Introduction to statistical seismology
Case Studies in Statistical Thinking

Justin Bois
Lecturer, Caltech
California moves and shakes
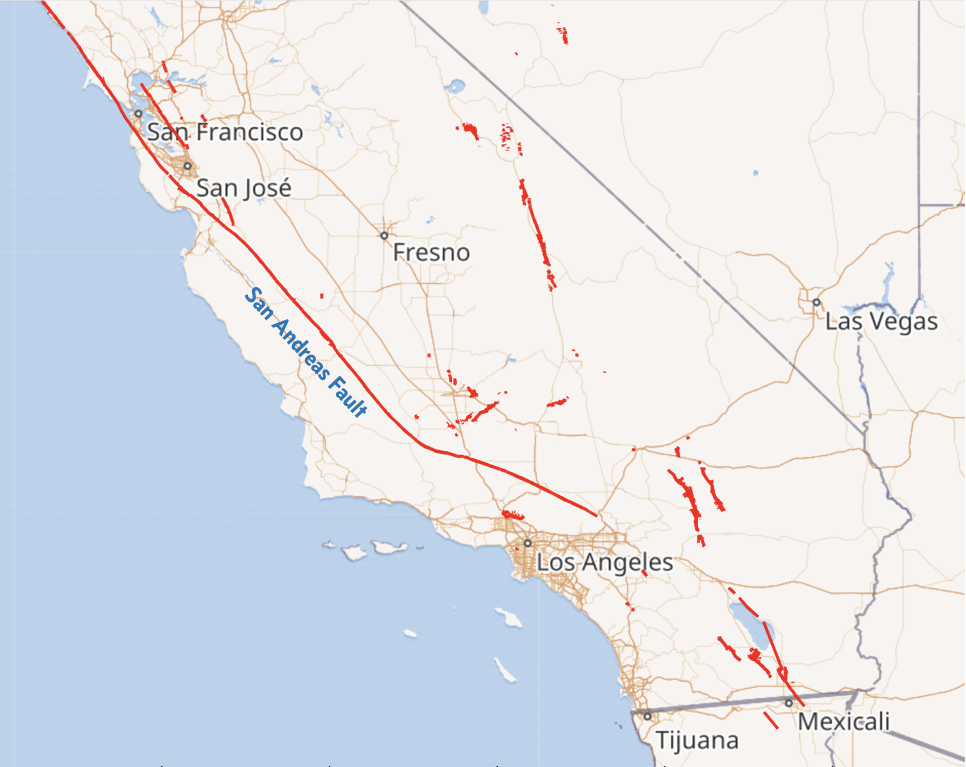
1 Fault data: USGS Quaternary Fault and Fold Database of the United States
The Parkfield region
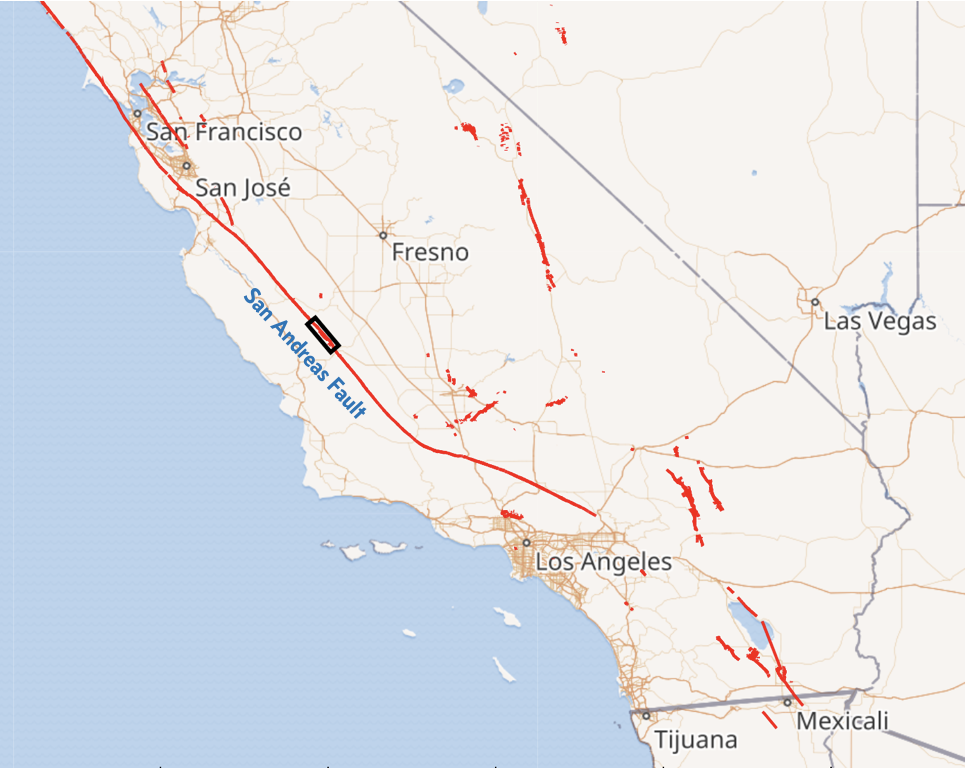
1 Fault data: USGS Quaternary Fault and Fold Database of the United States
