Neural machine translation
Natural Language Generation in Python

Biswanath Halder
Data Scientist
Encoder
- Accepts input sequence.
- Summarizes information in state vectors.
- State vectors passed to decoder.
- Outputs ignored.
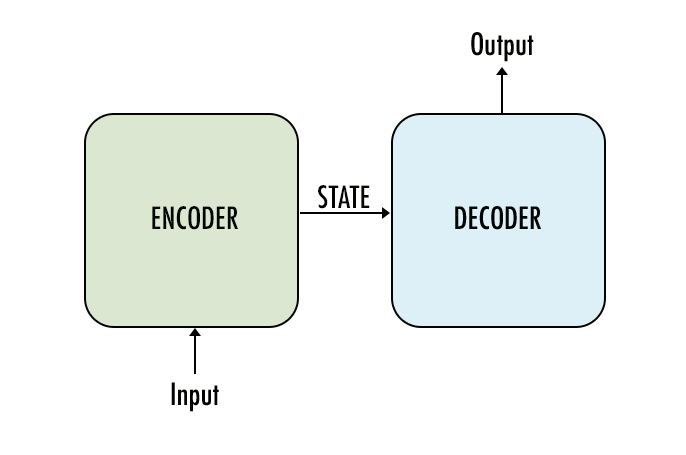
Decoder
- Initial state vectors from encoder.
- Final states ignored.
- Outputs the predicted sequence.

Teacher forcing
- Inference
- Behavior as usual.
- Input at each step - output from previous time step.
- Training
- Input is actual output for the current step.
- Not the predicted output from previous time step.
- Known as teacher-forcing.
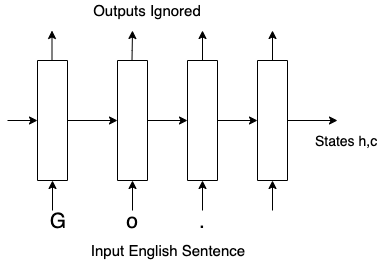
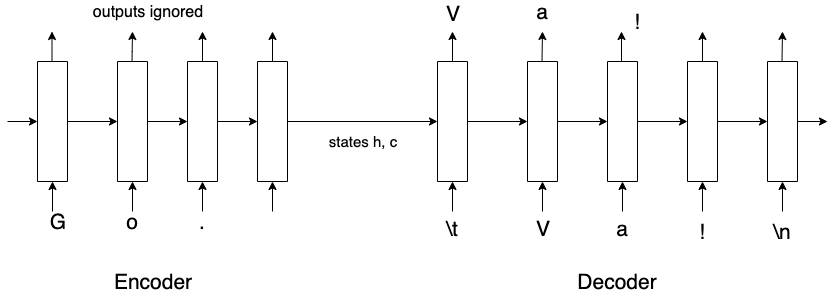
Encoder for translation
- Inputs : English sentences.
- Number of time steps : length of the sentence.
- States summarize the English sentences.
- Final states passed to decoder.
- Outputs ignored.
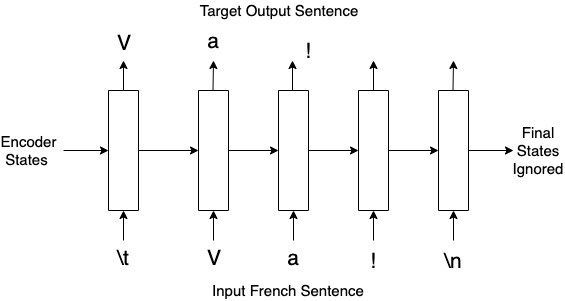
Decoder for translation
- Initial states : final states of the encoder.
- Inputs : French sentences.
- Outputs : translated sentences.
- Final states ignored.
- No of time-steps : length of French sentence.
