Validation set prediction framework
Modeling with Data in the Tidyverse

Albert Y. Kim
Assistant Professor of Statistical and Data Sciences
Validation set approach
Use two independent datasets to:
- Train/fit your model
- Evaluate your model's predictive power i.e. validate your model
Training/test set split
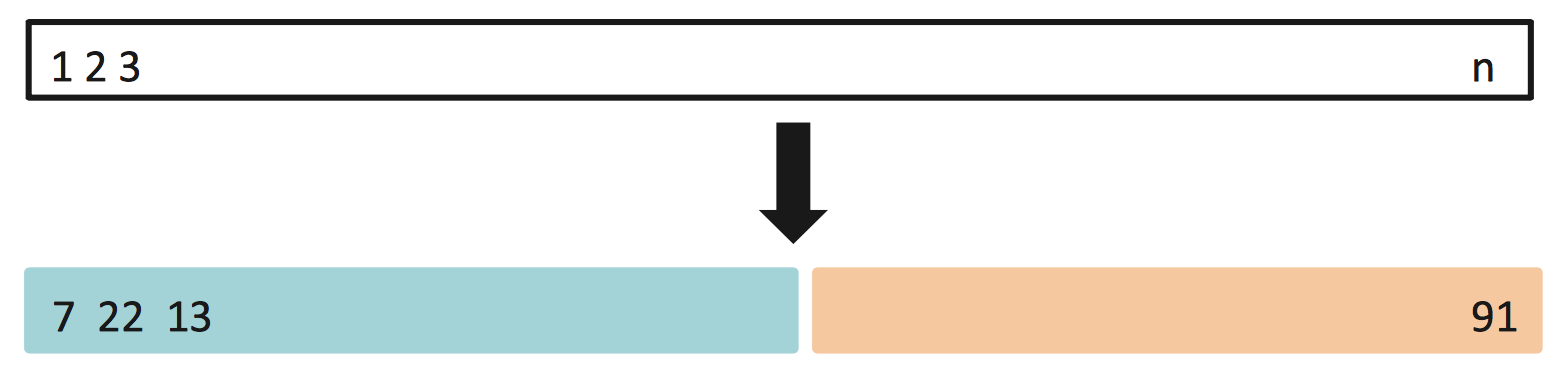
Randomly split all $n$ observations (white) into
- A training set (blue) to fit models
- A test set (orange) to make predictions on
Training/test set split in R
library(dplyr) # Randomly shuffle order of rows: house_prices_shuffled <- house_prices %>% sample_frac(size = 1, replace = FALSE)# Split into train and test: train <- house_prices_shuffled %>% slice(1:10000) test <- house_prices_shuffled %>% slice(10001:21613)
Training models on training data
train_model_price_1 <- lm(log10_price ~ log10_size + yr_built,
data = train)
get_regression_table(train_model_price_1)
# A tibble: 3 x 7
term estimate std_error statistic p_value lower_ci...
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>...
1 intercept 5.34 0.111 48.3 0 5.13...
2 log10_size 0.923 0.009 97.5 0 0.905...
3 yr_built -0.001 0 -23.0 0 -0.001...
Making predictions on test data
# Train model on train:
train_model_price_1 <- lm(log10_price ~ log10_size + yr_built,
data = train)
# Get predictions on test:
get_regression_points(train_model_price_1, newdata = test)
# A tibble: 11,613 x 6
ID log10_price log10_size yr_built log10_price_hat...
<int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>...
1 1 5.83 3.29 1951 5.71...
2 2 5.88 3.40 1922 5.84...
3 3 6.15 3.67 2002 5.99...
4 4 5.62 3 1953 5.43...
...
# ... with 11,603 more rows
Assessing predictions with RMSE
# Train model:
train_model_price_1 <- lm(log10_price ~ log10_size + yr_built,
data = train)
# Get predictions and compute RMSE:
get_regression_points(train_model_price_1, newdata = test) %>%
mutate(sq_residuals = residual^2) %>%
summarize(rmse = sqrt(mean(sq_residuals)))
# A tibble: 1 x 1
rmse
<dbl>
1 0.165
Comparing RMSE
# Train model:
train_model_price_3 <- lm(log10_price ~ log10_size + condition,
data = train)
# Get predictions and compute RMSE:
get_regression_points(train_model_price_3, newdata = test) %>%
mutate(sq_residuals = residual^2) %>%
summarize(rmse = sqrt(mean(sq_residuals)))
# A tibble: 1 x 1
rmse
<dbl>
1 0.168
Let's practice!
Modeling with Data in the Tidyverse

