Posterior estimation & inference
Bayesian Modeling with RJAGS

Alicia Johnson
Associate Professor, Macalester College
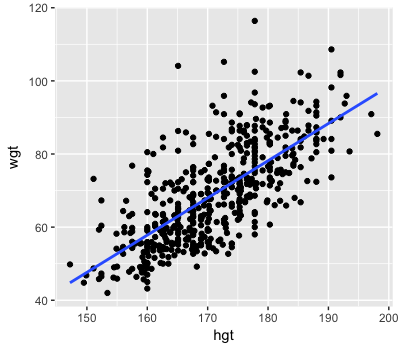
Bayesian regression model
$Y_i$ = weight of adult $i$ (kg)
$X_i$ = height of adult $i$ (cm)
$\;$
Model
$Y_i \sim N(m_i, s^2)$
$m_i = a + b X_i$
$a \sim N(0, 200^2)$
$b \sim N(1, 0.5^2)$
$s \sim \text{Unif}(0, 20)$
Posterior point estimation
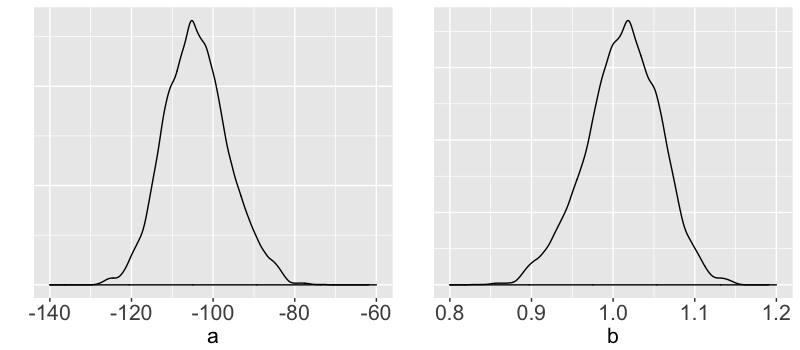
Posterior point estimation
summary(weight_sim_big)
1. Empirical mean and standard deviation for each variable,
plus standard error of the mean:
Mean SD Naive SE Time-series SE
a -104.038 7.85296 0.0248332 0.661515
b 1.012 0.04581 0.0001449 0.003849
s 9.331 0.29495 0.0009327 0.001216
2. Quantiles for each variable:
2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5%
a -118.6843 -109.5171 -104.365 -99.036 -87.470
b 0.9152 0.9828 1.014 1.044 1.098
s 8.7764 9.1284 9.322 9.524 9.933
Posterior mean of $a$ $\approx$ -104.038
Posterior mean of $b$ $\approx$ 1.012
Posterior point estimation
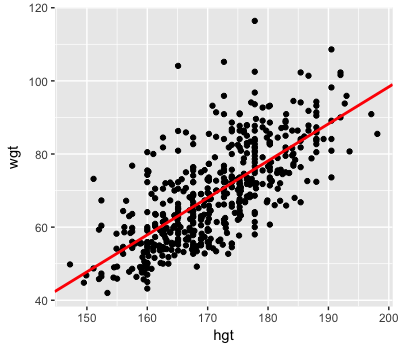
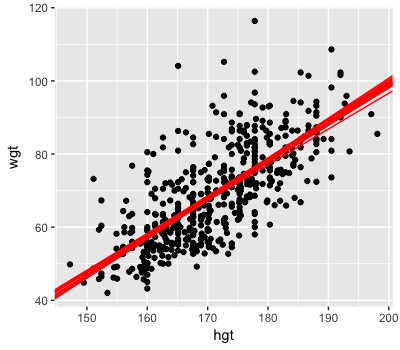
Posterior mean trend:
$m_i = -104.038 + 1.012 X_i$
Markov chain output:
head(weight_chains)
a b s
[1,] -113.9029 1.072505 8.772007
[2,] -115.0644 1.077914 8.986393
[3,] -114.6958 1.077130 9.679812
[4,] -115.0568 1.072668 8.814403
[5,] -114.0782 1.071775 8.895299
[6,] -114.3271 1.069477 9.016185
Posterior uncertainty
