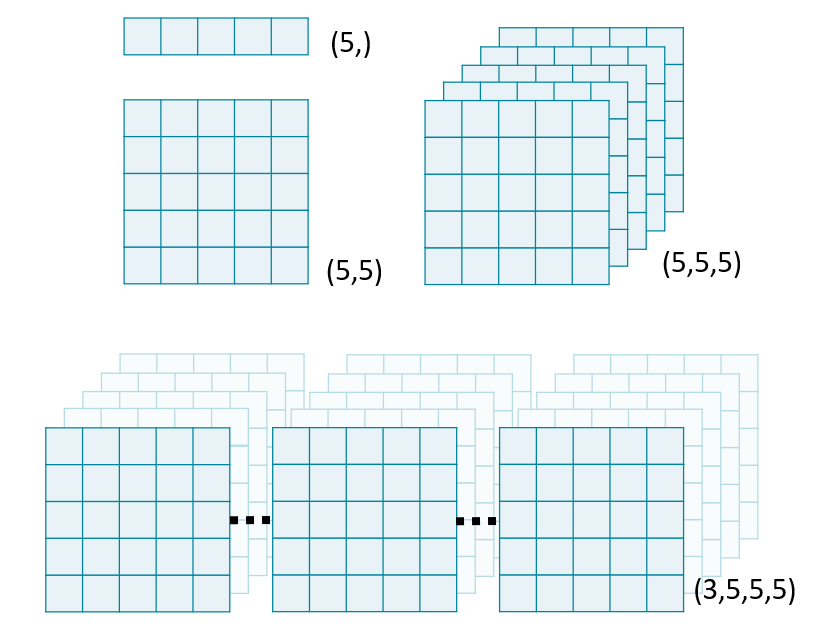
N-dimensional images
Biomedical Image Analysis in Python

Stephen Bailey
Instructor
Images of all shapes and sizes
im[row, col]
Images of all shapes and sizes
vol[pln, row, col]

Images of all shapes and sizes
im[row, col, ch]
Images of all shapes and sizes
im_ts[time, row, col, ch]
N-dimensional images are stacks of arrays
import imageio import numpy as npim1=imageio.imread('chest-000.dcm') im2=imageio.imread('chest-001.dcm') im3=imageio.imread('chest-002.dcm')im1.shape
(512, 512)
vol = np.stack([im1, im2, im3])vol.shape
(3, 512, 512)
Loading volumes directly
imageio.volread():
- read multi-dimensional data directly
- assemble a volume from multiple images
import os
os.listdir('chest-data')
['chest-000.dcm',
'chest-001.dcm',
'chest-002.dcm',
...,
'chest-049.dcm']
import imageio vol = imageio.volread('chest-data')vol.shape
(50, 512, 512)
Shape, sampling, and field of view
Image shape: number of elements along each axis
import imageio
vol = imageio.volread(
'chest-data')
# Image shape (in voxels)
n0, n1, n2 = vol.shape
n0, n1, n2
(50, 512, 512)
Field of view: physical space covered along each axis
Sampling rate: physical space covered by each element
# Sampling rate (in mm)
d0, d1, d2 = vol.meta['sampling']
d0, d1, d2
(2, 0.5, 0.5)
# Field of view (in mm)
n0 * d0, n1 * d1, n2 * d2
(100, 256, 256)
Let's practice!
Biomedical Image Analysis in Python