Visualizing Linear Relationships
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python

Jason Vestuto
Data Scientist
Quick Plots
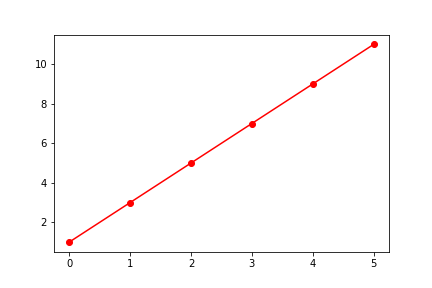
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(x, y, 'r-o')
plt.show()
Object Interface
# Import the pyplot module
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create figure and axis objects
fig, axis = plt.subplots()
# Prepare initial style options
options = dict(marker='o', color='blue')
Object Interface
# Call the plot method on the axis object
line = axis.plot(x, y, **options)
# Modify the axis object with set methods
_ = axis.set_ylabel('Times')
_ = axis.set_xlabel('Distances')
# Display figure
plt.show()
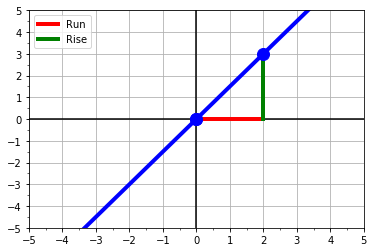
Visualizing Linear Data
- two points:
(x1,y1) = (0,0)(x2,y2) = (2,3)
- change in x and y:
dy = (y2 - y1) = 3 - 0dx = (x2 - x1) = 2 - 0
- slope = rise-over-run
slope = dy/dx = 3/2
- intercept:
- when
x=0:y1 = 0
- when
Let's practice!
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python

