Timeseries kinds and applications
Machine Learning for Time Series Data in Python

Chris Holdgraf
Fellow, Berkeley Institute for Data Science
Time Series
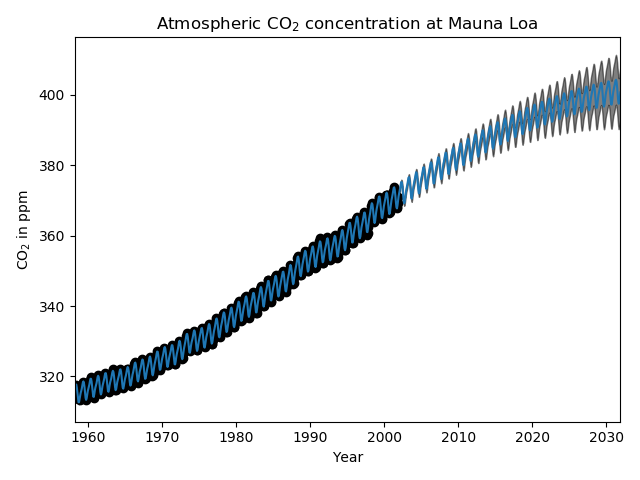

Time Series
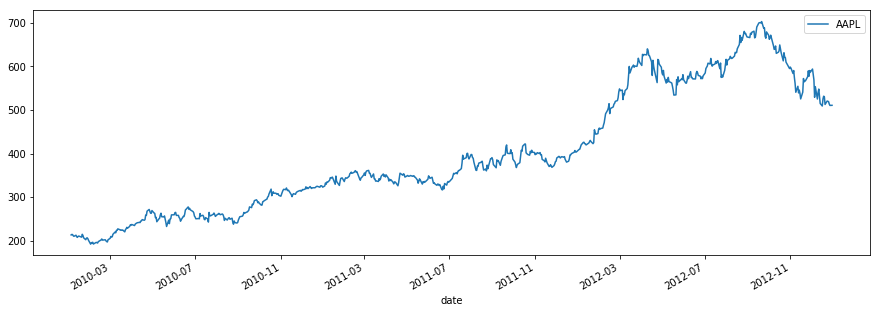
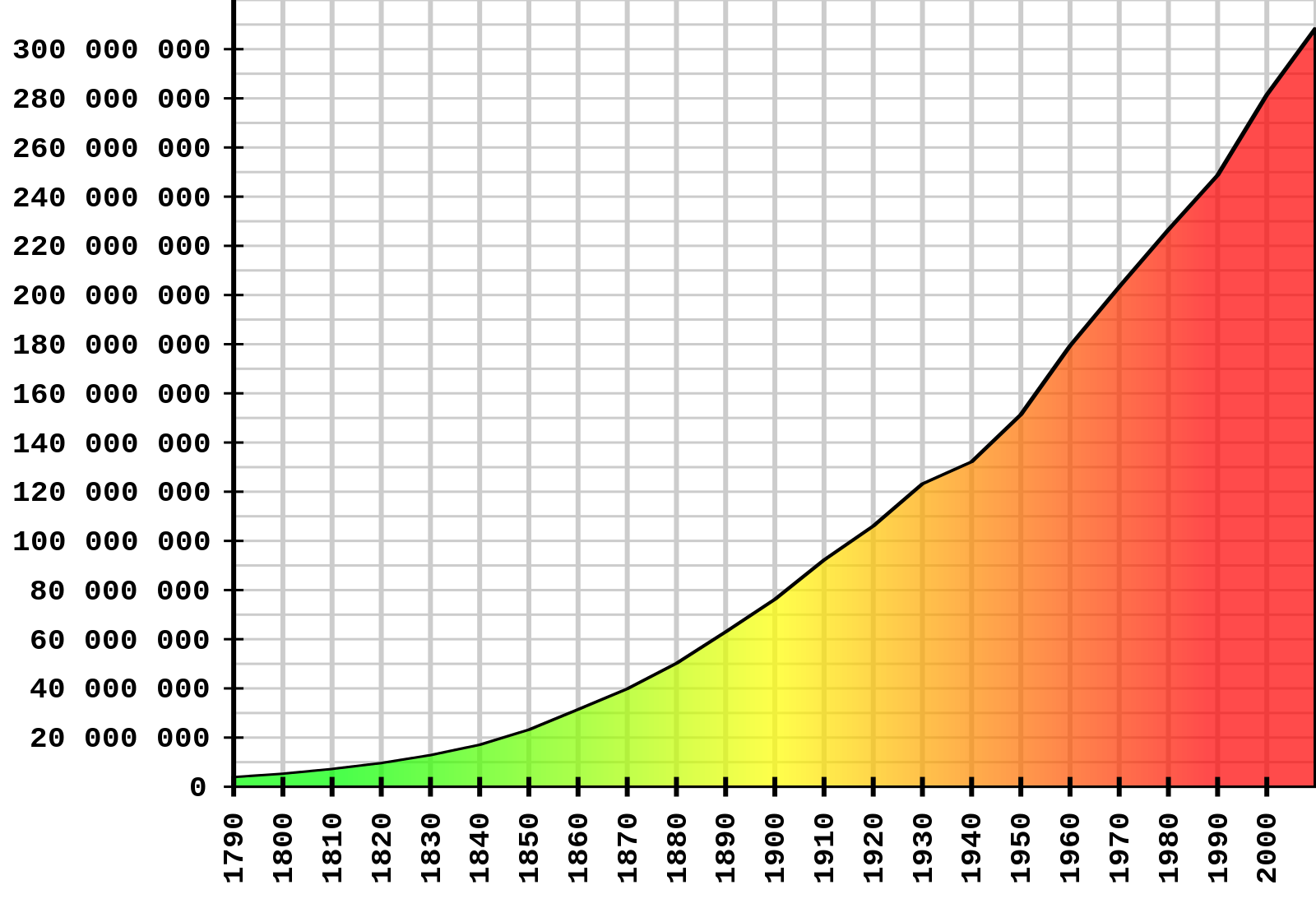
What makes a time series?
| Datapoint | Datapoint | Datapoint | Datapoint | Datapoint | Datapoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34 | 12 | 54 | 76 | 40 |
| Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2:00 | 2:01 | 2:02 | 2:03 | 2:04 | 2:05 |
| Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | Feb | March | April | May | Jun |
| Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint | Timepoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1e-9 | 2e-9 | 3e-9 | 4e-9 | 5e-9 | 6e-9 |
Reading in a time series with Pandas
