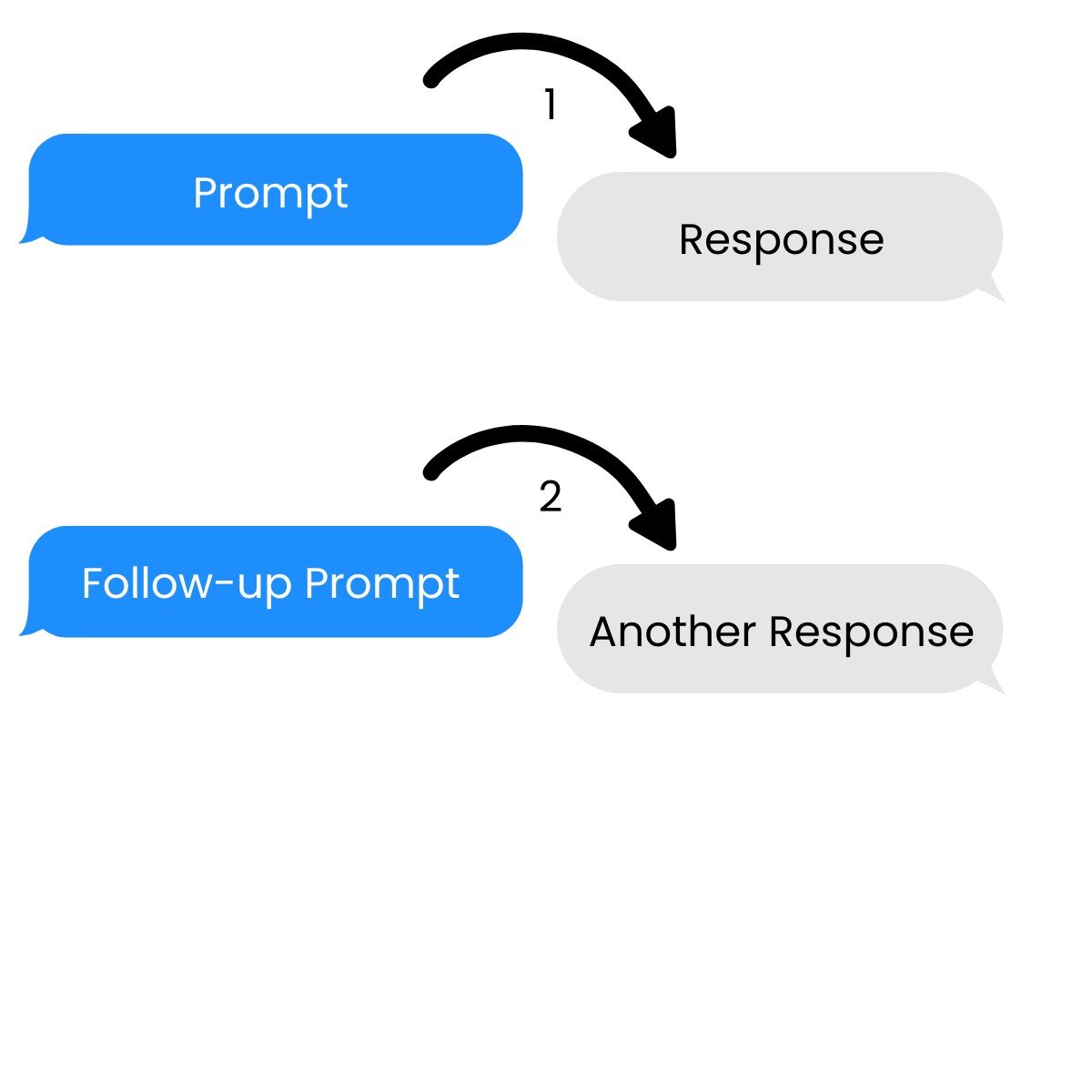
Multi-turn conversations
→ Build on previous prompts and responses
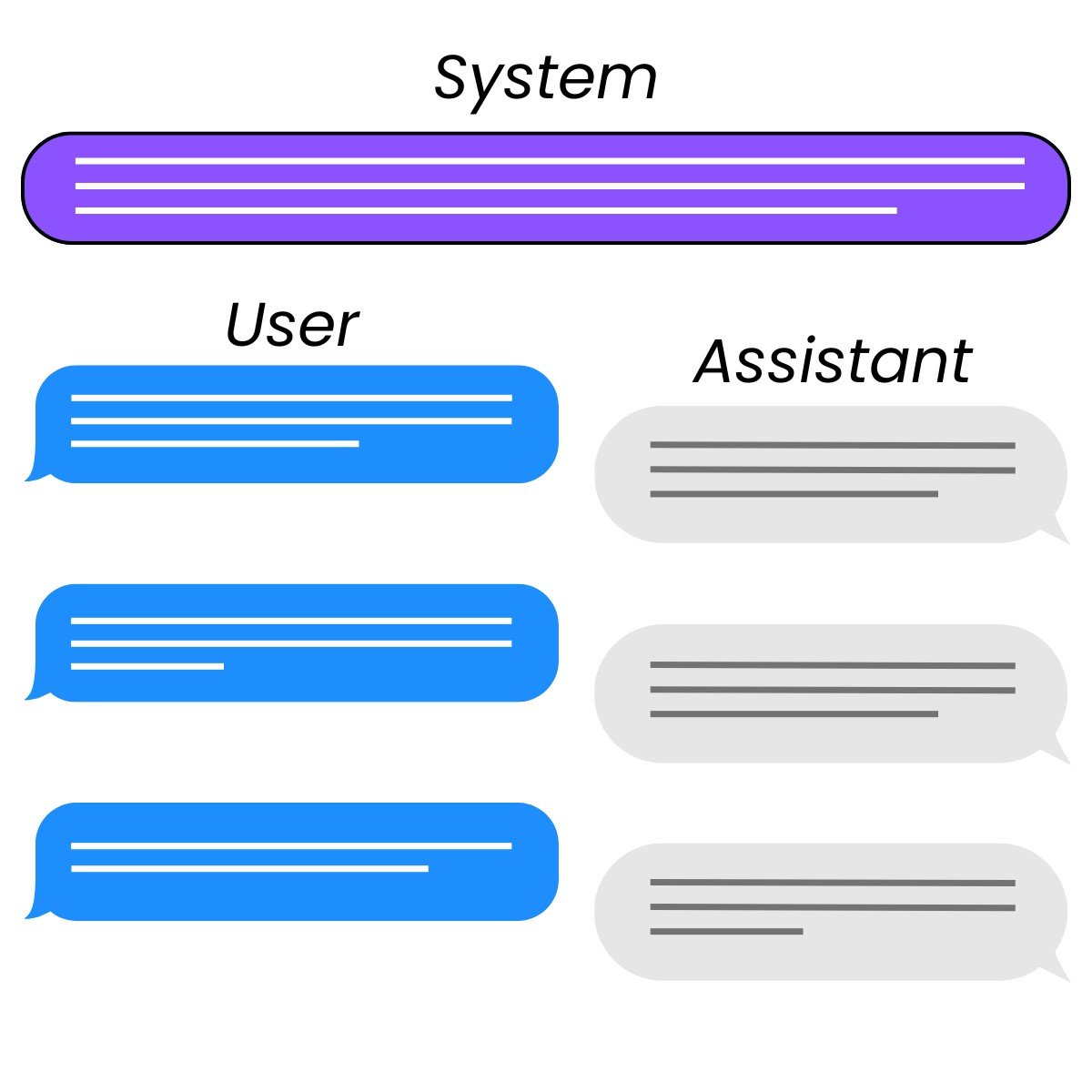
Roles
- System: controls assistant's behavior
- User: instruct the assistant
- Assistant: response to user instruction
- Can also be written by the developer to provide examples
Request setup
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
Prompt setup
messages=[{"role": "system",
"content": "You are a Python programming tutor who responds using concise,
one-sentence explanations."},
{"role": "user",
"content": "What is the difference between mutable and immutable objects?"}]
Making a request
response = client.chat.completions.create( model="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3", messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "You are a Python programming tutor who responds using concise, one-sentence explanations."}, {"role": "user", "content": "What is the difference between mutable and immutable objects?"}] )print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Mutable objects can be changed after creation (like lists), while immutable objects
cannot be modified once created (like tuples or strings).
Mitigating misuse
- System message: Can include guardrails
- Restrictions on model outputs

Mitigating misuse with system messages
sys_msg = """
You are finance education assistant that helps students study for exams.
If you are asked for specific, real-world financial advice with risk to their
finances, respond with only:
I'm sorry, I am not allowed to provide financial advice.
"""
Mitigating misuse with system messages
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3",
messages=[{"role": "system",
"content": sys_msg},
{"role": "user",
"content": "Which stocks should I invest in?"}]
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
I'm sorry, I am not allowed to provide financial advice.
Let's practice!
Working with DeepSeek in Python

