Exploring temporal structure
Case Studies: Network Analysis in R

Edmund Hart
Instructor
Are important products always important?
# Get unique Dates d <- sort(unique(amzn_raw$date))# Create graph from first date amzn_g <- graph_from_data_frame( amzn_raw %>% filter(date == d[1]) %>% select(from, to), directed = TRUE )
Are important products always important?
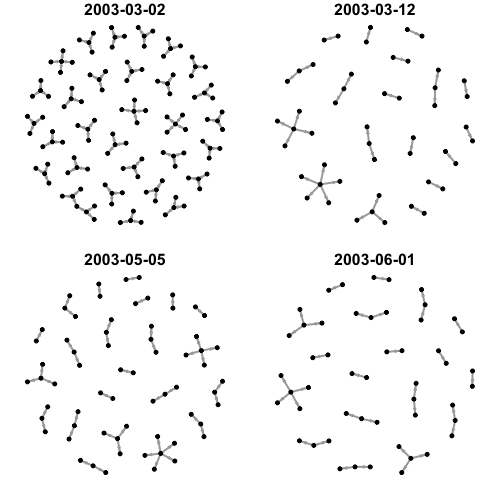
# Find products that are "important" high_out_degree <- degree(amzn_g, mode = "out") > 2 low_in_degree <- degree(amzn_g, mode = "in") < 1 important_nodes <- high_out_degree & low_in_degree imp_prod <- V(amzn_g)[importnant_nodes]# Store as a data frame to later join on tmp_df <- data.frame(imp_prod = as.numeric(names(imp_prod)))
## Create list to hold output time_graph <- list()## Create a 2x2 layout for plots and increase margins par(mfrow = c(2, 2), mar = c(1.1, 1.1, 1.1, 1.1))## Loop over the data to build for(i in 1:length(d)){## Create a data frame at each time stamp ip_df <- amzn_raw %>% filter(date == d[i]) %>% right_join(tmp_df, by = c("from" = "imp_prod")) %>% na.omit()## Create an igraph object from that data frame time_graph[[i]] <- ip_df %>% select(from, to) %>% graph_from_data_frame(directed = TRUE)## See what important vertices look like by date plot(time_graph[[i]], main = d[i]) }
Let's practice!
Case Studies: Network Analysis in R

