Time series
Analyzing Social Media Data in Python

Alex Hanna
Computational Social Scientist
Time series data
sum person
date
2012-10-23 01:00:00 314 Obama
2012-10-23 01:01:00 369 Obama
2012-10-23 01:02:00 527 Obama
2012-10-23 01:03:00 589 Obama
2012-10-23 01:04:00 501 Obama
...
print(tweets['created_at'])
0 Sat Jan 27 18:36:21 +0000 2018
1 Sat Jan 27 18:24:02 +0000 2018
2 Sat Jan 27 18:09:14 +0000 2018
...
tweets['created_at'] = pd.to_datetime(tweets['created_at'])print(tweets['created_at'])
0 2018-01-27 18:36:21
1 2018-01-27 18:24:02
2 2018-01-27 18:09:14
...
tweets = tweets.set_index('created_at')
Keywords as time series metrics
tweets['google'] = check_word_in_tweet('google', tweets)print(tweets['google'])
created_at
2018-01-27 18:36:21 False
2018-01-27 18:24:02 False
2018-01-27 18:30:12 False
2018-01-27 18:12:37 True
2018-01-27 18:11:06 True
....
print(np.sum(tweets['google']))
247
Generating keyword means
mean_google = tweets['google'].resample('1 min').mean()print(mean_google)
created_at
2018-01-27 18:07:00 0.085106
2018-01-27 18:08:00 0.285714
2018-01-27 18:09:00 0.161290
2018-01-27 18:10:00 0.222222
2018-01-27 18:11:00 0.169231
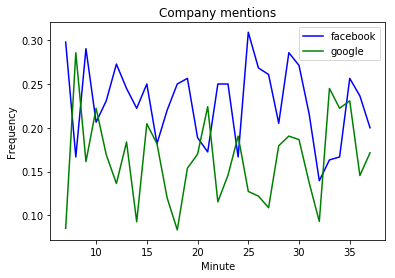
Plotting keyword means
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(
means_facebook.index.minute,
means_facebook, color = 'blue'
)
plt.plot(
means_google.index.minute,
means_google, color = 'green'
)
plt.xlabel('Minute')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.title('Company mentions')
plt.legend(('facebook', 'google'))
plt.show()
Let's practice!
Analyzing Social Media Data in Python

