Density of a multivariate normal distribution
Multivariate Probability Distributions in R

Surajit Ray
Professor, University of Glasgow
Why calculate the density of a distribution?
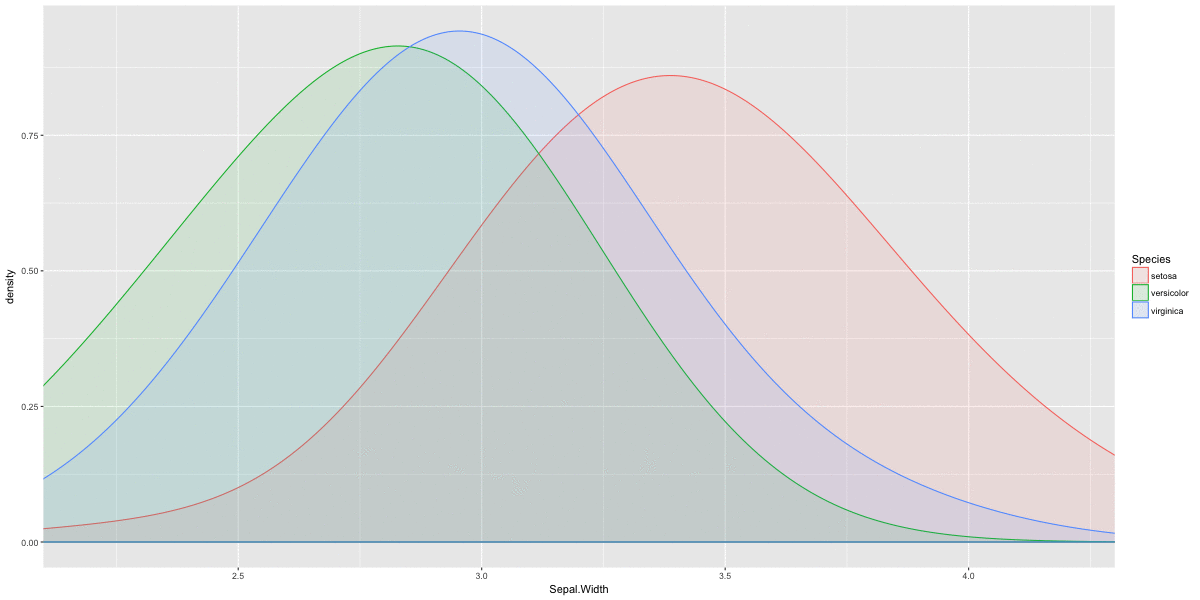
Why calculate the density of a distribution?
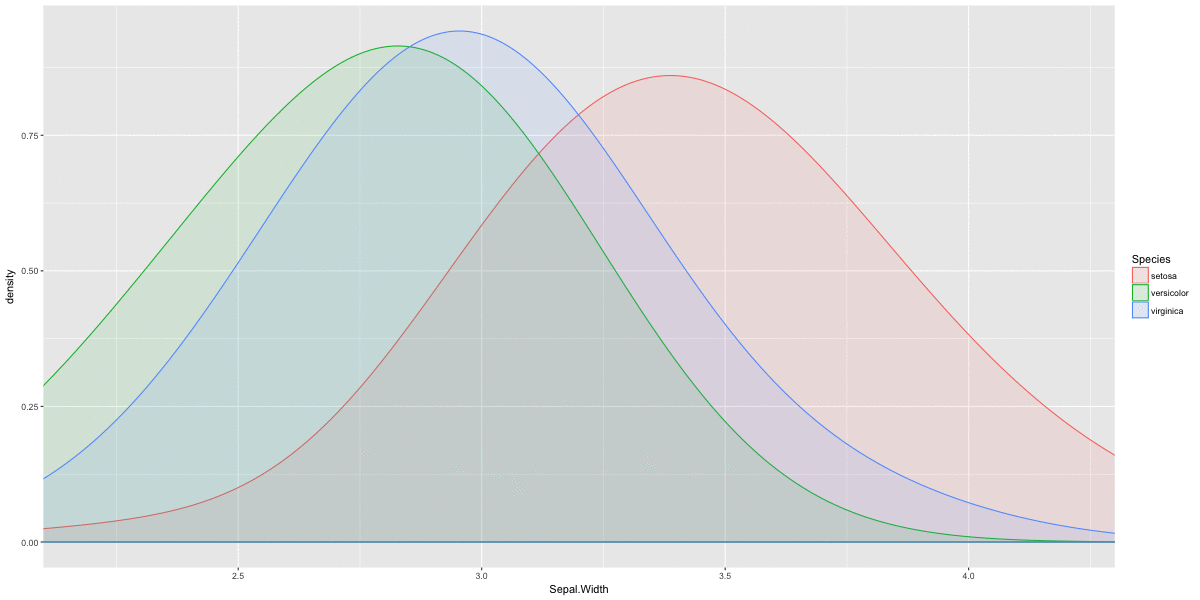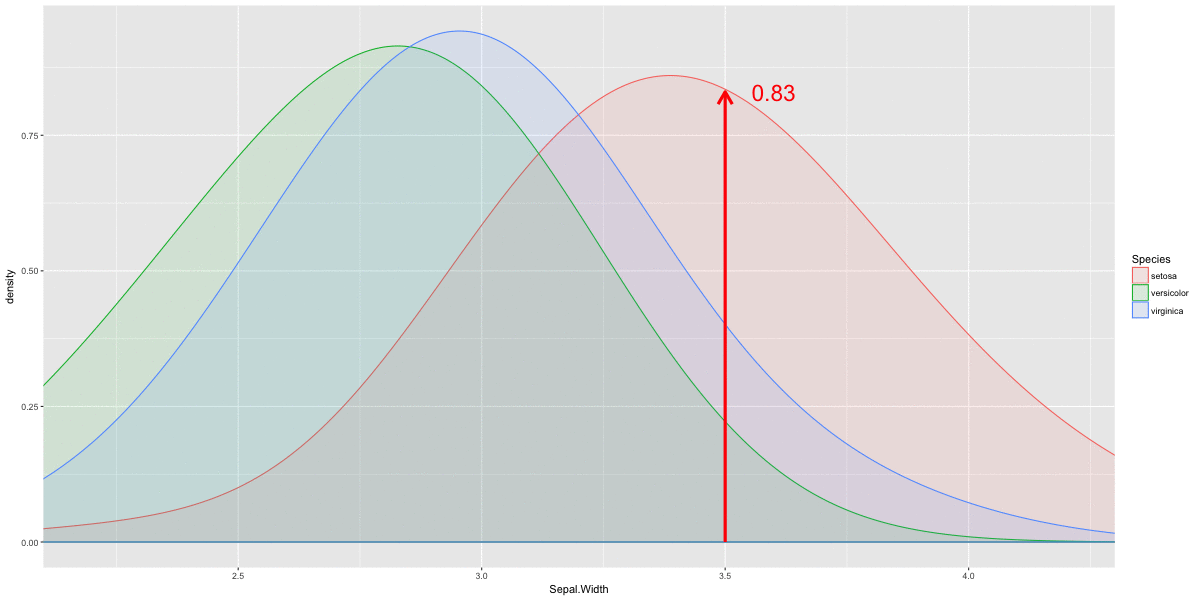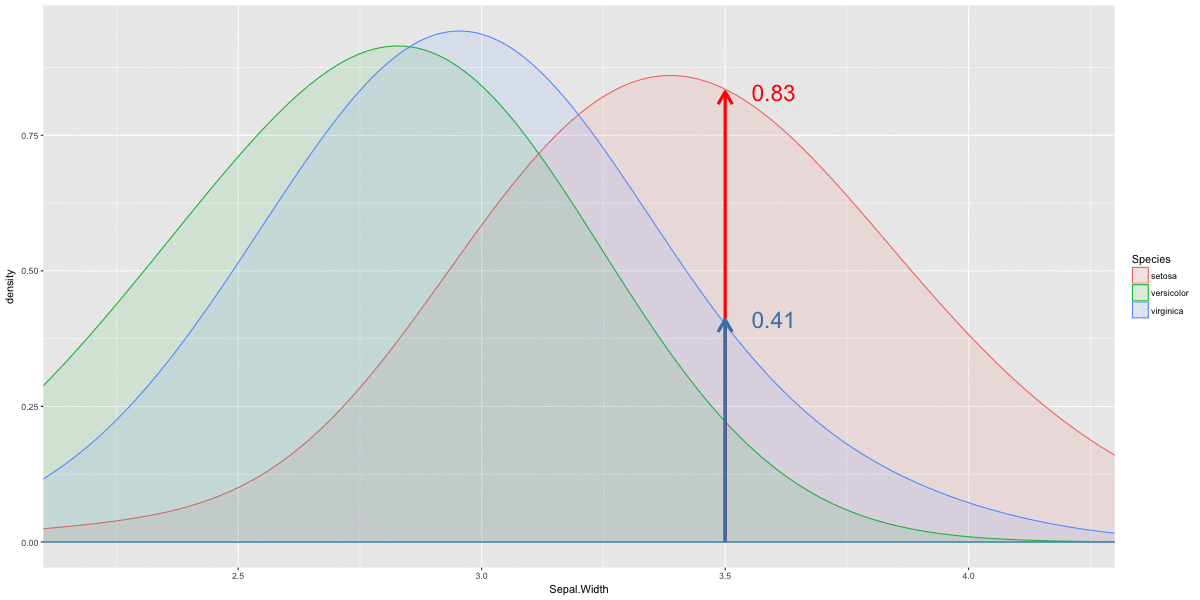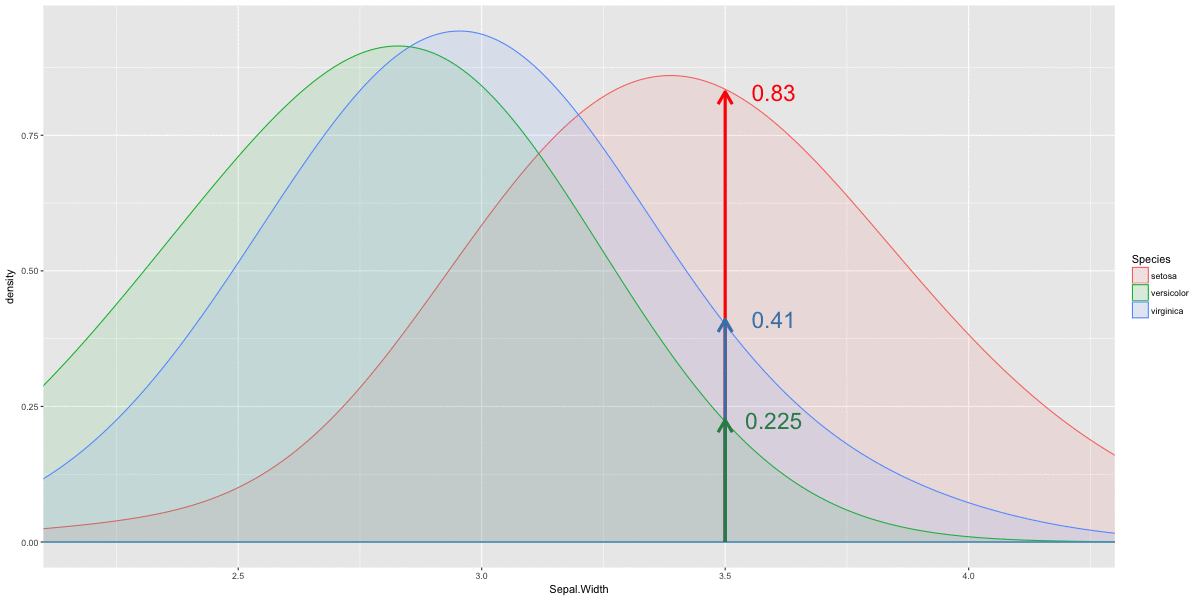
