Link functions- Probit compared to logit
Generalized Linear Models in R

Richard Erickson
Instructor
Why link functions?
- Understand and simulate GLMs
- Probit vs logit as example
Why probit?
- Demonstrate link function
- Used in some fields (e.g., toxicology)
- Preferred by some people
What is a probit?
- Probability unit
- Toxicology by Chester Bliss in 1934
- Computationally easier than logit
- Model know as probit analysis, probit regression, or probit model
Probit equation
Model of binary data
$Y = \text{Binomial}(p)$
Linked to linear equation
$\Phi^{-1} (p) = \beta_0 + \beta_1 x + \epsilon $
Probit function
Based upon cumulative normal
$\Phi(z) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2 \pi}} \int_{-\infty}^z e^{- \frac{1}{2} z^2} \, dz$
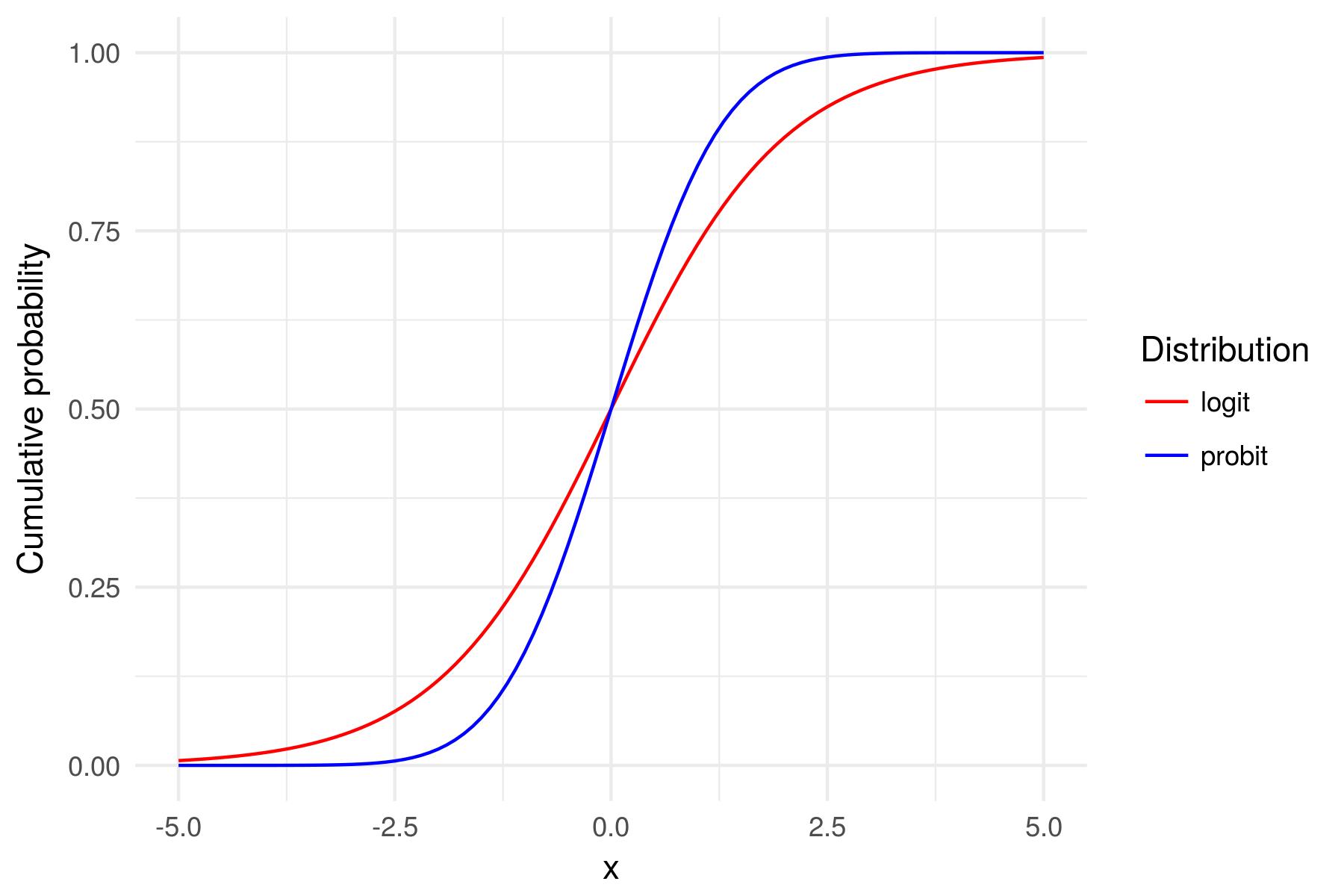
Fitting a probit in R
familyoption forglm()- Character:
glm(..., family = "binomial") - Function:
glm(..., family = binomial())
- Character:
- Default:
binomial(link = "logit") - Probit:
binomial(link = "probit") - Match instructions for DataCamp
Simulate with probit
Convert from probit scale to probability scale:
p = pnorm(-0.2)
Use probability with binomial distribution
rbinom(n = 10, size = 1, prob = p)
Simulate with logit
Convert from logit scale to probability scale:
p = plogis(-.2)
Use probability with a binomial distribution
rbinom(n = 10, size = 1, prob = p)
When to use probit vs logit?
- Largely domain specific
- Thicker tails of logit
- Either is tenable
Let's practice!
Generalized Linear Models in R

