Sharpe ratios; features and targets
Machine Learning for Finance in Python

Nathan George
Data Science Professor
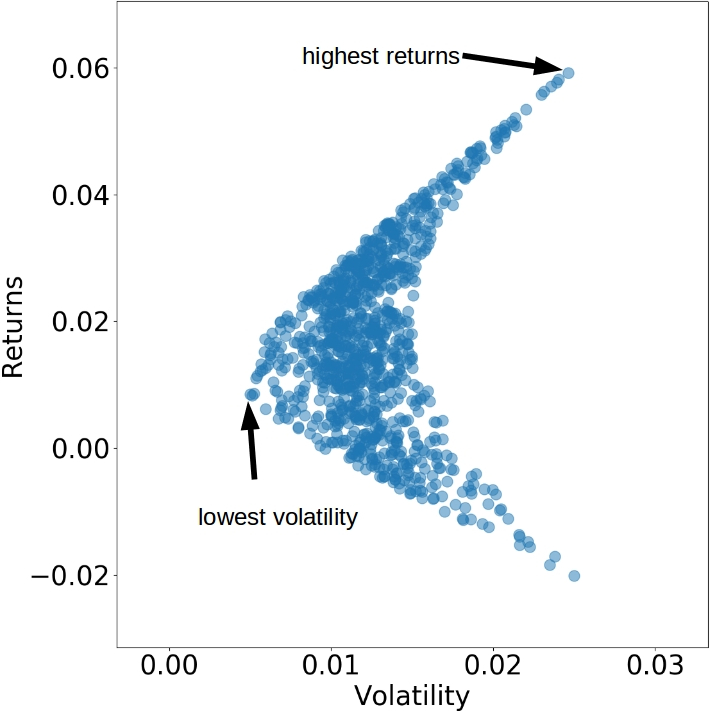

Getting our Sharpe ratios
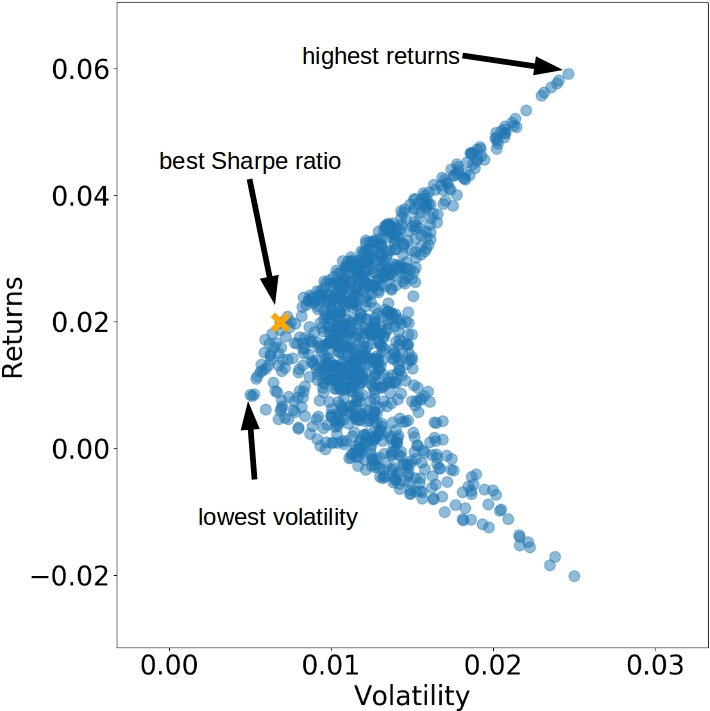
# empty dictionaries for sharpe ratios and best sharpe indexes by date sharpe_ratio, max_sharpe_idxs = {}, {}# loop through dates and get sharpe ratio for each portfolio for date in portfolio_returns.keys(): for i, ret in enumerate(portfolio_returns[date]): volatility = portfolio_volatility[date][i] sharpe_ratio.setdefault(date,[]).append(ret / volatility) # get the index of the best sharpe ratio for each date max_sharpe_idxs[date] = np.argmax(sharpe_ratio[date])
Create features
# calculate exponentially-weighted moving average of daily returns
ewma_daily = returns_daily.ewm(span=30).mean()
# resample daily returns to first business day of the month
ewma_monthly = ewma_daily.resample('BMS').first()
