Markov chains
Bayesian Modeling with RJAGS

Alicia Johnson
Associate Professor, Macalester College
Posterior simulation
Normal-Normal model:
$Y_i$ = change in reaction time (ms)
$Y_i \sim N(m, s^2)$
$m \sim N(50, 25^2)$
$s \sim \text{Unif}(0, 200)$
Approximate posteriors:
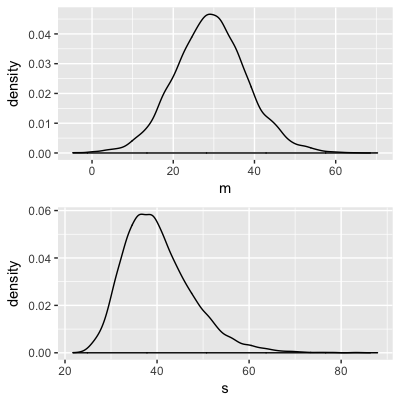
Markov chains
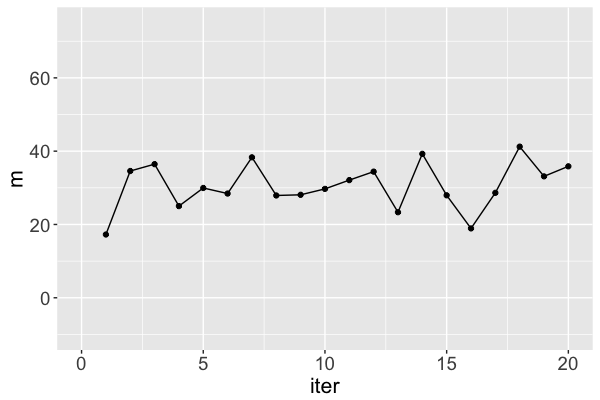
head(sleep_chains, 20)
mis a Markov chain, NOT a random sample from the posteriorRJAGSgoal: Utilize Markov chains to approximate posteriors that are otherwise too complicated to define or sample
m s iter
1 17.25796 31.46256 1
2 34.58469 37.88655 2
3 36.45480 39.58056 3
4 25.00971 39.69494 4
5 29.95475 35.90001 5
6 28.43894 37.46466 6
7 38.32427 35.44081 7
8 27.90956 42.07951 8
9 28.09270 52.36360 9
10 29.70648 28.30665 10
11 32.10350 46.64174 11
12 34.41397 28.86993 12
13 23.33649 37.46498 13
14 39.26587 32.91031 14
15 27.95317 43.13887 15
16 18.91718 44.64376 16
17 28.63141 43.49800 17
18 41.22929 47.42336 18
19 33.12585 42.81980 19
20 35.86270 30.47737 20
Markov chain dependence
head(sleep_chains, 20)
m s iter
1 17.25796 31.46256 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
...
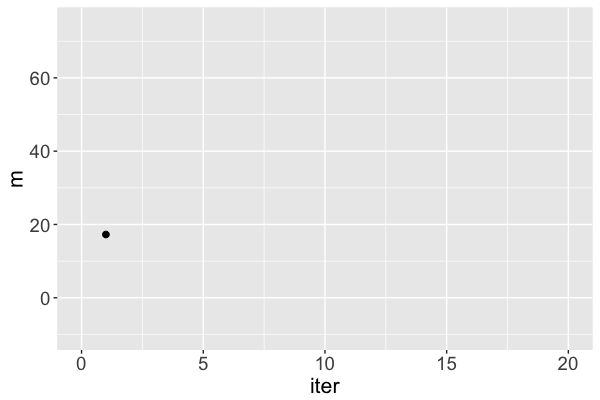
Markov chain dependence
head(sleep_chains, 20)
m s iter
1 17.25796 31.46256 1
2 34.58469 37.88655 2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
...
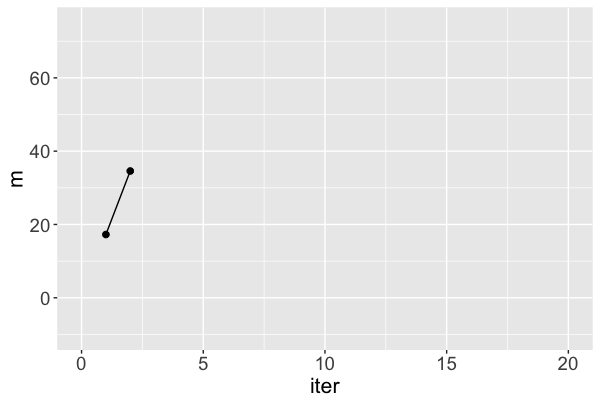
Markov chain dependence
head(sleep_chains, 20)
m s iter
1 17.25796 31.46256 1
2 34.58469 37.88655 2
3 36.45480 39.58056 3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
...
