Principal components in a regression analysis
Machine Learning for Marketing Analytics in R

Verena Pflieger
Data Scientist at INWT Statistics
PC in regression analysis I
mod1 <- lm(customerSatis ~ ., dataCustomers)library(car) vif(mod1)
nOrders nItemsOrdered nItemsSold salesOrdered
29.482287 24.437448 10.390998 5.134720
salesSold returnRatio shareOwnBrand shareSale
9.685617 23.778800 1.571607 1.178773
shareVoucher crDuration monetaryReturnRatio meanDaysBetwOrders
1.213011 1.757509 10.632243 1.698369
salesPerOrder salesPerItem itemsPerOrder itemsSoldPerOrder
6.563474 4.557981 4.821610 15.949072
# Create dataframe with customer satisfaction and first 6 components
dataCustComponents <- cbind(dataCustomers[, "customerSatis"],
pcaCust$x[,1:6]) %>%
as.data.frame
mod2 <- lm(customerSatis ~ ., dataCustComponents)
vif(mod2)
PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 PC6
1 1 1 1 1 1
summary(mod1)$adj.r.squared
0.8678583
summary(mod2)$adj.r.squared
0.7123822
summary(mod2)
Call:
lm(formula = customerSatis ~ ., data = dataCustComponents)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-3.9279 -0.2411 0.0179 0.2865 1.4972
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.985945 0.014039 212.682 < 2e-16 ***
PC1 -0.175434 0.006704 -26.167 < 2e-16 ***
PC2 0.296659 0.007643 38.815 < 2e-16 ***
PC3 -0.012816 0.010838 -1.182 0.237
PC4 -0.116651 0.011665 -10.000 < 2e-16 ***
PC5 0.101963 0.012508 8.152 1.09e-15 ***
PC6 0.126677 0.013072 9.691 < 2e-16 ***
- - -
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 0.4415 on 982 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.7141, Adjusted R-squared: 0.7124
F-statistic: 408.9 on 6 and 982 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
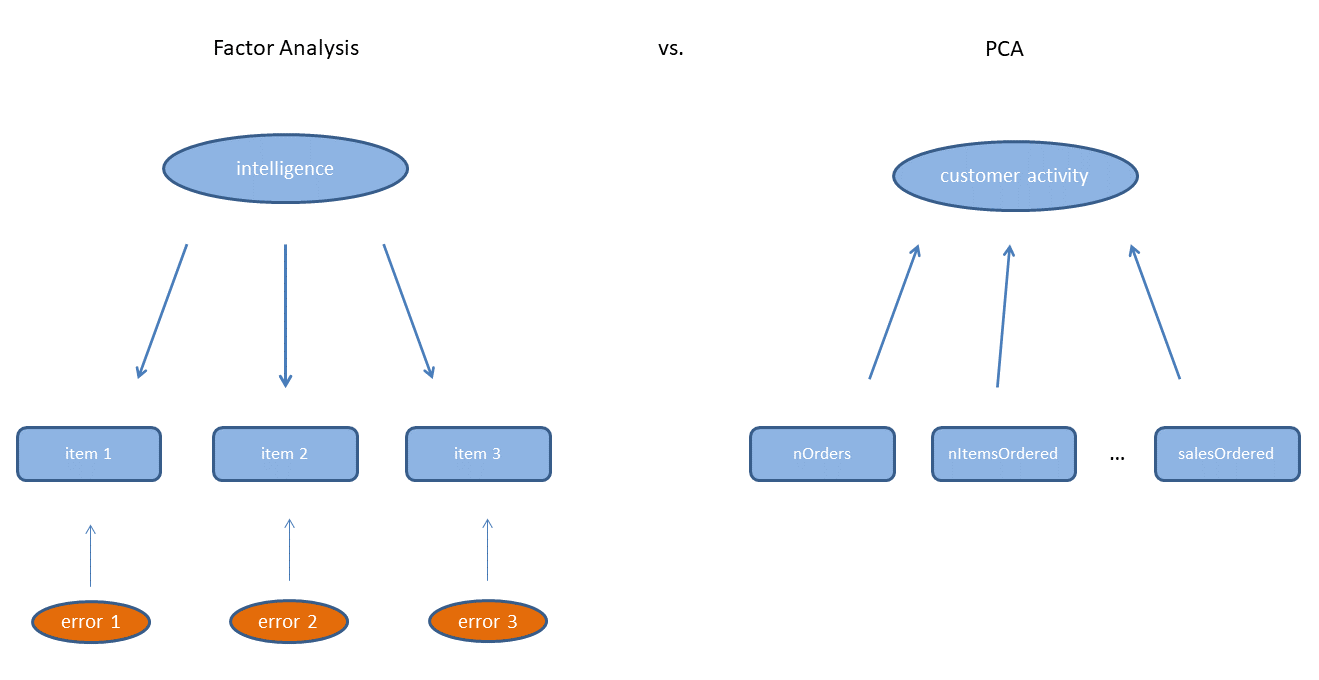
| Learnings about PCA | |
|---|---|
| You have learned... | to reduce the number of variables without losing too much information |
| that variables should be standardized before a PCA | |
| how to decide on the number of relevant components | |
| to interpret the selected components |
| Learnings from the model | |
|---|---|
| You have learned... | that the original variables can be reduced to 6 components, i.a., customer activity, return behavior and brand awareness |
| that using the first six components to explain customer satisfaction causes a decrease in explained variance, but solves the multicollinearity problem |
Let's practice!
Machine Learning for Marketing Analytics in R