Univariate normal functions dnorm()
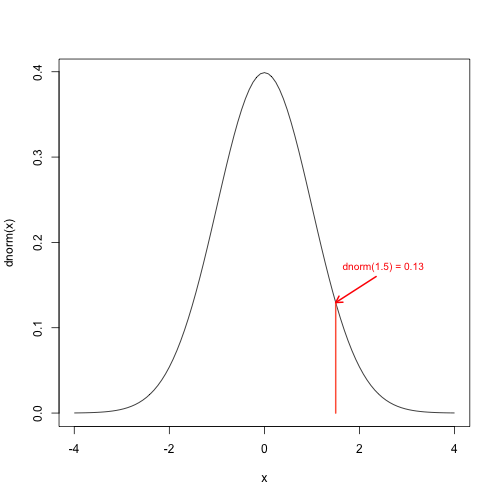
Probability density of a bivariate normal
Standard bivariate normal with $$ \mu = \begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix} , \Sigma = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} $$
dmvnorm() function
Density heights calculated at several locations (xy coordinates)
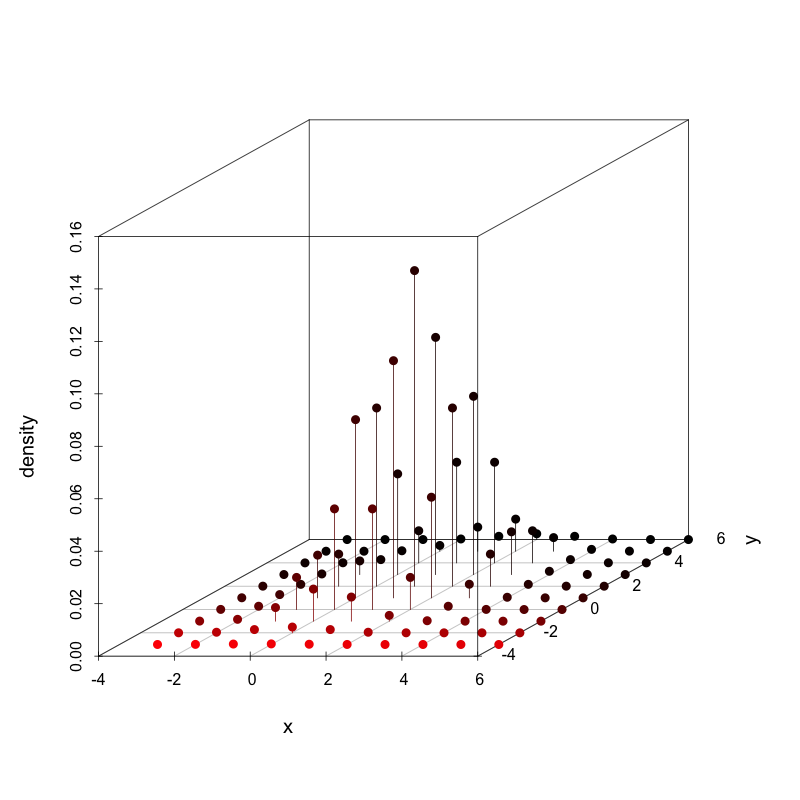
Density using dmvnorm
library(mvtnorm)
dmvnorm(x, mean, sigma)
xcan be a row vector or a matrix
mu1 <- c(1, 2)
sigma1 <- matrix(c(1, .5, .5, 2), 2)
dmvnorm(x = c(0, 0), mean = mu1, sigma = sigma1)
0.0384
Density at multiple points using dmvnorm
x <- rbind(c(0, 0), c(1, 1), c(0, 1)); x
