Choosing the right number of principal components
Machine Learning for Marketing Analytics in R

Verena Pflieger
Data Scientist at INWT Statistics
No. relevant components: explained variance
# Proportion of variance explained:
summary(pcaCust)
Importance of components:
PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4 PC5 PC6 PC7
Standard deviation 2.0951 1.8379 1.2960 1.20415 1.12301 1.07453 0.80486
Proportion of Variance 0.2743 0.2111 0.1050 0.09062 0.07882 0.07216 0.04049
Cumulative Proportion 0.2743 0.4855 0.5904 0.68106 0.75989 0.83205 0.87254
PC8 PC9 PC10 PC11 PC12 PC13
Standard deviation 0.78236 0.72452 0.61302 0.48428 0.36803 0.25901
Proportion of Variance 0.03826 0.03281 0.02349 0.01466 0.00847 0.00419
Cumulative Proportion 0.91079 0.94360 0.96709 0.98175 0.99021 0.99440
PC14 PC15 PC16
Standard deviation 0.20699 0.17126 0.13170
Proportion of Variance 0.00268 0.00183 0.00108
Cumulative Proportion 0.99708 0.99892 1.00000
No. relevant components: Kaiser-Guttman criterion
Kaiser-Guttman criterion: Eigenvalue > 1
pcaCust$sdev ^ 2
[1] 4.38961593 3.37778445 1.67965616 1.44997580 1.26115351 1.15461579
[7] 0.64780486 0.61209376 0.52492468 0.37579685 0.23452736 0.13544710
[13] 0.06708362 0.04284504 0.02933027 0.01734481
No. relevant components: screeplot
The screeplot or: "Find the elbow"
screeplot(pcaCust, type = "lines")
box()
abline(h = 1, lty = 2)
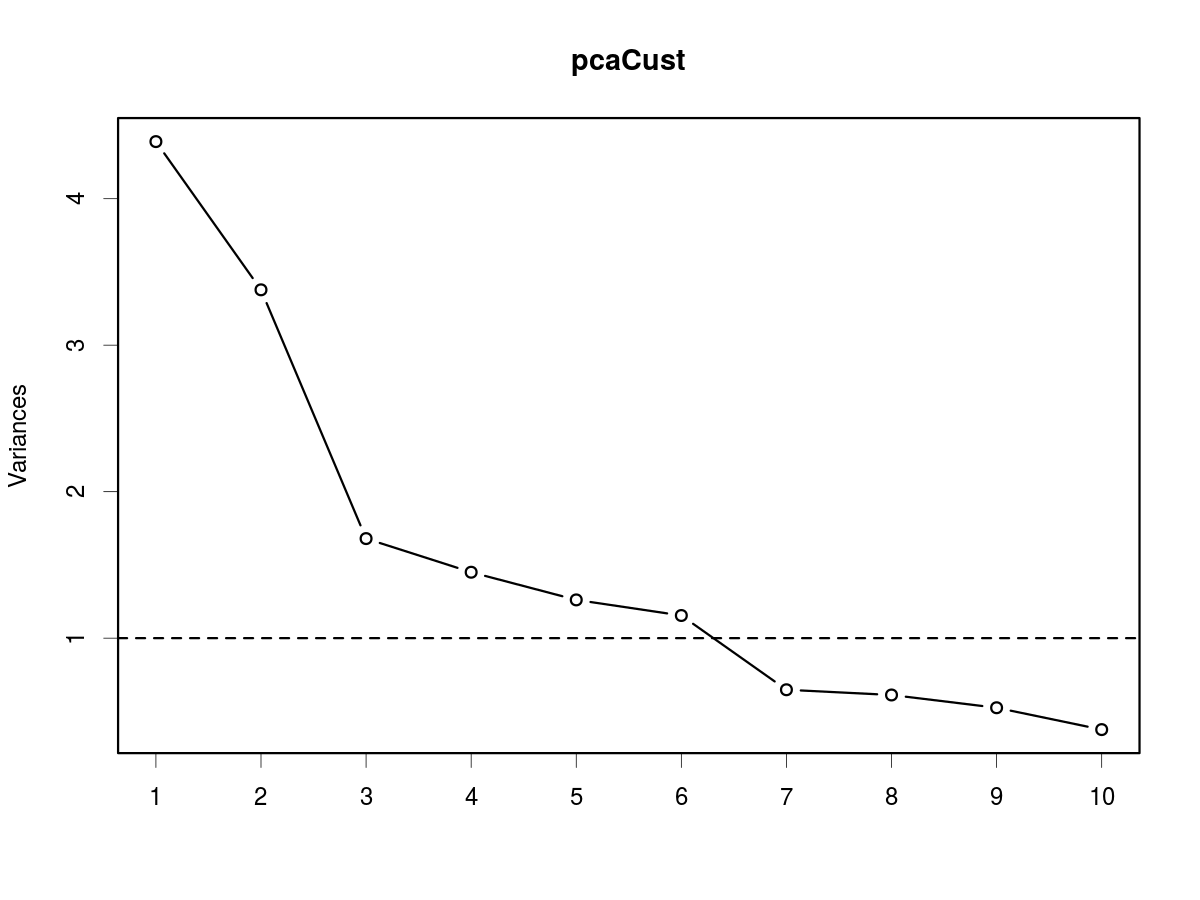
Suggested number of components by criterion
| Explained Variance | Kaiser-Guttman | Screeplot |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 6 | 6 |
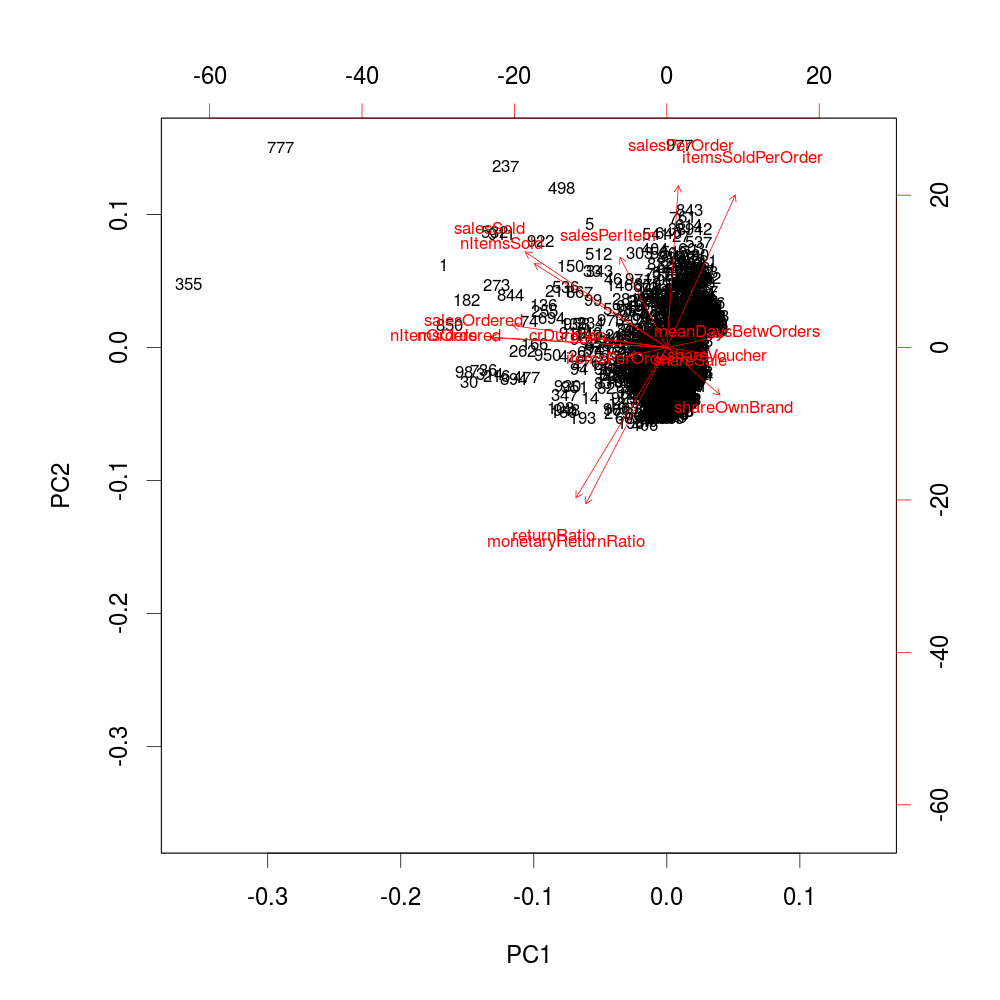
The biplot
biplot(pcaCust, choices = 1:2, cex = 0.7)
Hands on!
Machine Learning for Marketing Analytics in R

