Portfolio composition and backtesting
Introduction to Portfolio Risk Management in Python

Dakota Wixom
Quantitative Analyst | QuantCourse.com
Calculating portfolio returns
Portfolio Return Formula:
$$ R_p = R_{a_1} w_{a_1} + R_{a_2} w_{a_2} + ... + R_{a_n} w_{a_1} $$
- $ R_p$: Portfolio return
- $ R_{a_n}$: Return for asset n
- $ w_{a_n}$: Weight for asset n
Assuming StockReturns is a pandas DataFrame of stock returns, you can calculate the portfolio return for a set of portfolio weights as follows:
import numpy as np
portfolio_weights = np.array([0.25, 0.35, 0.10, 0.20, 0.10])
port_ret = StockReturns.mul(portfolio_weights, axis=1).sum(axis=1)
port_ret
Date
2017-01-03 0.008082
2017-01-04 0.000161
2017-01-05 0.003448
...
StockReturns["Portfolio"] = port_ret
Equally weighted portfolios in Python
Assuming StockReturns is a pandas DataFrame of stock returns, you can calculate the portfolio return for an equally weighted portfolio as follows:
import numpy as np
numstocks = 5
portfolio_weights_ew = np.repeat(1/numstocks, numstocks)
StockReturns.iloc[:,0:numstocks].mul(portfolio_weights_ew, axis=1).sum(axis=1)
Date
2017-01-03 0.008082
2017-01-04 0.000161
2017-01-05 0.003448
...
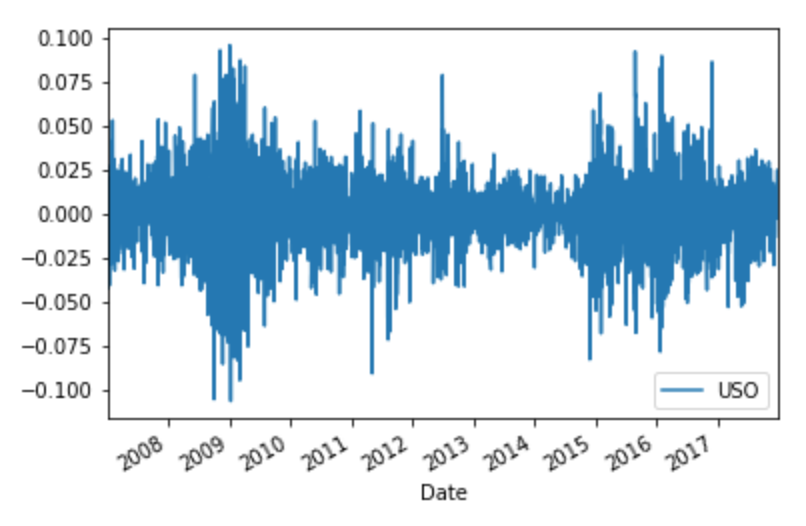
Plotting portfolio returns in Python
To plot the daily returns in Python:
StockPrices["Returns"] = StockPrices["Adj Close"].pct_change()
StockReturns = StockPrices["Returns"]
StockReturns.plot()
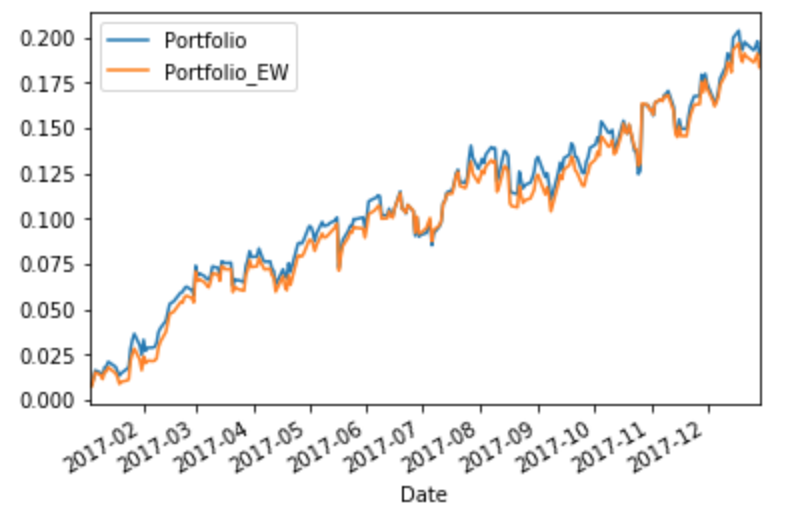
Plotting portfolio cumulative returns
In order to plot the cumulative returns of multiple portfolios:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
CumulativeReturns = ((1 + StockReturns).cumprod() - 1)
CumulativeReturns[["Portfolio","Portfolio_EW"]].plot()
Market capitalization
Market capitalization
Market capitalization: The value of a company's publicly traded shares.
Also referred to as Market cap.
Market-cap weighted portfolios
In order to calculate the market cap weight of a given stock n:
$$ w_{mcap_n} = \frac{mcap_n}{ \sum_{i=1}^n mcap_i } $$
Market-Cap weights in Python
To calculate market cap weights in python, assuming you have data on the market caps of each company:
import numpy as np
market_capitalizations = np.array([100, 200, 100, 100])
mcap_weights = market_capitalizations/sum(market_capitalizations)
mcap_weights
array([0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0.2])
Let's practice!
Introduction to Portfolio Risk Management in Python