[1,] 0 0
[2,] 1 1
[3,] 0 1
dmvnorm(x = x, mean = mu, sigma = sigma)
[1] 0.0384 0.0904 0.0679
Plotting bivariate densities with perspective plot
Steps:
- Create grid of $x$ and $y$ coordinates
- Calculate density on grid
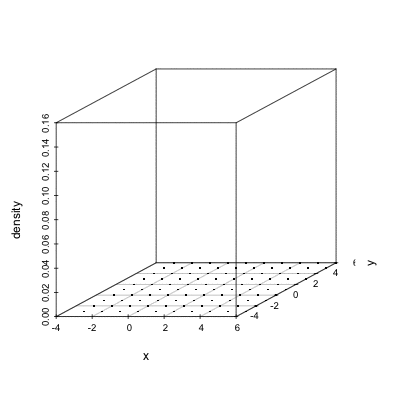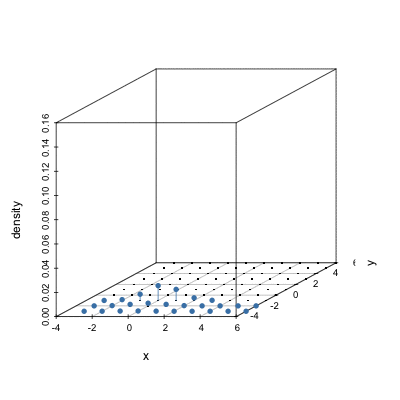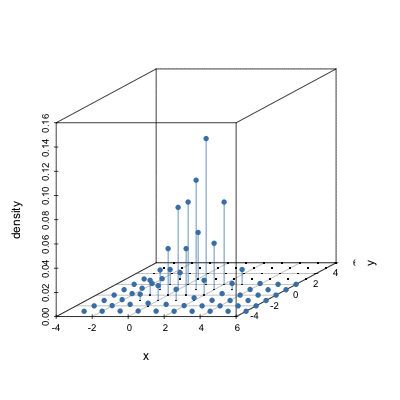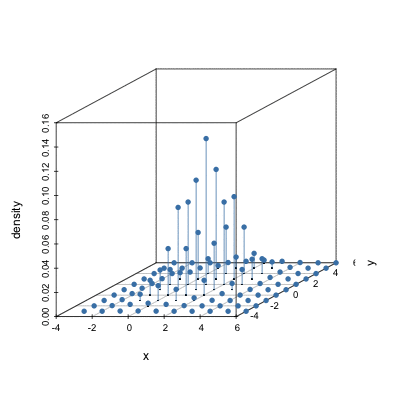
