Valeurs aberrantes, levier et influence
Introduction à la régression dans R

Richie Cotton
Data Evangelist at DataCamp
Ensemble de données sur les gardons
roach <- fish %>%
filter(species == "Roach")
| species | length_cm | mass_g |
|---|---|---|
| Gardon | 12,9 | 40 |
| Gardon | 16,5 | 69 |
| Gardon | 17,5 | 78 |
| Gardon | 18,2 | 87 |
| Gardon | 18,6 | 120 |
| ... | ... | ... |
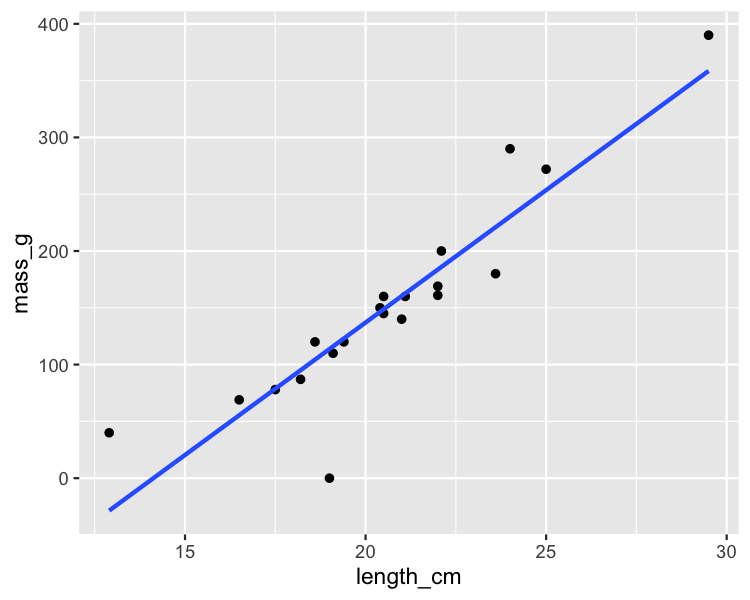
Quels points sont des valeurs aberrantes ?
ggplot(roach, aes(length_cm, mass_g)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)
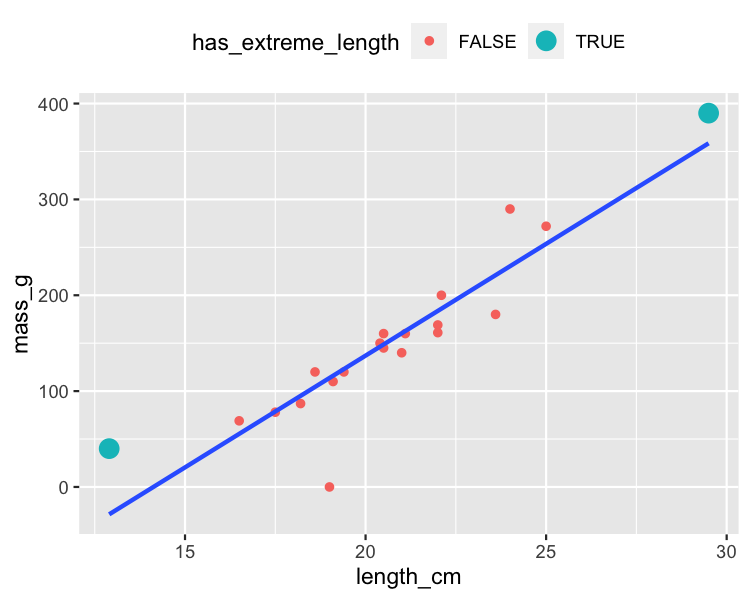
Valeurs explicatives extrêmes
roach %>%
mutate(
has_extreme_length = length_cm < 15 | length_cm > 26
) %>%
ggplot(aes(length_cm, mass_g)) +
geom_point(aes(color = has_extreme_length)) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)
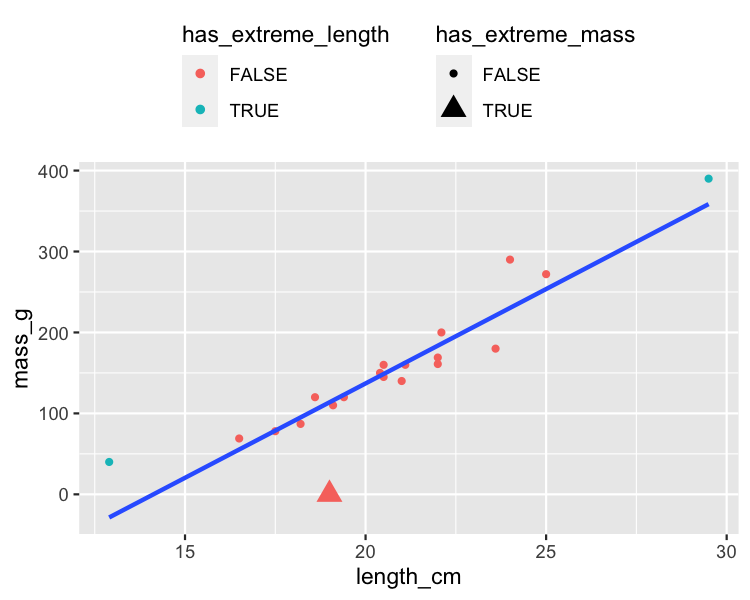
Valeurs de réponse éloignées de la ligne de régression
roach %>%
mutate(
has_extreme_length = length_cm < 15 | length_cm > 26,
has_extreme_mass = mass_g < 1
) %>%
ggplot(aes(length_cm, mass_g)) +
geom_point(
aes(
color = has_extreme_length,
shape = has_extreme_mass
)
) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE)
Levier
Le levier est une mesure de l'extrême variation des valeurs des variables explicatives.
mdl_roach <- lm(mass_g ~ length_cm, data = roach)