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = pd.read_csv('data.csv')
data.head()
date symbol close volume
0 2010-01-04 AAPL 214.009998 123432400.0
46 2010-01-05 AAPL 214.379993 150476200.0
92 2010-01-06 AAPL 210.969995 138040000.0
138 2010-01-07 AAPL 210.580000 119282800.0
184 2010-01-08 AAPL 211.980005 111902700.0
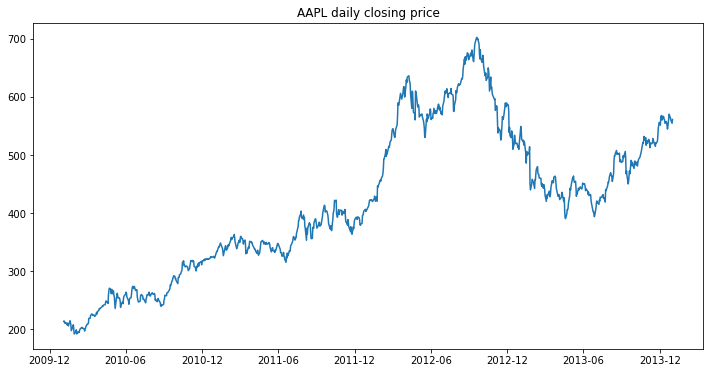
Plotting a pandas timeseries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
data.plot('date', 'close', ax=ax)
ax.set(title="AAPL daily closing price")
A timeseries plot
Why machine learning?
We can use really big data and really complicated data
Why machine learning?
We can...
- Predict the future
- Automate this process
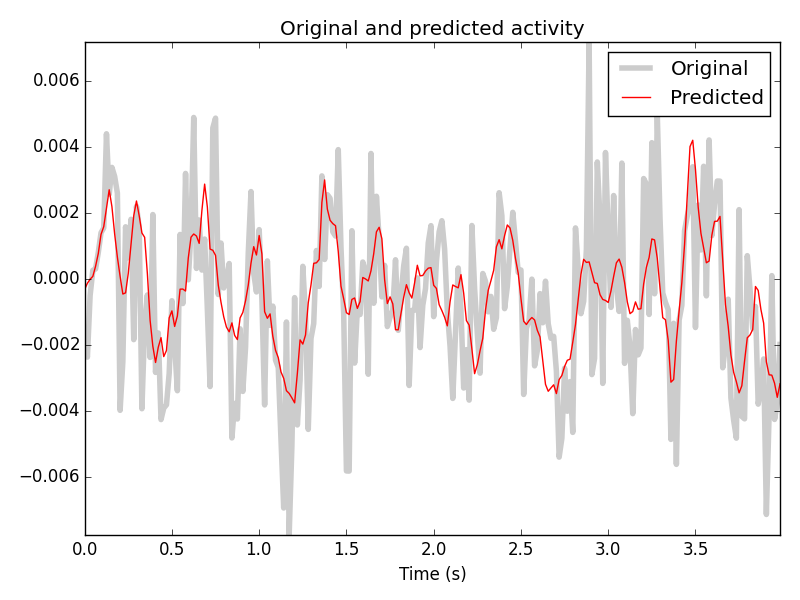
Why combine these two?

A machine learning pipeline
- Feature extraction
- Model fitting
- Prediction and validation
Let's practice!
Machine Learning for Time Series Data in Python