Plotting bivariate densities with perspective plot
Steps:
- Create grid of $x$ and $y$ coordinates
- Calculate density on grid
- Convert densities into a matrix
- Create perspective plot using
persp()function
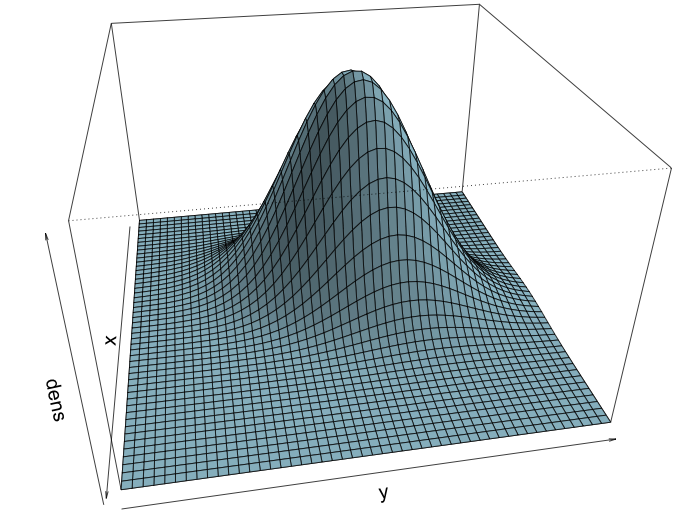
Code for plotting bivariate densities
# Create grid
d <- expand.grid(seq(-3, 6, length.out = 50 ), seq(-3, 6, length.out = 50))