hatvalues(mdl_roach)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
0.3137 0.1255 0.0935 0.0763 0.0684 0.0619 0.0605
8 9 10 11 12 13 14
0.0568 0.0503 0.0501 0.0501 0.0506 0.0509 0.0581
15 16 17 18 19 20
0.0581 0.0593 0.0884 0.0995 0.1334 0.3947
La colonne .hat
library(broom)
augment(mdl_roach)
# A tibble: 20 × 8
mass_g length_cm .fitted .resid .hat .sigma .cooksd .std.resid
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 40 12.9 -28.6 68.6 0.314 33.8 1.07 2.17
2 69 16.5 55.4 13.6 0.126 39.1 0.0104 0.381
3 78 17.5 78.7 -0.711 0.0935 39.3 0.0000197 -0.0196
4 87 18.2 95.0 -8.03 0.0763 39.2 0.00198 -0.219
5 120 18.6 104. 15.6 0.0684 39.1 0.00661 0.424
...
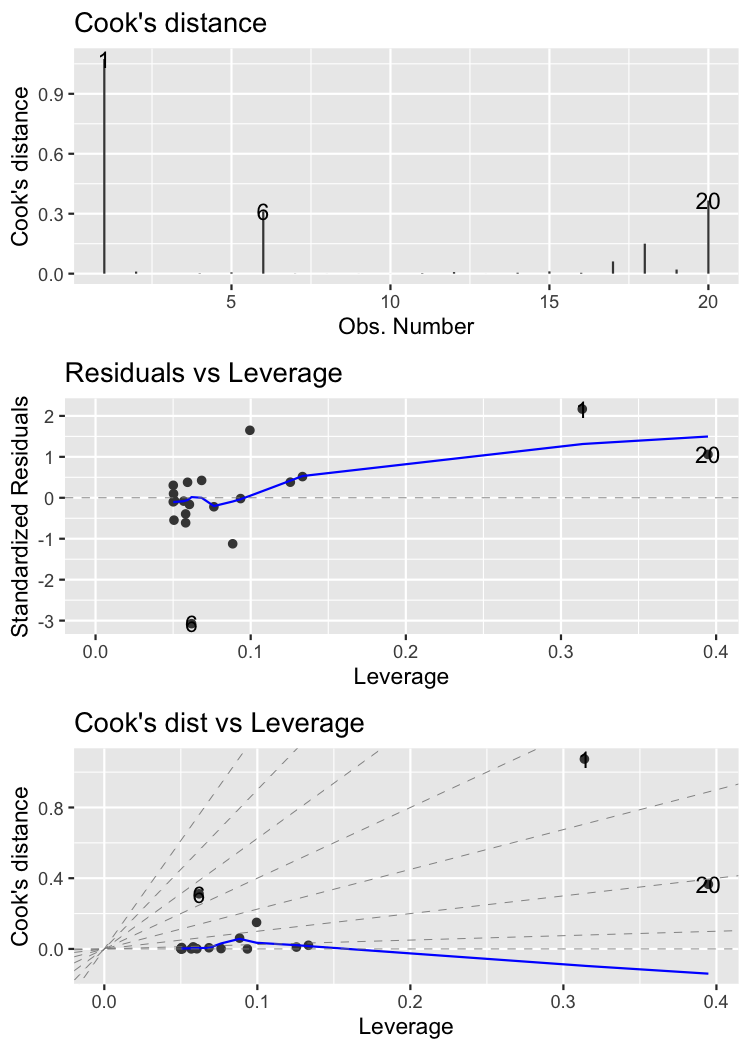
Gardons à fort levier
mdl_roach %>%
augment() %>%
select(mass_g, length_cm, leverage = .hat) %>%
arrange(desc(leverage)) %>%
head()
# A tibble: 6 x 3
mass_g length_cm leverage
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 390 29.5 0.395 # really long roach
2 40 12.9 0.314 # really short roach
3 272 25 0.133
4 69 16.5 0.126
5 290 24 0.0995
6 78 17.5 0.0935
Influence
L'influence mesure dans quelle mesure le modèle changerait si vous retiriez l'observation de l'ensemble de données lors de la modélisation.

Distance de Cook
La distance de Cook est la mesure d'influence la plus couramment utilisée.
cooks.distance(mdl_roach)
1 2 3 4 5 6
1.07e+00 1.04e-02 1.97e-05 1.98e-03 6.61e-03 3.12e-01
