Types of model outcomes
Nonlinear Modeling with Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) in R

Noam Ross
Senior Research Scientist, EcoHealth Alliance
Types of outcomes
Continuous outcomes
- Speed of a motorcycle (mph)
- Fuel efficiency of a car (mpg)
- Level of pollution in soil (g/kg)
Binary outcomes
- Presence or absence of an organism in a location
- Whether a purchase was made
- Yes/No answer on a survey
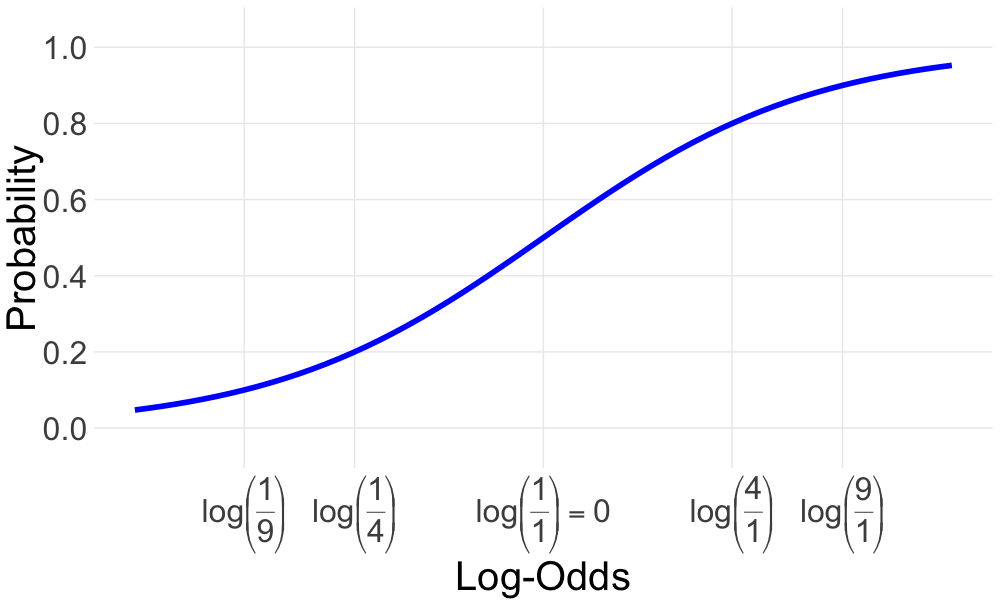
Probabilities and log-odds: logistic function
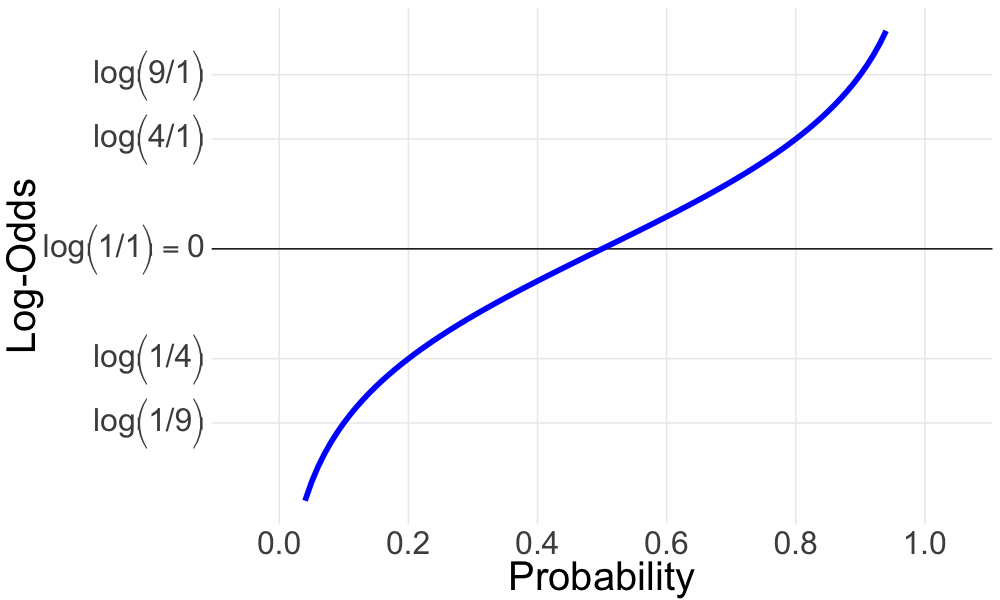
Probabilities and log-odds: logit function
Logistic and logit functions in R
plogis() # Logistic
qlogis() # Logit
qlogis(plogis(0.5))
0.5
qlogis(0.25) == log(1/3)
TRUE
Logistic GAMs with mgcv
gam(y ~ x1 + s(x2),
data = dat,
family = binomial,
method = "REML")
Family: binomial
Link function: logit
Formula:
y ~ s(x1) + s(x2)
Parametric coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 0.7330 0.1208 6.07 1.28e-09 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Approximate significance of smooth terms:
edf Ref.df Chi.sq p-value
s(x1) 1.367 1.646 25.83 1.23e-05 ***
s(x2) 5.754 6.890 51.37 8.12e-09 ***
plogis(0.733)
0.6754633
head(csale)
purchase n_acts bal_crdt_ratio avg_prem_balance retail_crdt_ratio
1 0 11 0.00000 2494.414 0.00000
2 0 0 36.09506 2494.414 11.49123
3 0 6 17.60000 2494.414 0.00000
4 0 8 12.50000 2494.414 0.80000
5 0 8 59.10000 2494.414 20.80000
6 0 1 90.10000 2494.414 11.49123
avg_fin_balance mortgage_age cred_limit
1 1767.197 182.0000 12500
2 1767.197 138.9601 0
3 0.000 138.9601 0
4 1021.000 138.9601 0
5 797.000 93.0000 0
6 4953.000 138.9601 0
Let's practice!
Nonlinear Modeling with Generalized Additive Models (GAMs) in R

