Least-Squares Optimization
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python

Jason Vestuto
Data Scientist
Minima of RSS
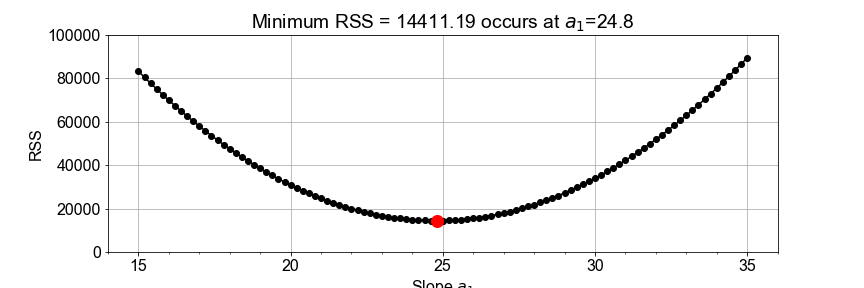
Setting RSS slope = zero, and some calculus, yields:
- $a_1 = covariance(x, y) / variance(x) $
- $a_0 = mean(y) - a_1 \times mean(x) $
Optimized by Numpy
Numpy expressions of optimal slope and intercept
x_mean = np.mean(x)
y_mean = np.mean(y)
x_dev = x - x_mean
y_dev = y - y_mean
a1 = np.sum( x_dev * y_dev ) / np.sum( x_dev**2 )
a0 = y_mean - (a1*x_mean)
Optimized by Scipy
from scipy import optimize
x_data, y_data = load_data()
def model_func(x, a0, a1):
return a0 + (a1*x)
param_opt, param_cov = optimize.curve_fit(model_func, x_data, y_data)
a0 = param_opt[0] # a0 is the intercept in y = a0 + a1*x
a1 = param_opt[1] # a1 is the slope in y = a0 + a1*x
Optimized by Statsmodels
from statsmodels.formula.api import ols
x_data, y_data = load_data()
df = pd.DataFrame(dict(x_name=x_data, y_name=y_data))
model_fit = ols(formula="y_name ~ x_name", data=df).fit()
y_model = model_fit.predict(df)
x_model = x_data
a0 = model_fit.params['Intercept']
a1 = model_fit.params['x_name']
Let's practice!
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python