The Parkfield region
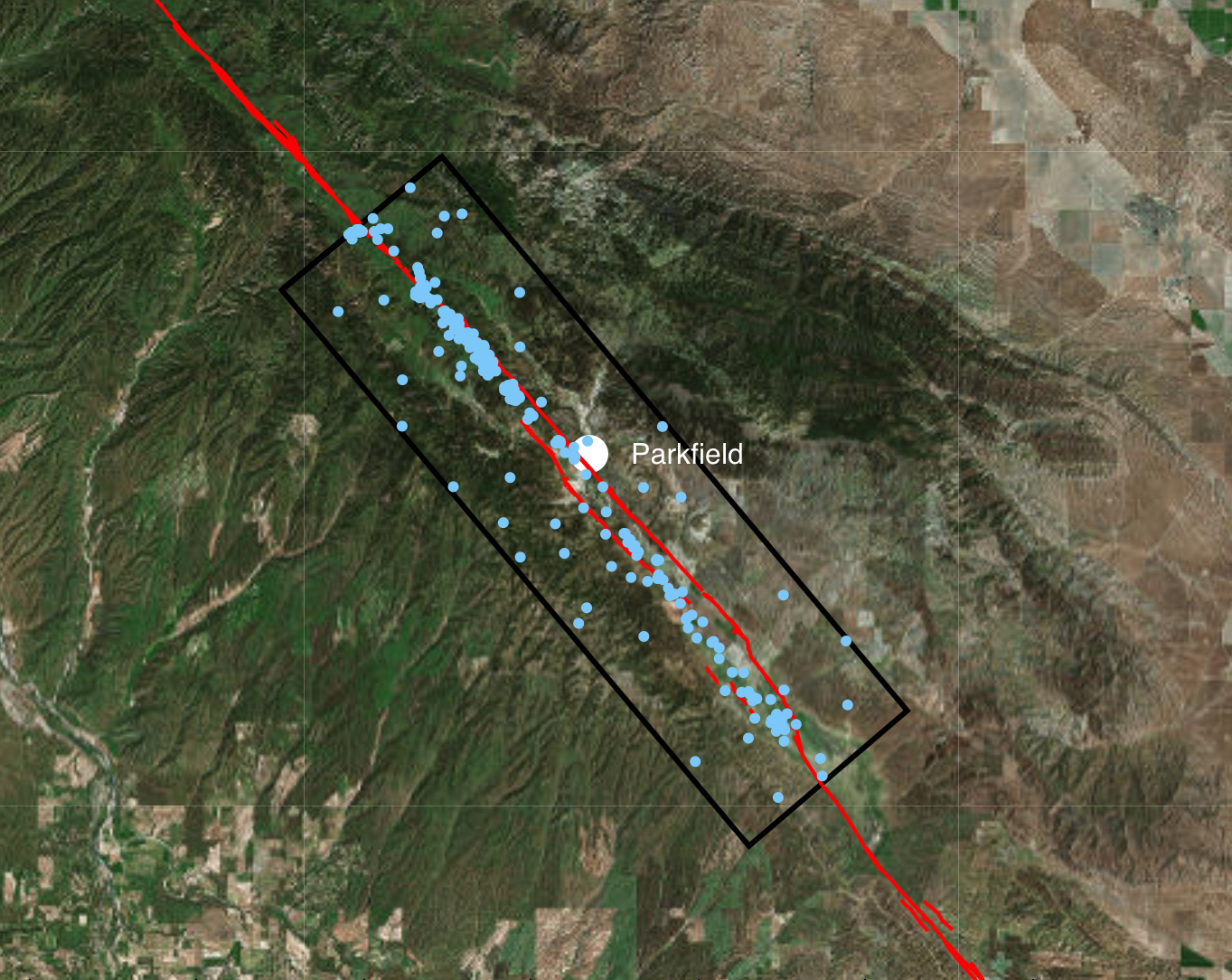
1 Fault data: USGS Quaternary Fault Fault and Fold Database of the United States 2 Earthquake data: USGS ANSS Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog (ComCat)
The Parkfield region

1 Image: Linda Tanner, CC-BY-2.0
Seismic Japan
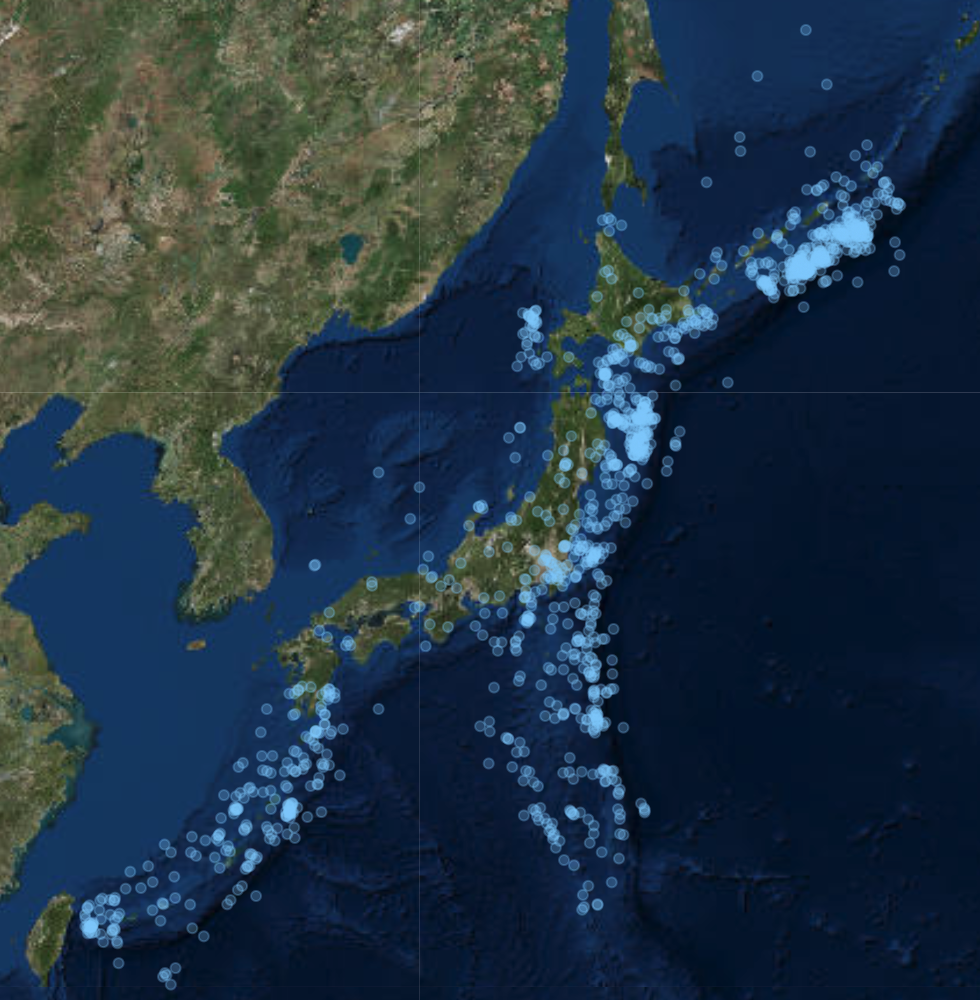
1 Data source: USGS ANSS Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog (ComCat)