7 8 9 10 11 12
8.53e-04 1.99e-04 2.57e-04 2.56e-04 2.45e-03 7.95e-03
13 14 15 16 17 18
1.37e-04 4.82e-03 1.15e-02 4.52e-03 6.12e-02 1.50e-01
19 20
2.06e-02 3.66e-01
La colonne *.cooksd
library(broom)
augment(mdl_roach)
# A tibble: 20 x 9
mass_g length_cm .fitted .se.fit .resid .hat .sigma .cooksd .std.resid
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 40 12.9 -28.6 21.4 68.6 0.314 33.8 1.07 2.17
2 69 16.5 55.4 13.5 13.6 0.126 39.1 0.0104 0.381
3 78 17.5 78.7 11.7 -0.711 0.0935 39.3 0.0000197 -0.0196
4 87 18.2 95.0 10.5 -8.03 0.0763 39.2 0.00198 -0.219
5 120 18.6 104. 9.98 15.6 0.0684 39.1 0.00661 0.424
...
Les gardons les plus influents
mdl_roach %>%
augment() %>%
select(mass_g, length_cm, cooks_dist = .cooksd) %>%
arrange(desc(cooks_dist)) %>%
head()
# A tibble: 6 x 3
mass_g length_cm cooks_dist
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 40 12.9 1.07 # really short roach
2 390 29.5 0.366 # really long roach
3 0 19 0.312 # zero mass roach
4 290 24 0.150
5 180 23.6 0.0612
6 272 25 0.0206
Suppression du gardon le plus influent
roach_not_short <- roach %>%
filter(length != 12.9)
ggplot(roach, aes(length_cm, mass_g)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm", se = FALSE) +
geom_smooth(
method = "lm", se = FALSE,
data = roach_not_short, color = "red"
)
Passons à la pratique !
Introduction à la régression dans R