Encoder-decoder during training
Shape of input and target vectors
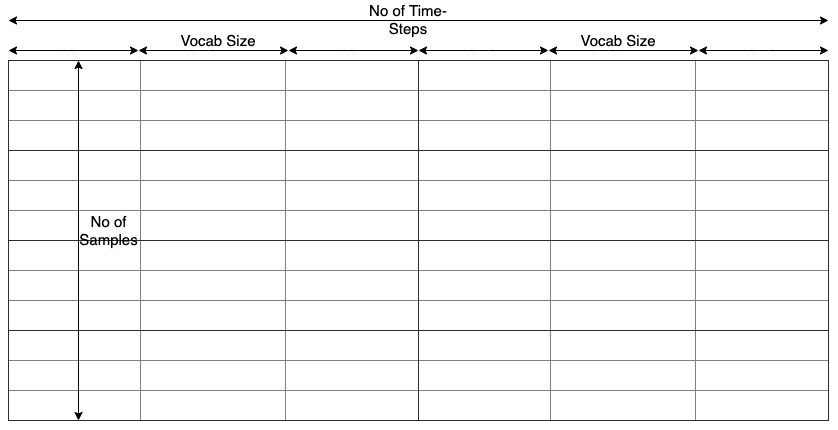
Define input and target vectors
- Find the step sizes.
max_len_eng_sent = max([len(sentence) for sentence in english_sentences])
max_len_fra_sent = max([len(sentence) for sentence in french_sentences])
- Define the input and target vectors.
eng_input_data = np.zeros((len(english_sentences), max_len_eng_sent,
len(english_vocab)), dtype='float32')
fra_input_data = np.zeros((len(french_sentences), max_len_fra_sent,
len(french_vocab)), dtype='float32')
target_data = np.zeros((len(french_sentences), max_len_fra_sent,
len(french_vocab)), dtype='float32')
Initialize input and target vectors
for i in range(no_of_sentences):
# Iterate over each character of English sentences
for k, ch in enumerate(english_sentences[i]):
eng_input_data[i, k, eng_char_to_idx[ch]] = 1.
# Iterate over each character of French sentences
for k, ch in enumerate(french_sentences[i]):
fra_input_data[i, k, fra_char_to_idx[ch]] = 1.
# Target data will be one timestep ahead
if k > 0:
target_data[i, k-1, fra_char_to_idx[ch]] = 1.
Keras functional APIs
# This returns a input vector of size 784
inputs = Input(shape=(784,))
# A dense layer of 64 units is called on a vector returning a tensor
predictions = Dense(64, activation='relu')(inputs)
# This creates a model with an Input layer and an output of a dense layer
model = Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=predictions)
Build the encoder
- Create input layer followed by the LSTM layer of 256 units.
encoder_input = Input(shape = (None, len(english_vocab)))
encoder_LSTM = LSTM(256, return_state = True)
- Feed input to the LSTM layer and get output.
encoder_outputs, encoder_h, encoder_c = encoder_LSTM(encoder_input)
- Ignore the output and save the states.
encoder_states = [encoder_h, encoder_c]
Build the decoder
- Create the input layer followed by the LSTM layer.
decoder_input = Input(shape=(None, len(french_vocab)))
decoder_LSTM = LSTM(256, return_sequences=True, return_state = True)
- Get the output from the LSTM layer.
decoder_out, _ , _ = decoder_LSTM(decoder_input,
initial_state=encoder_states)
- Feed LSTM output to a dense layer to get the final output.
decoder_dense = Dense(len(french_vocab), activation='softmax')
decoder_out = decoder_dense (decoder_out)
Combine the encoder and the decoder
- Combine encoder and decoder.
model = Model(inputs=[encoder_input, decoder_input], outputs=[decoder_out])
- Check model summary.
model.summary()
Compile and train the network
- Compile and train the model.
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy')
model.fit(x=[input_data_prefix, input_data_suffix], y=target_data,
batch_size=64, epochs=1, validation_split=0.2)
Let's practice!
Natural Language Generation in Python