# Calculate density on grid
dens1 <- dmvnorm(as.matrix(d), mean=c(1,2), sigma=matrix(c(1, .5, .5, 2), 2))
# Convert to matrix
dens1 <- matrix(dens1, nrow = 50 )
# Use perspective plot
persp(dens1, theta = 80, phi = 30, expand = 0.6, shade = 0.2, col = "lightblue", xlab = "x", ylab = "y", zlab = "dens")

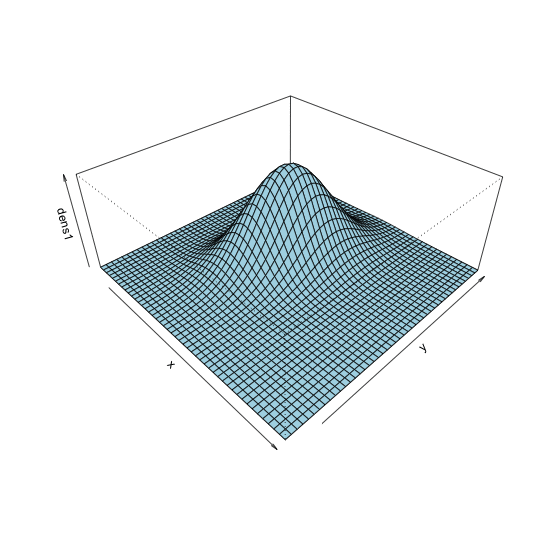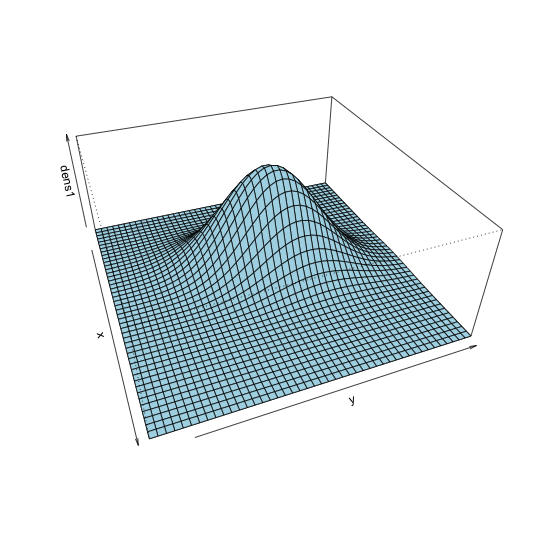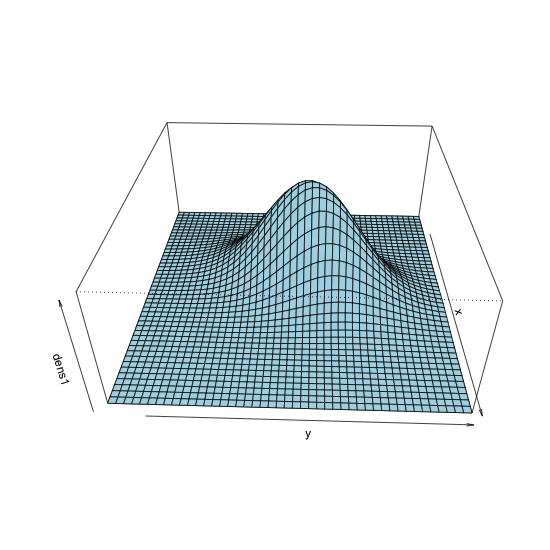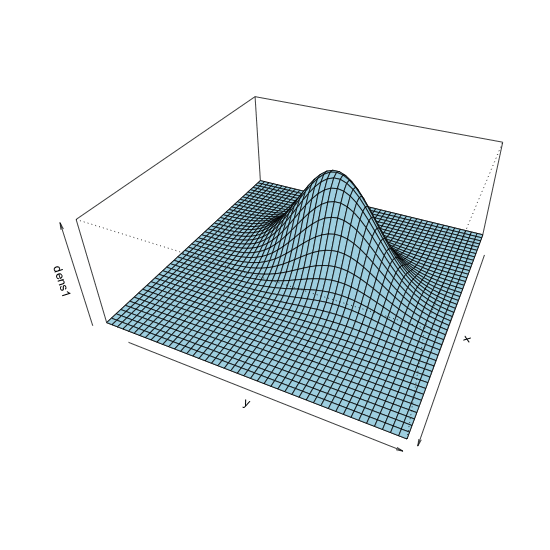
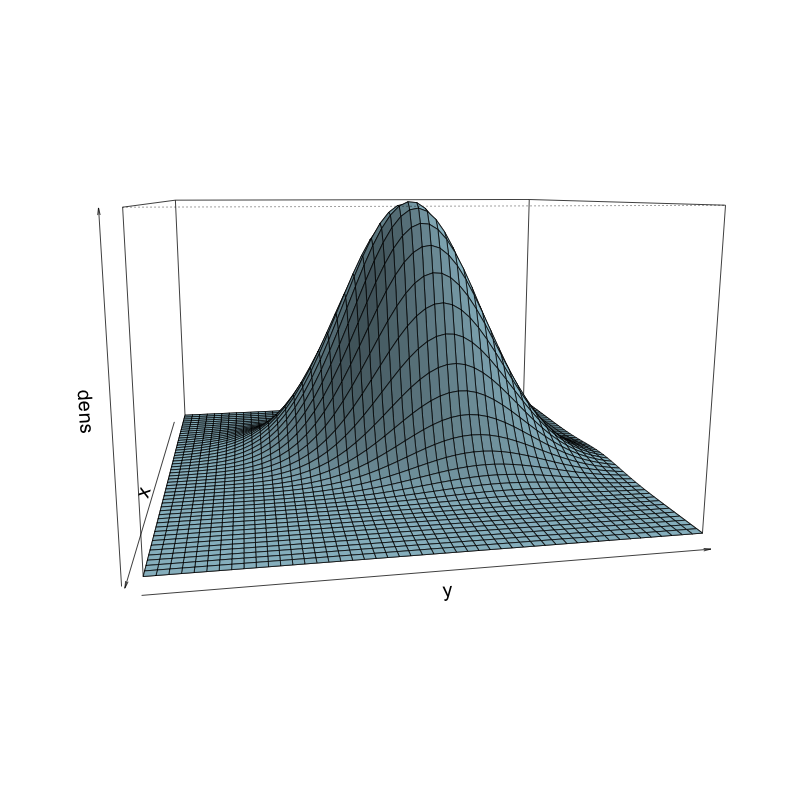
Changing viewing angle in perspective plot
persp() with theta = 30, phi = 30
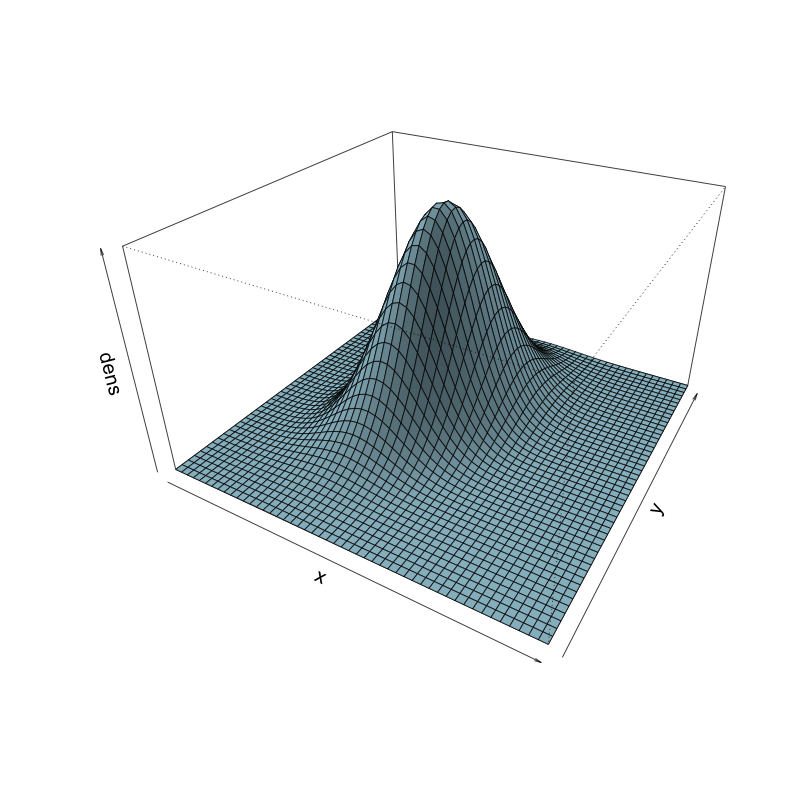
persp() with theta = 80, phi = 10
Let's practice!
Multivariate Probability Distributions in R

