Shapely geometries and spatial relationships
Working with Geospatial Data in Python

Dani Arribas-Bel
Geographic Data Science Lab (University of Liverpool)
Scalar geometry values
cities = geopandas.read_file("ne_110m_populated_places.shp")
cities.head()
name geometry
0 Vatican City POINT (12.45338654497177 41.90328217996012)
1 San Marino POINT (12.44177015780014 43.936095834768)
2 Vaduz POINT (9.516669472907267 47.13372377429357)
3 Lobamba POINT (31.19999710971274 -26.46666746135247)
4 Luxembourg POINT (6.130002806227083 49.61166037912108)
brussels = cities.loc[170, 'geometry']
print(brussels)
POINT (4.33137074969045 50.83526293533032)
Scalar geometry values
brussels = cities.loc[170, 'geometry']
print(brussels)
POINT (4.33137074969045 50.83526293533032)
type(brussels)
shapely.geometry.point.Point
The Shapely python package
type(brussels)
shapely.geometry.point.Point
Shapely
- Python Package for the manipulation and analysis of geometric objects
- Provides the
Point,LineStringandPolygonobjects - GeoSeries (GeoDataFrame 'geometry' column) consists of shapely objects
Geometry objects
Accessing from a GeoDataFrame:
brussels = cities.loc[170, 'geometry']
paris = cities.loc[235, 'geometry']
belgium = countries.loc[countries['name'] == 'Belgium', 'geometry'].squeeze()
france = countries.loc[countries['name'] == 'France', 'geometry'].squeeze()
uk = countries.loc[countries['name'] == 'United Kingdom', 'geometry'].squeeze()
Creating manually:
from shapely.geometry import Point
p = Point(1, 2)
print(p)
POINT (1 2)
Spatial methods
The area of a geometry:
belgium.area
3.8299974609075753
The distance between 2 geometries:
brussels.distance(paris)
2.8049127723186214
And many more! (e.g. centroid, simplify, ...)
Spatial relationships
geopandas.GeoSeries([belgium, france, uk, paris, brussels, line]).plot()
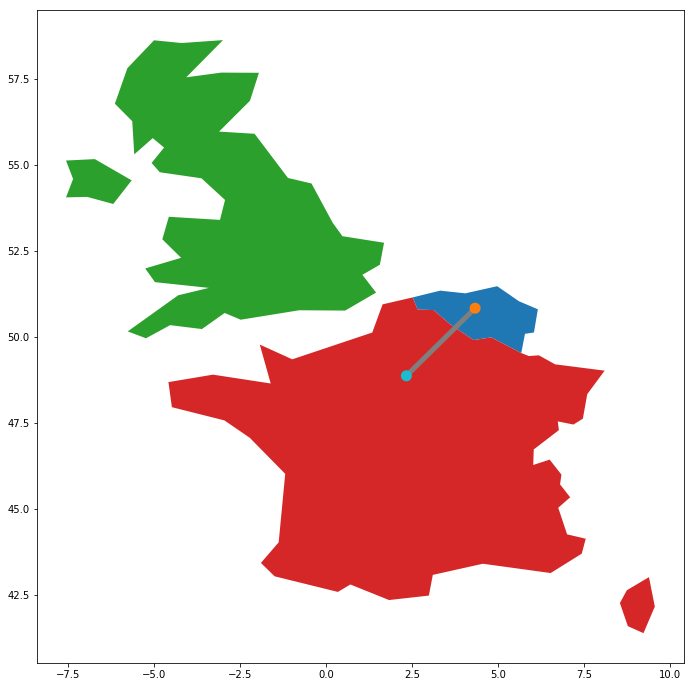
Spatial relationships
belgium.contains(brussels)
True
france.contains(brussels)
False
brussels.within(belgium)
True
belgium.touches(france)
True
line.intersects(france)
True
line.intersects(uk)
False
Let's practice!
Working with Geospatial Data in Python

