Introduction to MongoDB
Introduction to MongoDB in Python

Filip Schouwenaars
Machine Learning Researcher
Data is everywhere!
Example: Student course data
| student_id | name | course_code | title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amina | CS101 | Intro to Coding |
| 1 | Amina | MATH201 | Algebra Basics |
| 2 | Luca | CS101 | Intro to Coding |
How to store data
Students
| student_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Amina |
| 2 | Luca |
How to store data
Students
| student_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Amina |
| 2 | Luca |
Courses
| course_code | title |
|---|---|
| CS101 | Intro to Coding |
| MATH201 | Algebra Basics |
How to store data
Students
| student_id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Amina |
| 2 | Luca |
Enrollments
| student_id | course_code |
|---|---|
| 1 | CS101 |
| 1 | MATH201 |
| 2 | CS101 |
Courses
| course_code | title |
|---|---|
| CS101 | Intro to Coding |
| MATH201 | Algebra Basics |
Relational model
- Used by relational databases
- Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL
When relational databases fall short
- Great for structured, consistent data
- What about complex, variable data?
- More tables needed for extra details
- Becomes harder to manage as things grow
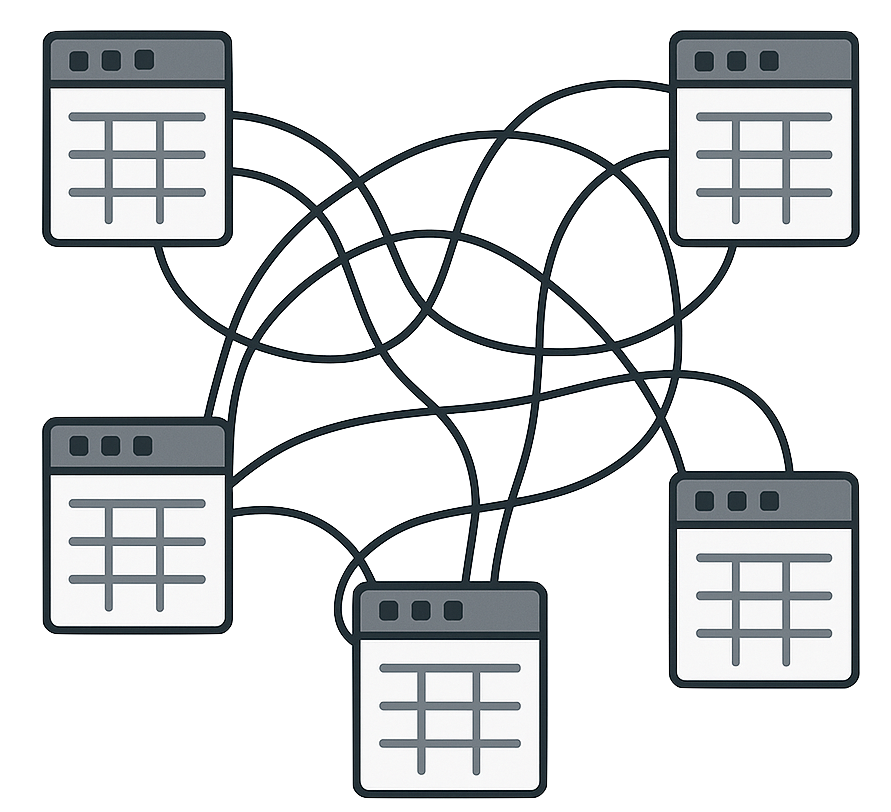
Enter MongoDB
- Document-based, not table-based
- Flexible: each record can look different
- No strict schema required
- Store nested, structured data easily

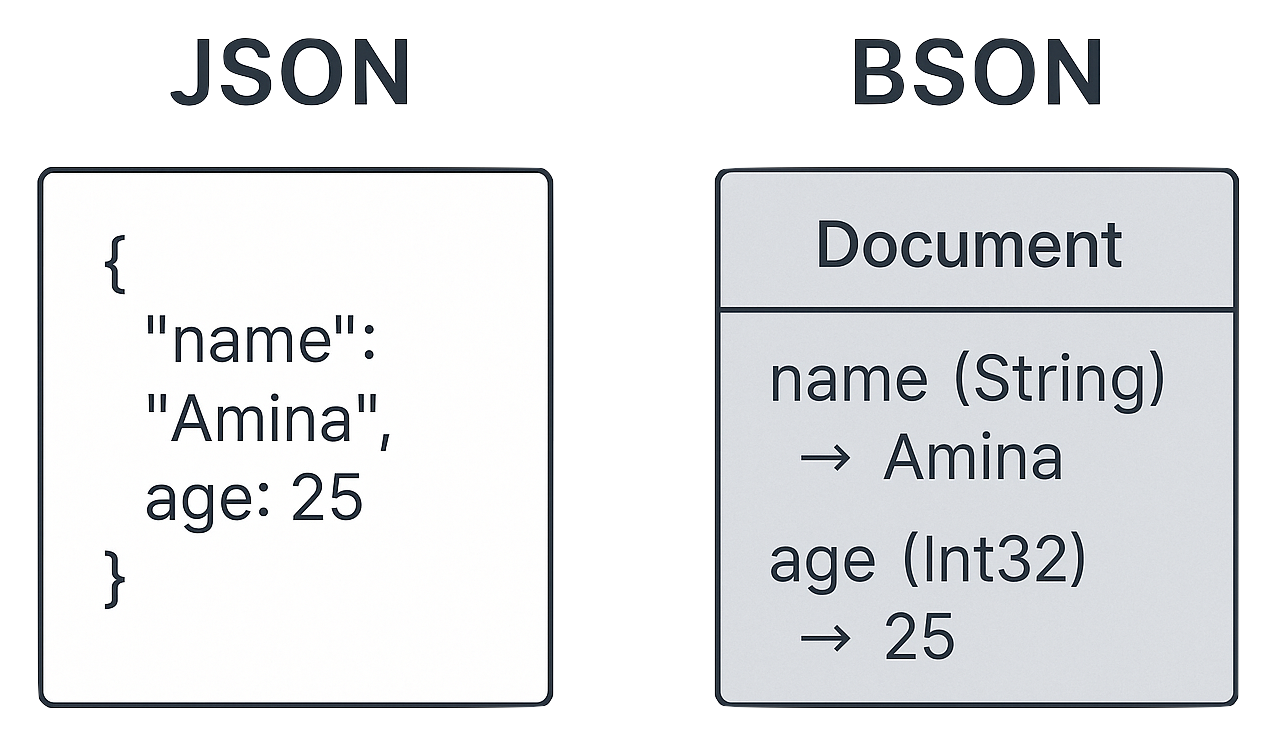
BSON, a special kind of JSON
- BSON = Binary JSON
- Similar, but faster and more efficient
- Extra data types like Date and Binary
- MongoDB uses BSON under the hood
Connecting to MongoDB
from pymongo import MongoClient# Create client (localhost) client = MongoClient()# Create client (remote server) client2 = MongoClient("mongodb+srv://usr:[email protected]")
Let's practice!
Introduction to MongoDB in Python