ECDF of magnitudes, Japan, 1990-1999
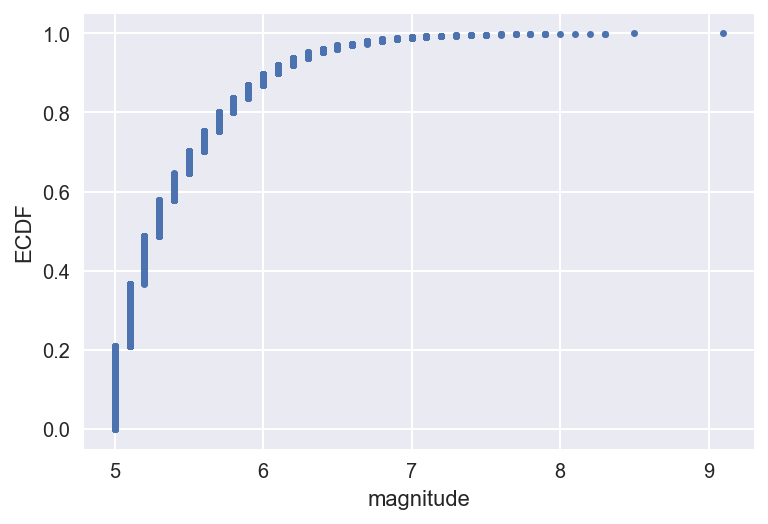
1 Data source: USGS ANSS Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog (ComCat)
Location parameters
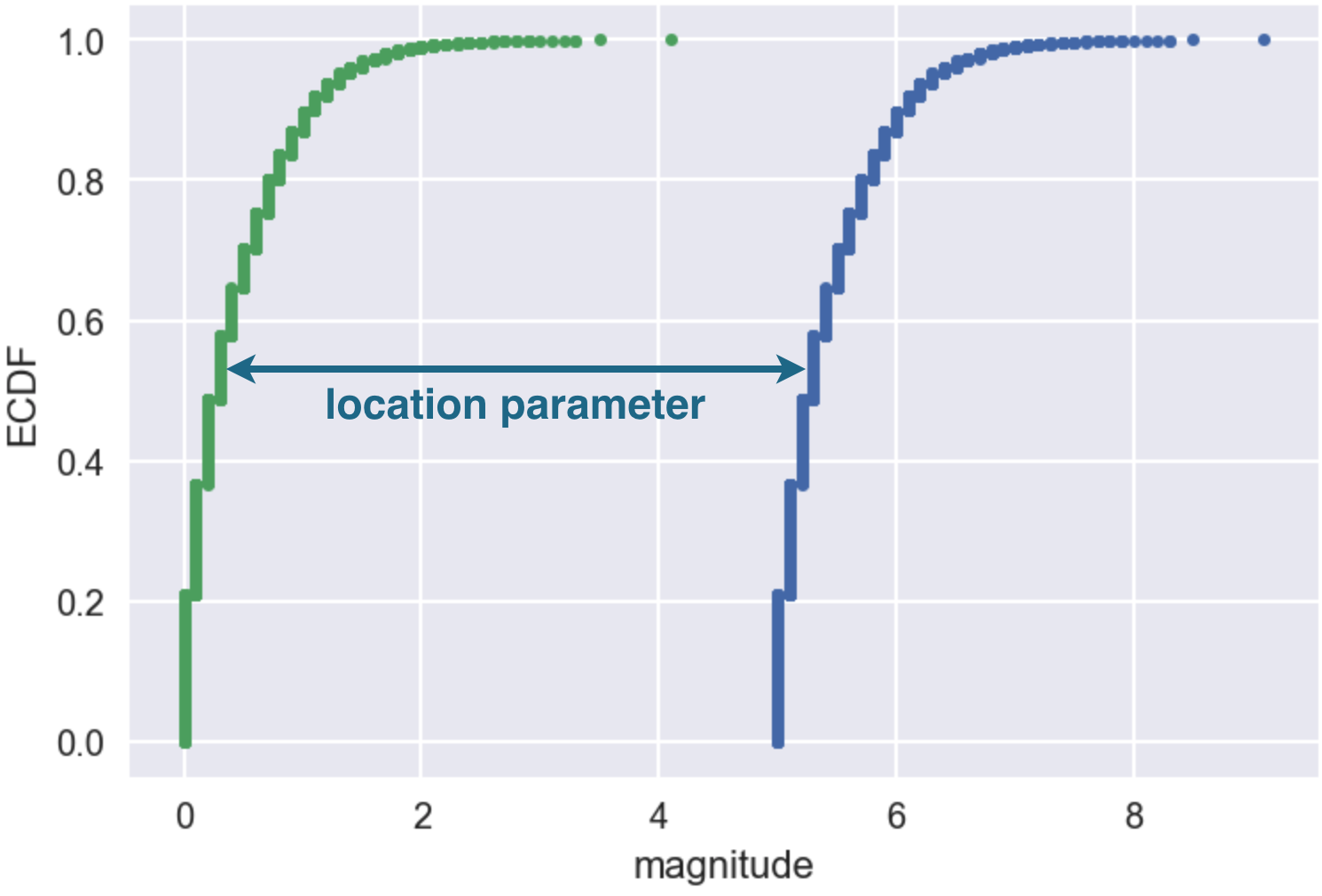
$$m' \equiv m - 5 \sim \text{Exponential}$$
$$m' \equiv m - m_t \sim \text{Exponential}$$
The Gutenberg-Richter Law