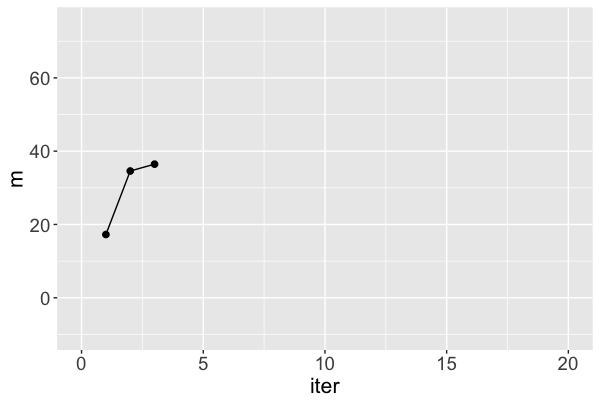
m s iter
1 17.25796 31.46256 1
2 34.58469 37.88655 2
3 36.45480 39.58056 3
4 25.00971 39.69494 4
5 29.95475 35.90001 5
6 28.43894 37.46466 6
7 38.32427 35.44081 7
8 27.90956 42.07951 8
9 28.09270 52.36360 9
10 29.70648 28.30665 10
11 32.10350 46.64174 11
12 34.41397 28.86993 12
13 23.33649 37.46498 13
14 39.26587 32.91031 14
15 27.95317 43.13887 15
16 18.91718 44.64376 16
17 28.63141 43.49800 17
18 41.22929 47.42336 18
19 33.12585 42.81980 19
20 35.86270 30.47737 20
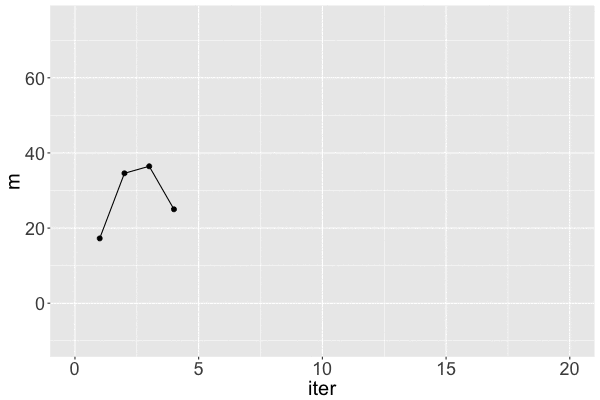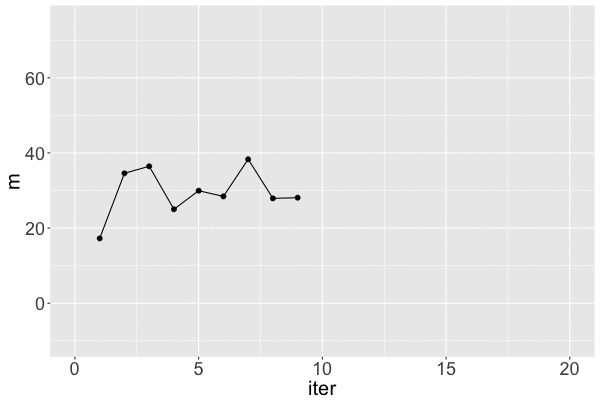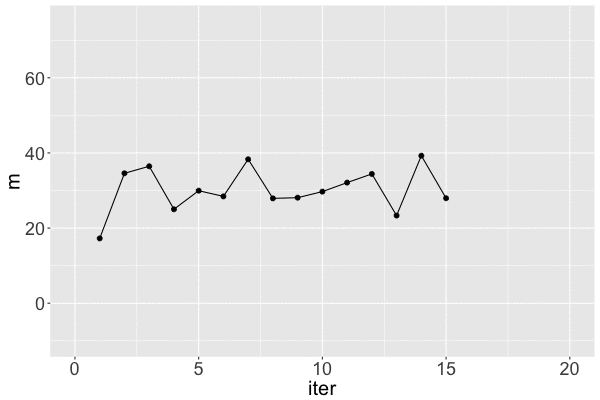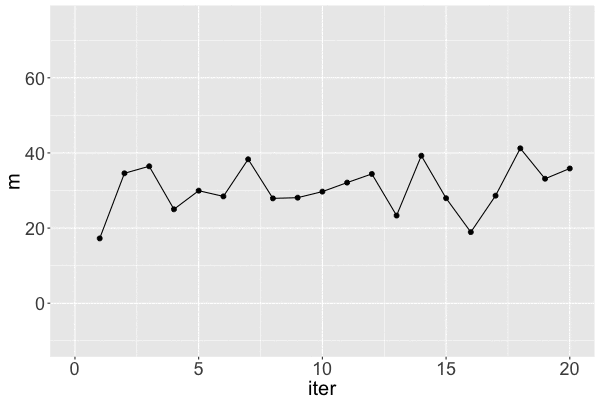
