The "spatial join" operation
Working with Geospatial Data in Python

Dani Arribas-Bel
Geographic Data Science Lab (University of Liverpool)
Spatial relationships I
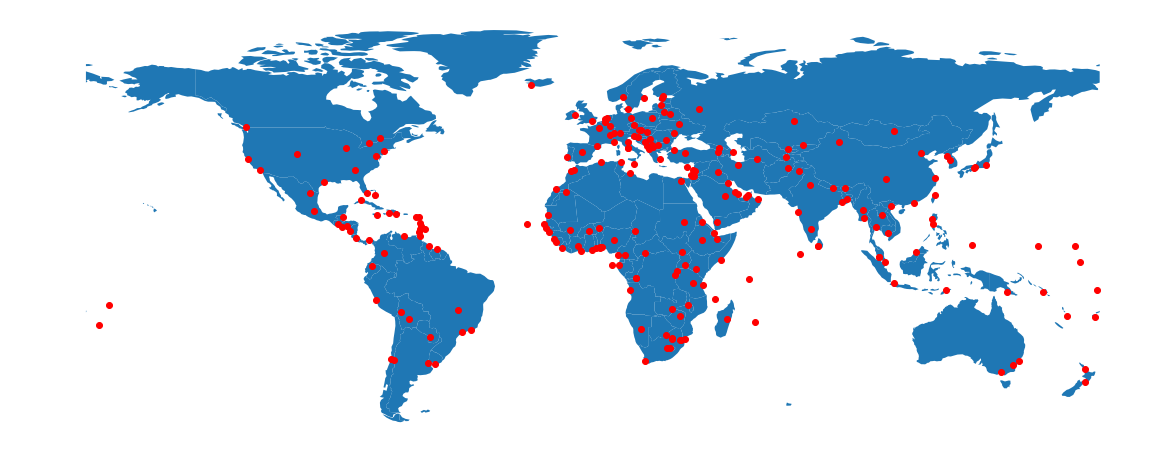
Spatial relationships II
Which cities are located within Brazil?
brazil = countries.loc[22, 'geometry']
cities[cities.within(brazil)]
name geometry
169 Brasília POINT (-47.91799814700306 -15.78139437287899)
238 Rio de Janeiro POINT (-43.22696665284366 -22.92307731561596)
239 São Paulo POINT (-46.62696583905523 -23.55673372837896)
But what if we want to know for each city in which country it is located?
The Spatial Join
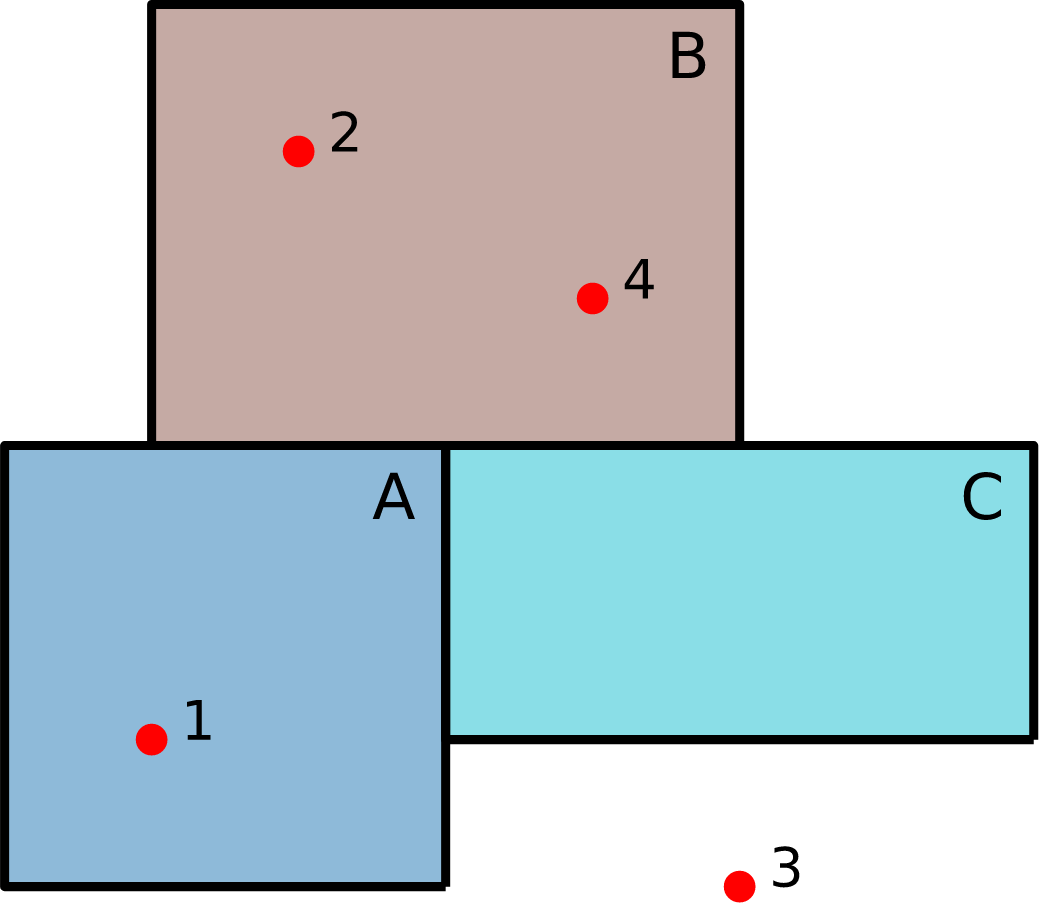