The magnitudes of earthquakes in a given region over a given time period are Exponentially distributed
One parameter, given by $\overline{m} - m_t$, describes earthquake magnitudes for a region
The b-value
$$b = (\overline{m}-m_t) \cdot \ln 10$$
# Completeness threshold
mt = 5
# b-value
b = (np.mean(magnitudes) - mt) * np.log(10)
print(b)
0.9729214742632566
ECDF of all magnitudes
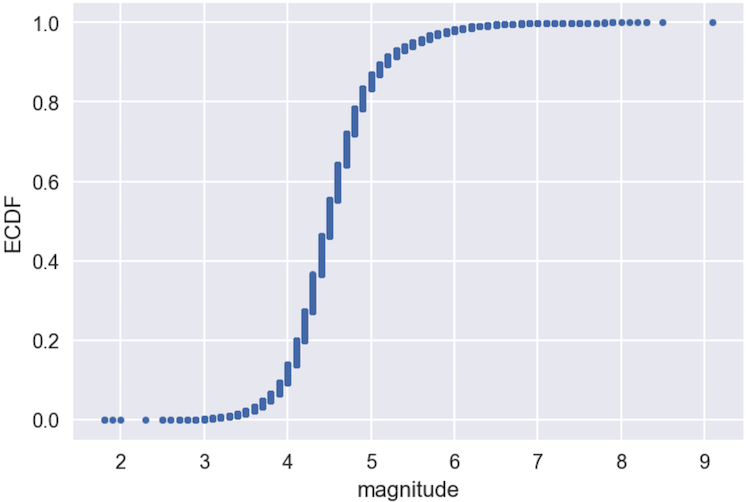