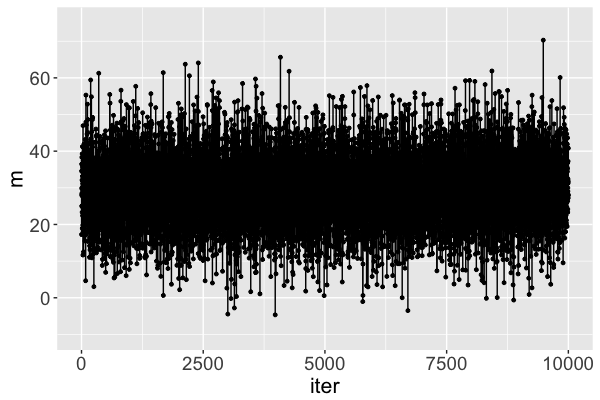
Markov chain dependence
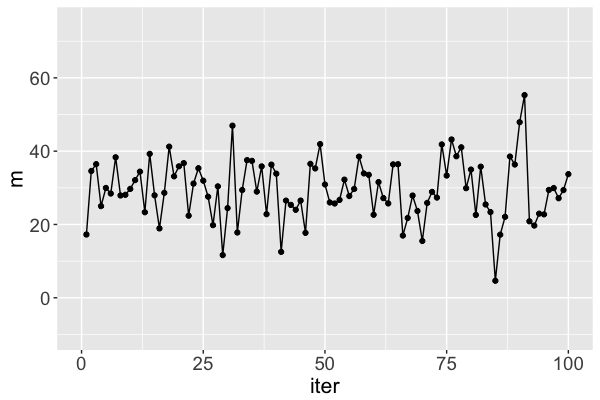
Markov chain trace plot
Markov chain distribution
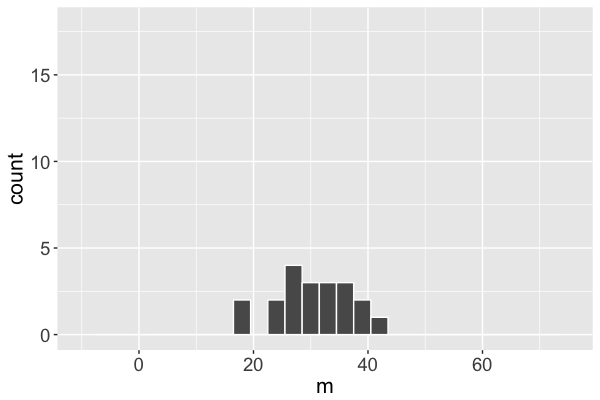
Markov chain distribution

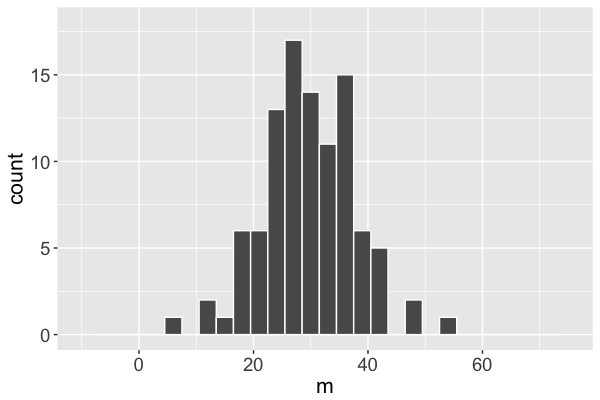
Markov chain distribution

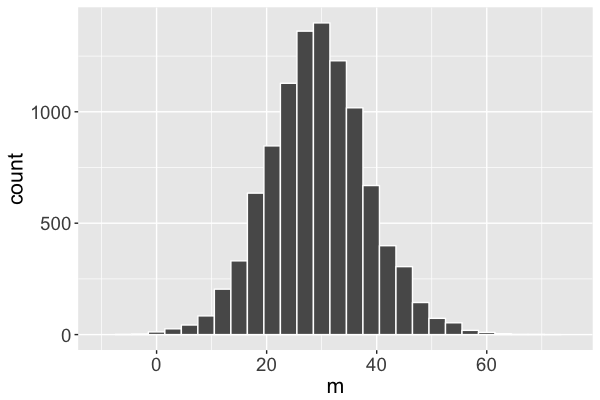
Markov chain distribution: an approximation of the posterior!

The $m$ Markov chain...
traverses the sample space of $m$,
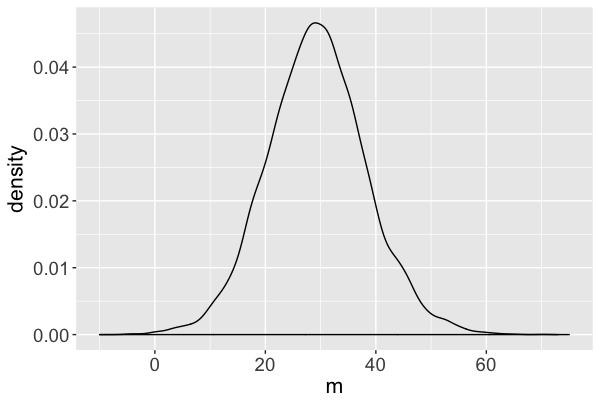
mimics a random sample, and
converges to the posterior.
Let's practice!
Bayesian Modeling with RJAGS

