Neural Machine Translation
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for Language Modeling with Keras

David Cecchini
Data Scientist
Encoder and decoders
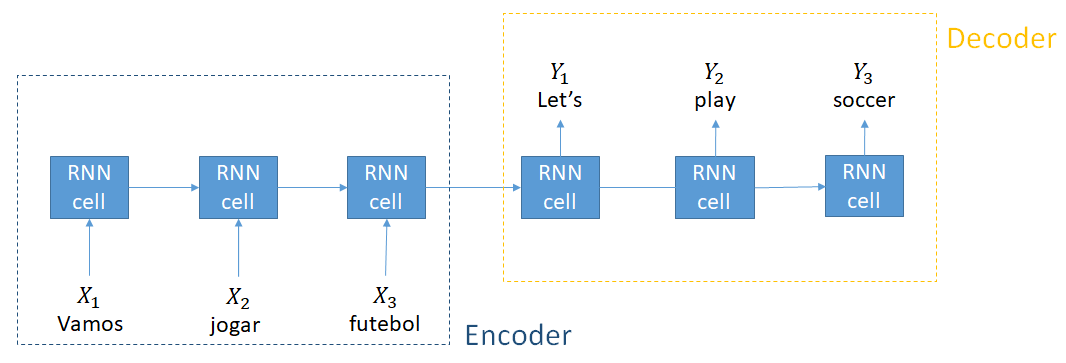
Encoder example
# Instantiate the model model = Sequential()# Embeding layer for input language model.add(Embedding(input_language_size, input_wordvec_dim, input_length=input_language_len, mask_zero=True))# Add LSTM layer model.add(LSTM(128))# Repeat the last vector model.add(RepeatVector(output_language_len))
Decoder example
# Right after the encoder model.add(LSTM(128, return_sequences=True))# Add Time Distributed model.add(TimeDistributed(Dense(eng_vocab_size, activation='softmax')))
Data prep
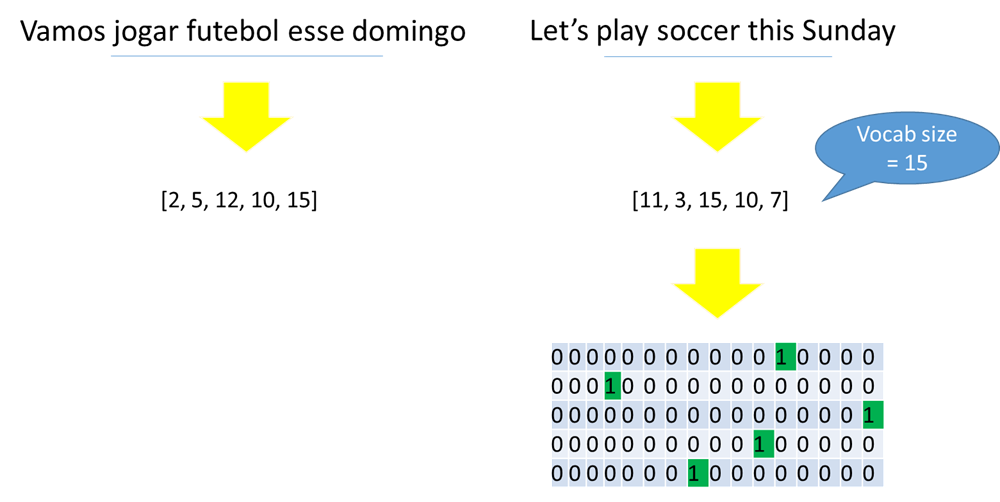
Data preparation for the input language
# Import modules
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
# Use the Tokenizer class tokenizer = Tokenizer() tokenizer.fit_on_texts(input_texts_list)# Text to sequence of numerical indexes X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(input_texts_list)# Pad sequences X = pad_sequences(X, maxlen=length, padding='post')
Tokenize the output language
# Use the Tokenizer class tokenizer = Tokenizer() tokenizer.fit_on_texts(output_texts_list)# Text to sequence of numerical indexes Y = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(output_texts_list)# Pad sequences Y = pad_sequences(Y, maxlen=length, padding='post')
One-hot encode the output language
# Instantiate a temporary variable ylist = list()# Loop over the sequence of numerical indexes for sequence in Y:# One=hot encode each index on current sentence encoded = to_categorical(sequence, num_classes=vocab_size)# Append one-hot encoded values to the list ylist.append(encoded)# Transform to np.array and reshape Y = np.array(ylist).reshape(Y.shape[0], Y.shape[1], vocab_size)
Note on training and evaluating
Training the model:
model.fit(X, Y, epochs=N)
Evaluating:
- Use BLEU
nltk.translate.bleu_score
Let's practice!
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for Language Modeling with Keras