1 Data source: USGS ANSS Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog (ComCat)
ECDF of all magnitudes
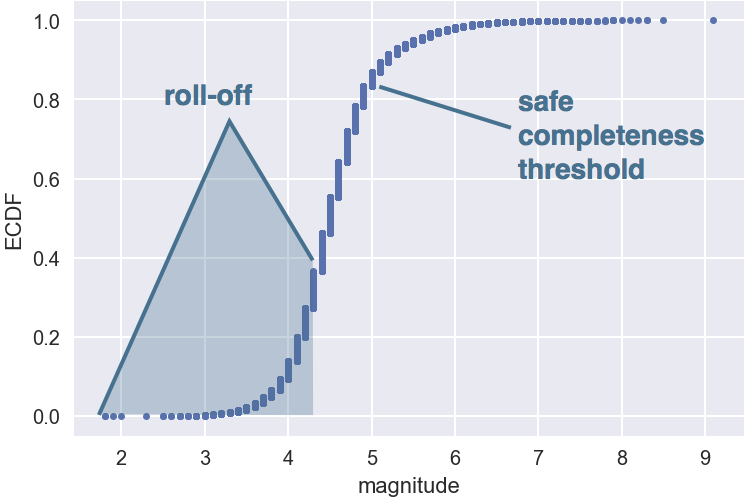
1 Data source: USGS ANSS Comprehensive Earthquake Catalog (ComCat)
Completeness threshold
The magnitude, $m_t$, above which all earthquakes in a region can be detected
Let's practice!
Case Studies in Statistical Thinking