# shift ewma 1 month forward
ewma_monthly = ewma_monthly.shift(1).dropna()
Calculate features and targets
targets, features = [], []# create features from price history and targets as ideal portfolio for date, ewma in ewma_monthly.iterrows(): # get the index of the best sharpe ratio best_idx = max_sharpe_idxs[date] targets.append(portfolio_weights[date][best_idx]) features.append(ewma) targets = np.array(targets) features = np.array(features)
# latest date date = sorted(covariances.keys())[-1]cur_returns = portfolio_returns[date] cur_volatility = portfolio_volatility[date]plt.scatter(x=cur_volatility, y=cur_returns, alpha=0.1, color='blue') best_idx = max_sharpe_idxs[date] plt.scatter(cur_volatility[best_idx], cur_returns[best_idx], marker='x', color='orange') plt.xlabel('Volatility') plt.ylabel('Returns') plt.show()
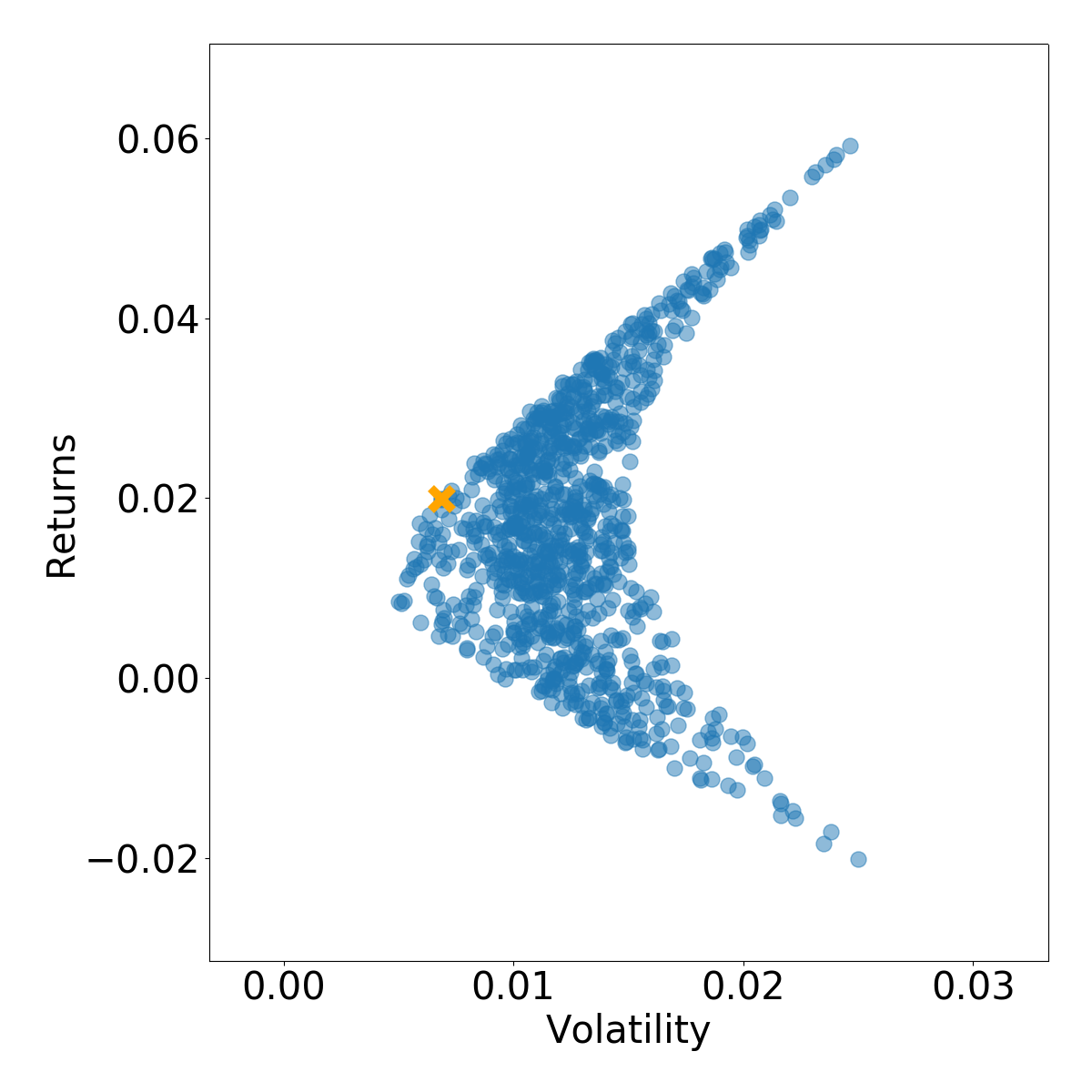
Get Sharpe!
Machine Learning for Finance in Python

