What's in a Bayesian Model?
Bayesian Regression Modeling with rstanarm

Jake Thompson
Psychometrician, ATLAS, University of Kansas
Posterior distributions
- Posterior distributions sampled in groups called chains
- Each sample in a chain is an iteration

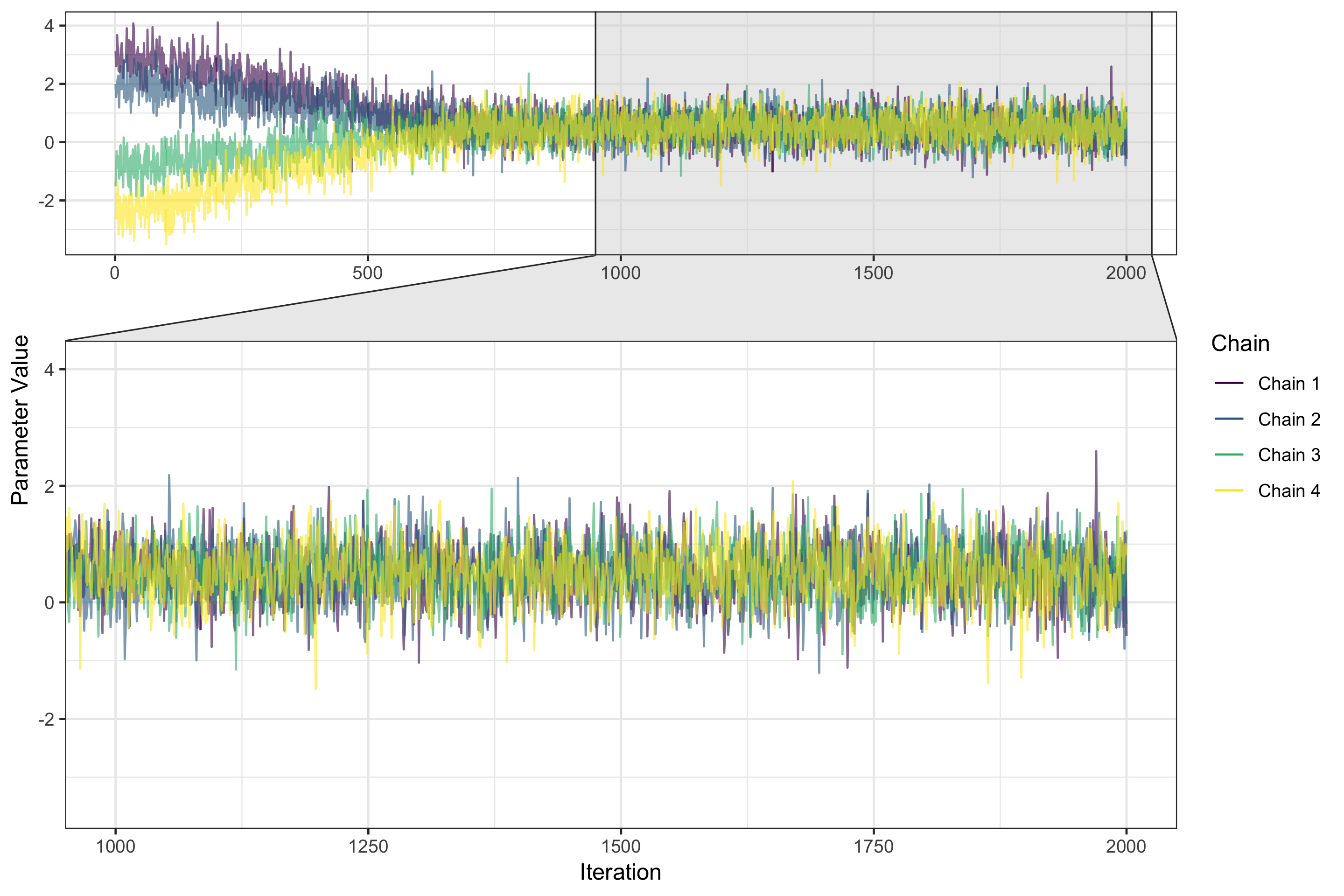
Changing the number and length of chains
stan_model <- stan_glm(kid_score ~ mom_iq, data = kidiq,
chains = 3, iter = 1000, warmup = 500)
summary(stan_model)
Model Info:
function: stan_glm
family: gaussian [identity]
formula: kid_score ~ mom_iq
algorithm: sampling
priors: see help('prior_summary')
sample: 1500 (posterior sample size)
observations: 434
predictors: 2
Estimates:
mean sd 2.5% 25% 50% 75% 97.5%
(Intercept) 25.8 6.0 14.1 21.7 25.6 29.9 37.5
mom_iq 0.6 0.1 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.7
sigma 18.3 0.6 17.2 17.9 18.3 18.7 19.6
mean_PPD 86.9 1.3 84.5 86.0 86.9 87.7 89.2
log-posterior -1885.4 1.2 -1888.4 -1885.9 -1885.1 -1884.5 -1884.0
Diagnostics:
mcse Rhat n_eff
(Intercept) 0.2 1.0 1500
mom_iq 0.0 1.0 1500
sigma 0.0 1.0 1500
mean_PPD 0.0 1.0 1500
log-posterior 0.0 1.0 619
For each parameter, mcse is Monte Carlo standard error, n_eff is a crude measure of effective sample size, and Rhat is the potential scale reduction factor on split chains (at convergence Rhat=1).

How many iterations?
- Fewer iterations = shorter estimation time
- Not enough iteration = convergence problems
Let's practice!
Bayesian Regression Modeling with rstanarm