SPATIAL JOIN = transferring attributes from one layer to another based on their spatial relationship
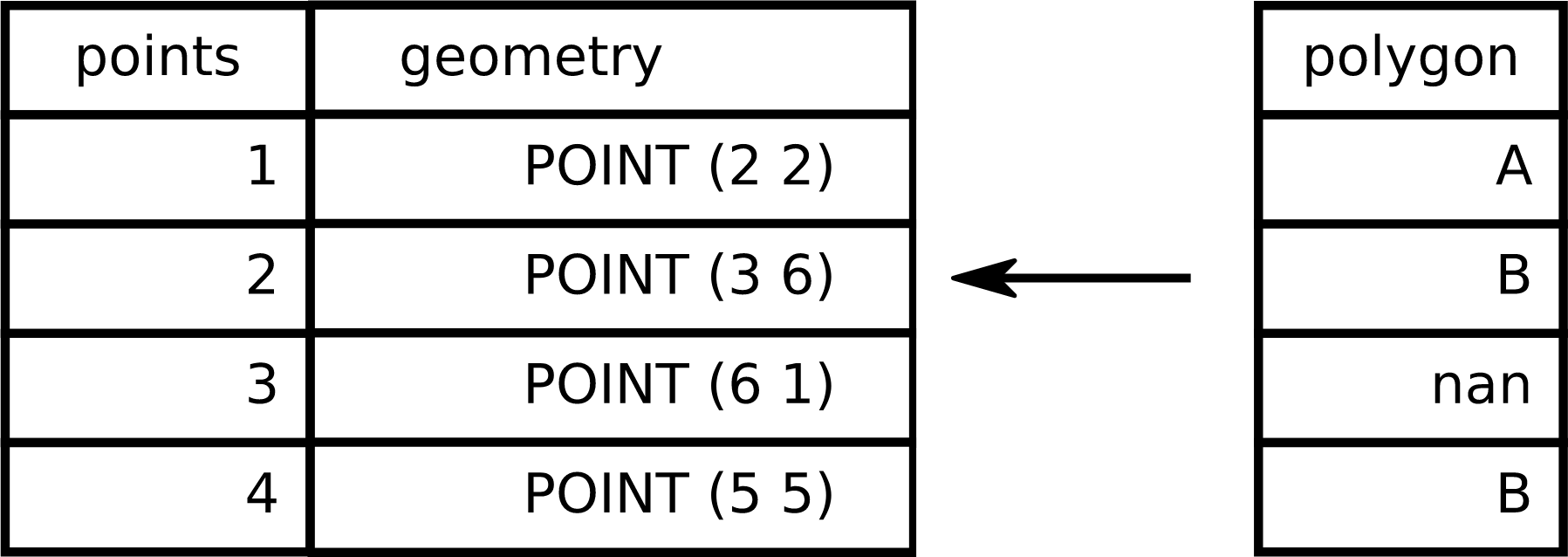
The spatial join with GeoPandas
joined = geopandas.sjoin(cities,
countries[['name', 'geometry']],
op="within")
joined.head()
name_left geometry name_right
0 Vatican City POINT (12.45338654497177 41.90328217996012) Italy
1 San Marino POINT (12.44177015780014 43.936095834768) Italy
226 Rome POINT (12.481312562874 41.89790148509894) Italy
2 Vaduz POINT (9.516669472907267 47.13372377429357) Austria
212 Vienna POINT (16.36469309674374 48.20196113681686) Austria
Let's practice!
Working with Geospatial Data in Python

