Compare graph distance vs. geographic distance
Case Studies: Network Analysis in R

Edmund Hart
Instructor
Graph distance
farthest_vertices(trip_g_simp)
$vertices
+ 2/300 vertices, named, from 20dcfff:
[1] 336 340
$distance
[1] 5
get_diameter(trip_g_simp)
+ 4/300 vertices, named, from 20dcfff:
[1] 336 267 76 340
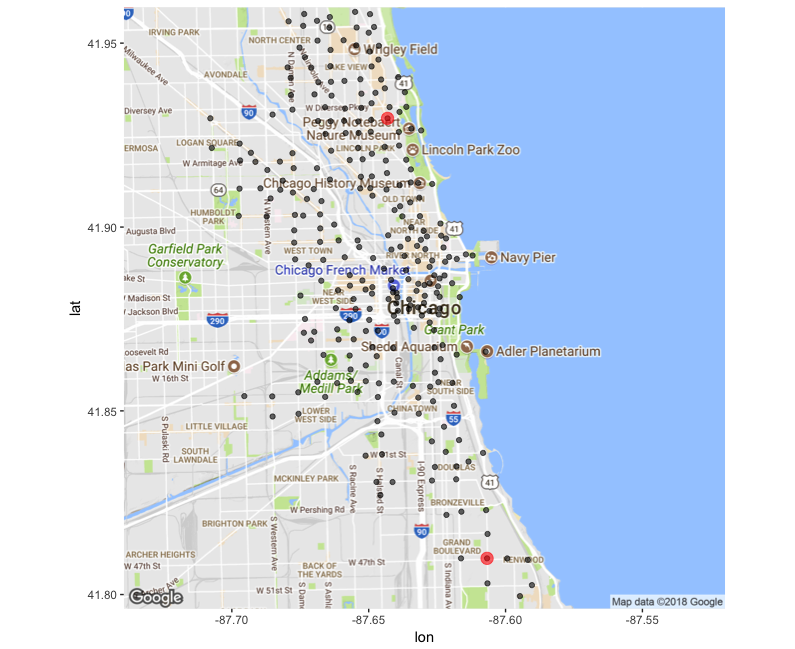
Geographic distance
library(geosphere)# Get the to stations coordinates st_to <- bike_dat %>% filter(from_station_id == 336) %>% sample_n(1) %>% select(from_longitude, from_latitude) # Get the from stations coordinates st_from <- bike_dat %>% filter(from_station_id == 340) %>% sample_n(1) %>% select(from_longitude, from_latitude)# find the geographic distance farthest_dist <- distm(st_from, st_to, fun = distHaversine) farthest_dist
[1, ] 13660.66
Geographic distance
bike_dist <- function(station_1, station_2, divy_bike_df){
st1 <- divy_bike_df %>%
filter(from_station_id == station_1) %>%
sample_n(1) %>%
select(from_longitude, from_latitude)
st2 <- divy_bike_df %>%
filter(from_station_id == station_2) %>%
sample_n(1) %>%
select(from_longitude, from_latitude)
farthest_dist <- distm(st1, st2, fun = distHaversine)
return(farthest_dist)
}
Let's practice!
Case Studies: Network Analysis in R