Posterior mean trend:
$m_i = -104.038 + 1.012 X_i$
Markov chain output:
head(weight_chains)
a b s
[1,] -113.9029 1.072505 8.772007
[2,] -115.0644 1.077914 8.986393
[3,] -114.6958 1.077130 9.679812
[4,] -115.0568 1.072668 8.814403
[5,] -114.0782 1.071775 8.895299
[6,] -114.3271 1.069477 9.016185
Posterior credible intervals
summary(weight_sim_big)
1. Empirical mean and standard deviation for each variable,
plus standard error of the mean:
Mean SD Naive SE Time-series SE
a -104.038 7.85296 0.0248332 0.661515
b 1.012 0.04581 0.0001449 0.003849
s 9.331 0.29495 0.0009327 0.001216
2. Quantiles for each variable:
2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5%
a -118.6843 -109.5171 -104.365 -99.036 -87.470
b 0.9152 0.9828 1.014 1.044 1.098
s 8.7764 9.1284 9.322 9.524 9.933
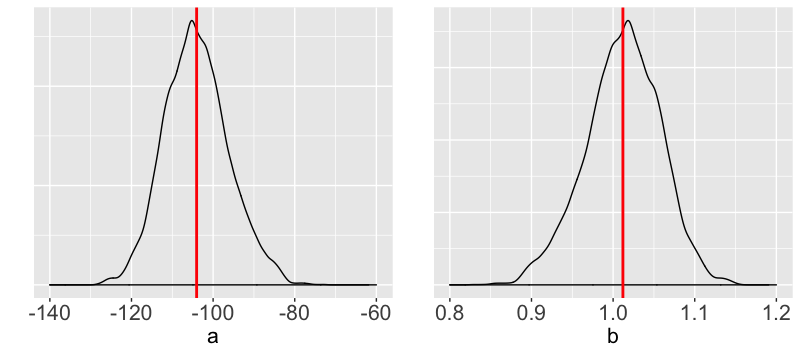
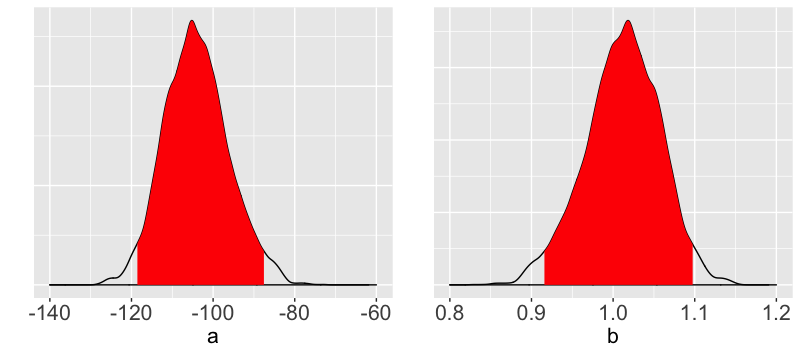
95% posterior credible interval for $a$: (-118.6843, -87.470)
95% posterior credible interval for $b$: (0.9152, 1.098)
Posterior credible intervals

Interpretation
In light of our priors & observed data, there's a 95% (posterior) chance that $b$ is between 0.9152 & 1.098 kg/cm.
Posterior probabilities
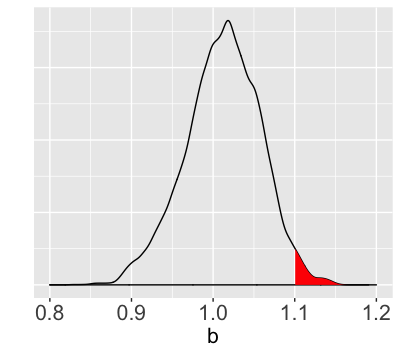
table(weight_chains$b > 1.1)
FALSE TRUE
97835 2165
mean(weight_chains$b > 1.1)
0.02165
Interpretation:
There's a 2.165% posterior chance that $b$ exceeds 1.1 kg/cm.
Let's practice!
Bayesian Modeling with RJAGS

